Implicit OAuth Workflow
The DS Server Angular components implement an integrated, implicit OAuth security handling. In case, the client ID and client secret is passed as a property to the view, the component takes care of the complete OAuth workflow to request a valid access token.
| <tx-ds-document-editor | |
| width="1024px" | |
| height="1024px" | |
| serviceURL="https://trial.dsserver.io" | |
| oauthClientID="dsserver.u5NQQHkgjmCRAOeChUVc19zNFJ9aivKz" | |
| oauthClientSecret="tPGgkutg8oYuSHPbfuRfE5DMf9arUCEg" | |
| </tx-ds-document-editor> |
The following diagram shows the client credentials workflow that connects the client DocumentEditor directly with DS Server by sending the client credentials to DS Server to retrieve a valid access token:
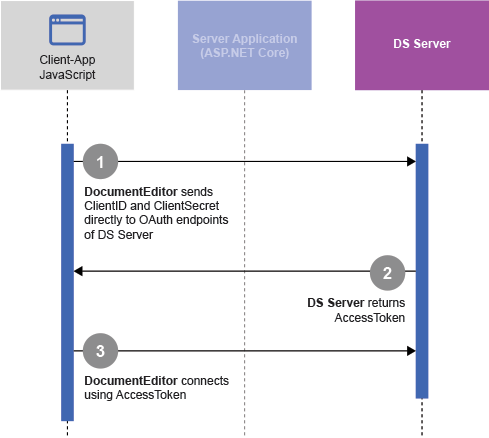
Using Access Tokens
The disadvantage of the above method is that the client credentials are exposed client-side. To avoid that, the components can be authorized directly with an access token:
| <tx-ds-document-editor | |
| width="500px" | |
| height="500px" | |
| serviceURL="https://trial.dsserver.io" | |
| accessToken="Ghgf6376722GGJHFFJGHDOOIGD56657665"> | |
| </tx-ds-document-editor> |
The next diagram shows the authorization with an access token that has been acquired by a server application in between:
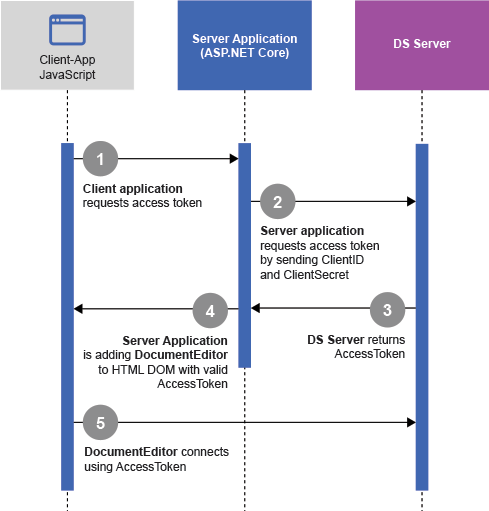
In order to retrieve the access token from the DS Server Web API endpoints, a server-side process is required. In this case, the credentials are securely stored on the server and the client will only see the used access token.
Web API
To demonstrate this process, an ASP.NET Core web application is used to provide a Web API that requests the OAuth access tokens from DS Server in order to return a valid access token. This endpoint is then called by Angular before the view component is rendered.
The following code shows the implementation of the Web API method AccessToken:
| [HttpGet] | |
| [Route("AccessToken")] | |
| public async System.Threading.Tasks.Task<ActionResult> AccessTokenAsync() { | |
| // security credentials | |
| string clientId = ""; | |
| string clientSecret = ""; | |
| string serviceUrl = "https://trial.dsserver.io"; | |
| string ClientCredentials = "client_credentials"; | |
| AccessTokenResponse token; | |
| HttpClient m_client = new HttpClient(); | |
| // generate the payload | |
| var payload = new Dictionary<string, string> { | |
| ["grant_type"] = ClientCredentials, | |
| }; | |
| // token endpoint | |
| string requestUri = $"{serviceUrl}/oauth/token"; | |
| // create the request message | |
| var tokenRequest = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Post, requestUri) { | |
| Content = new StringContent( | |
| UrlEncode(payload), | |
| Encoding.UTF8, | |
| "application/x-www-form-urlencoded") | |
| }; | |
| // Add basic auth header containing client id and secret | |
| string credentials = $"{clientId}:{clientSecret}"; | |
| byte[] credentialsUtf8 = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(credentials); | |
| string credentialsB64 = Convert.ToBase64String(credentialsUtf8); | |
| tokenRequest.Headers.Authorization = | |
| new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Basic", credentialsB64); | |
| // send the request | |
| var tokenResponse = await m_client.SendAsync(tokenRequest); | |
| // retrieve and return the token | |
| var tokenResponseStream = await tokenResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync(); | |
| token = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<AccessTokenResponse>(tokenResponseStream); | |
| return Ok(token); | |
| } | |
| public string UrlEncode(Dictionary<string, string> dict) { | |
| return string.Join("&", dict.Keys.Select(k => $"{k}={WebUtility.UrlEncode(dict[k])}")); | |
| } |
Injectable Service
In the Angular application, a service is implemented to call the Web API and to return the access token:
| import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http'; | |
| import { Inject, Injectable } from '@angular/core'; | |
| import { Resolve } from '@angular/router'; | |
| @Injectable({ | |
| providedIn: 'root' | |
| }) | |
| export class OauthService implements Resolve<any> { | |
| public _http: HttpClient; | |
| public _baseUrl: string; | |
| constructor(http: HttpClient, @Inject('BASE_URL') baseUrl: string) { | |
| this._http = http; | |
| this._baseUrl = baseUrl; | |
| } | |
| resolve() { | |
| return this._http.get<any>(this._baseUrl + 'oauth/accesstoken'); | |
| } | |
| } |
The service implements a resolve() method that is invoked when the navigation starts. The router waits for the data to be resolved before the route is finally activated. This must be defined in the imports section of the app.module.ts:
| import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; | |
| import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; | |
| import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms'; | |
| import { HttpClientModule, HTTP_INTERCEPTORS } from '@angular/common/http'; | |
| import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router'; | |
| import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; | |
| import { NavMenuComponent } from './nav-menu/nav-menu.component'; | |
| import { HomeComponent } from './home/home.component'; | |
| import { DocumentEditorModule } from '@txtextcontrol/tx-ng-ds-document-editor'; | |
| import { OauthService } from './oauth.service'; | |
| @NgModule({ | |
| declarations: [ | |
| AppComponent, | |
| NavMenuComponent, | |
| HomeComponent, | |
| ], | |
| imports: [ | |
| BrowserModule.withServerTransition({ appId: 'ng-cli-universal' }), | |
| HttpClientModule, | |
| FormsModule, | |
| RouterModule.forRoot([ | |
| { | |
| path: '', | |
| component: HomeComponent, | |
| pathMatch: 'full', | |
| resolve: { token: OauthService } }, | |
| ]), | |
| DocumentEditorModule | |
| ], | |
| providers: [], | |
| bootstrap: [AppComponent], | |
| }) | |
| export class AppModule { } |
In the home.component.ts, the result of this attached service is passed to the property _accessToken:
| import { ApplicationInitStatus, Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; | |
| import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; | |
| @Component({ | |
| selector: 'app-home', | |
| templateUrl: './home.component.html' | |
| }) | |
| export class HomeComponent implements OnInit { | |
| _accessToken: string = ""; | |
| constructor(private _routes: ActivatedRoute) { } | |
| ngOnInit(): void { | |
| this._routes.data.subscribe((response: any) => { | |
| this._accessToken = response.token.accessToken; | |
| }) | |
| } | |
| } |
This _accessToken is then used directly in the home.component.html:
| <tx-ds-document-editor | |
| width="500px" | |
| height="500px" | |
| serviceURL="https://trial.dsserver.io" | |
| accessToken="{{ _accessToken }}"> | |
| </tx-ds-document-editor> |
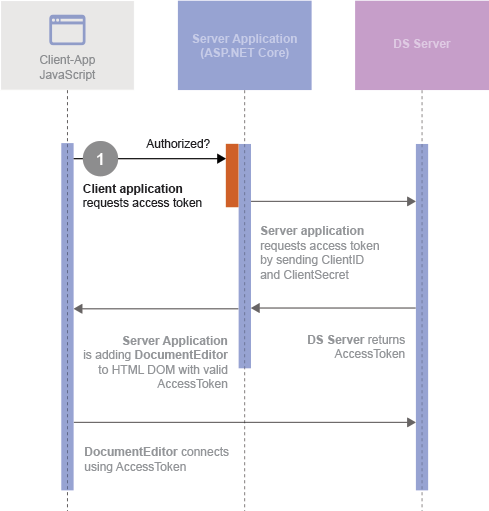
Is this Safe?
The positive of the above method is that the client credentials are not exposed client-side. But the security problem is now shifted to the server as the Web API is exposed and could be accessed by other requests. In order to avoid that, the Web API should be secured. For example by using one of the following concepts:
- CORS: Enable only specific hosts.
- Security Middleware: Filter requests (used in this demo).
- Another Authorization: Use second authorization (login) for the Web API.
You can test this method by downloading the sample from our GitHub repository. Let us know, if you have any questions.

