Implementing a Security Middleware for Angular Document Editor Applications in C#
This article shows how to implement a security middleware for Angular Document Editor applications using ASP.NET Core. The middleware is used to validate access tokens and to protect the Document Editor API.

When building a backend for the TX Text Control Document Editor and Document Viewer, the TX Text Control NuGet packages implement the necessary endpoints and handlers to communicate between the client-side libraries and the backend.
Middleware that checks for an access token is recommended to secure these endpoints. This demo implementation does not create and store access tokens, but illustrates how incoming requests can be checked for an access token. Typically, your actual authorization layer, such as OAuth, creates the access tokens.
The request flow with integrated custom security middleware is illustrated in the following diagram.
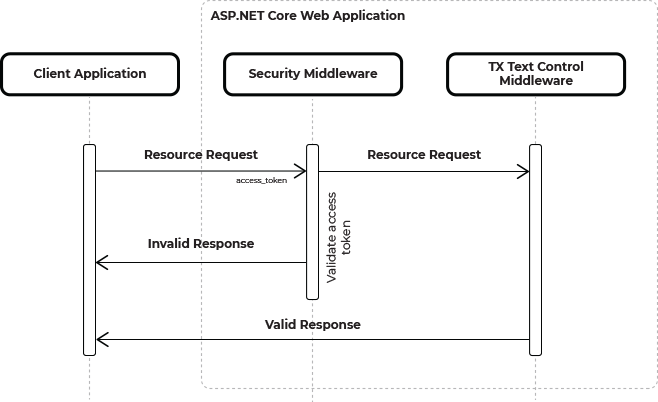
When the client-side Angular package requests resources from the backend, the implemented custom security middleware intercepts the request and validates a security access token sent with the request.
Security Middleware
The security middleware is implemented in the TXSecurityMiddleware class. It basically checks a security token passed as a query string against a stored access token. To illustrate this workflow, the access token is simply hard-coded into the application settings.
namespace TXTextControl
{
public class TXSecurityMiddleware
{
private IConfiguration configuration;
public TXSecurityMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IConfiguration configuration)
{
m_next = next;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
private RequestDelegate m_next;
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
var access_token = this.configuration.GetSection("Security")["AccessToken"];
// Check if the request is a TX Text Control request
if (context.WebSockets.IsWebSocketRequest &&
context.WebSockets.WebSocketRequestedProtocols.Contains("TXTextControl.Web") ||
(context.Request.Query.ContainsKey("access_token") &&
context.GetEndpoint()?.DisplayName?.Contains("TXTextControl.Web.MVC.DocumentViewer") == true))
{
// Retrieve access token from the query string
var accessToken = context.Request.Query["access_token"];
// Showcase only: Easy comparison of tokens
if (accessToken != access_token)
{
throw new UnauthorizedAccessException();
}
else
{
await m_next.Invoke(context);
}
}
else if (m_next != null)
{
await m_next.Invoke(context);
}
}
}
}The middleware is registered in the Program.cs request pipeline.
app.UseWebSockets();
// Add the TX Security Middleware to the request pipeline
app.UseMiddleware<TXTextControl.TXSecurityMiddleware>();
// TX Text Control specific middleware
app.UseTXWebSocketMiddleware();The backend also implements an HttpGet method that returns an access token to simulate a common token workflow such as OAuth, where an access token is exchanged for a user id and user secret. In this sample workflow, the method simply returns a valid access token.
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class TXSecurityTokenController : ControllerBase
{
private IConfiguration configuration;
public TXSecurityTokenController(IConfiguration configuration)
{
this.configuration = configuration;
}
[HttpGet]
public SecurityToken Get()
{
return new SecurityToken() { AccessToken = this.configuration.GetSection("Security")["AccessToken"] };
}
}Requesting Resources
When the client-side Angular application requests resources from the backend, the security token is passed as a query string. The following code shows where the Angular application retrieves the access token from the backend endpoint.
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
interface SecurityToken {
accessToken: string;
}
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrl: './app.component.css'
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
public securityToken: SecurityToken | undefined;
constructor(private http: HttpClient) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.getTokens();
}
getTokens() {
this.http.get<SecurityToken>('/txsecuritytoken').subscribe(
(result) => {
this.securityToken = result;
},
(error) => {
console.error(error);
}
);
}
title = 'tx-security.client';This retrieved access token is then used as the query string in the webSocketURL property.
<h1 id="tableLabel">Security Token Sample</h1>
<p>
This component demonstrates how to retrieve a security token from the server and how to use it.
</p>
<p *ngIf="!securityToken"><em>Loading... Please refresh once the ASP.NET backend has started. See <a href="https://aka.ms/jspsintegrationangular">https://aka.ms/jspsintegrationangular</a> for more details.</em></p>
<table *ngIf="securityToken">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>AccessToken retrieved:</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
{{ securityToken.accessToken }}
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div *ngIf="securityToken">
<tx-document-editor width="1000px"
height="500px"
webSocketURL="wss://localhost:7289/TXWebSocket?access_token={{ securityToken.accessToken }}">
</tx-document-editor>
</div>After the token is validated, the editor is initialized.
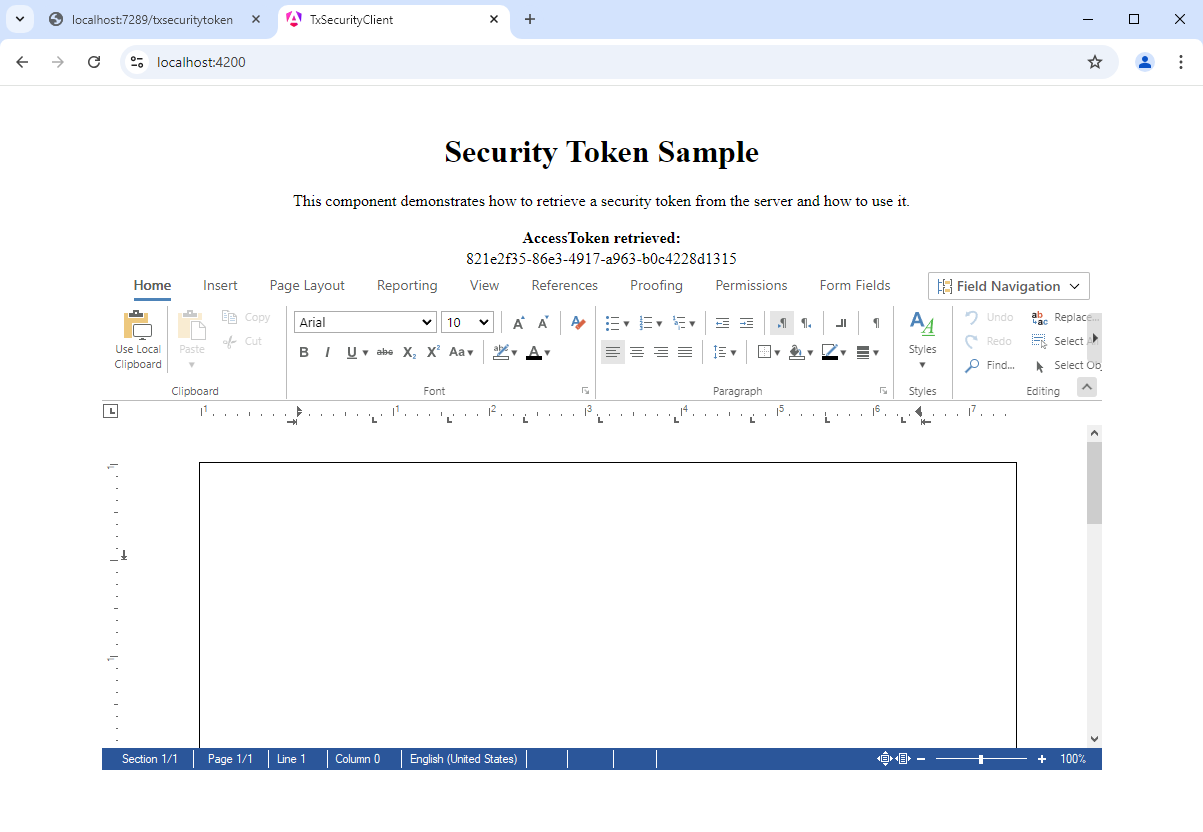
Download the complete project from GitHub and test it on your own.
![]()
Download and Fork This Sample on GitHub
We proudly host our sample code on github.com/TextControl.
Please fork and contribute.
Requirements for this sample
- TX Text Control .NET Server 32.0 SP2
- Visual Studio 2022
ASP.NET
Integrate document processing into your applications to create documents such as PDFs and MS Word documents, including client-side document editing, viewing, and electronic signatures.
- Angular
- Blazor
- React
- JavaScript
- ASP.NET MVC, ASP.NET Core, and WebForms
Related Posts
DS Server: Authorizing Angular Client Components
The DS Server Angular components implement an integrated, implicit OAuth security handling. In case, the client ID and client secret is passed as a property to the view, the component takes care…
Building an ASP.NET Core Backend (Linux and Windows) for the Document Editor…
This article shows how to create a backend for the Document Editor and Viewer using ASP.NET Core. The backend can be hosted on Windows and Linux and can be used in Blazor, Angular, JavaScript, and…
Impressions from .NET Developer Conference DDC 2024
This week we sponsored the .NET Developer Conference DDC 2024 in Cologne, Germany. It was a great event with many interesting talks and workshops. Here are some impressions of the conference.
Back from Florida: Impressions from VSLive! Orlando 2024
We had an incredible time showcasing our digital document processing SDKs at VSLive! Orlando 2024 as a silver sponsor! Throughout the event, we interacted with hundreds of developers, shared…
Exporting Password Protected Documents to PDF in .NET C#
This article shows how to export password protected documents to PDF in .NET C# using TX Text Control .NET Server. Existing password protected documents can be imported, modified and exported to…






