Converting Paragraphs to Styles by Comparing Formatting Attributes
This example shows how to identify paragraphs that are commonly formatted, and then convert them to style sheets. The example checks for character and paragraph formatting and compares them using Reflection.

A smart way to maintain the same look and feel throughout a document is to use stylesheets in professional documents. TX Text Control provides a rich set of features for using styles in your documents.
Another use case is when you receive a document that does not have any styles, but does have formatted text. In these scenarios, it may be helpful to convert the existing paragraphs that have common formatting to styles.
The Sample Application
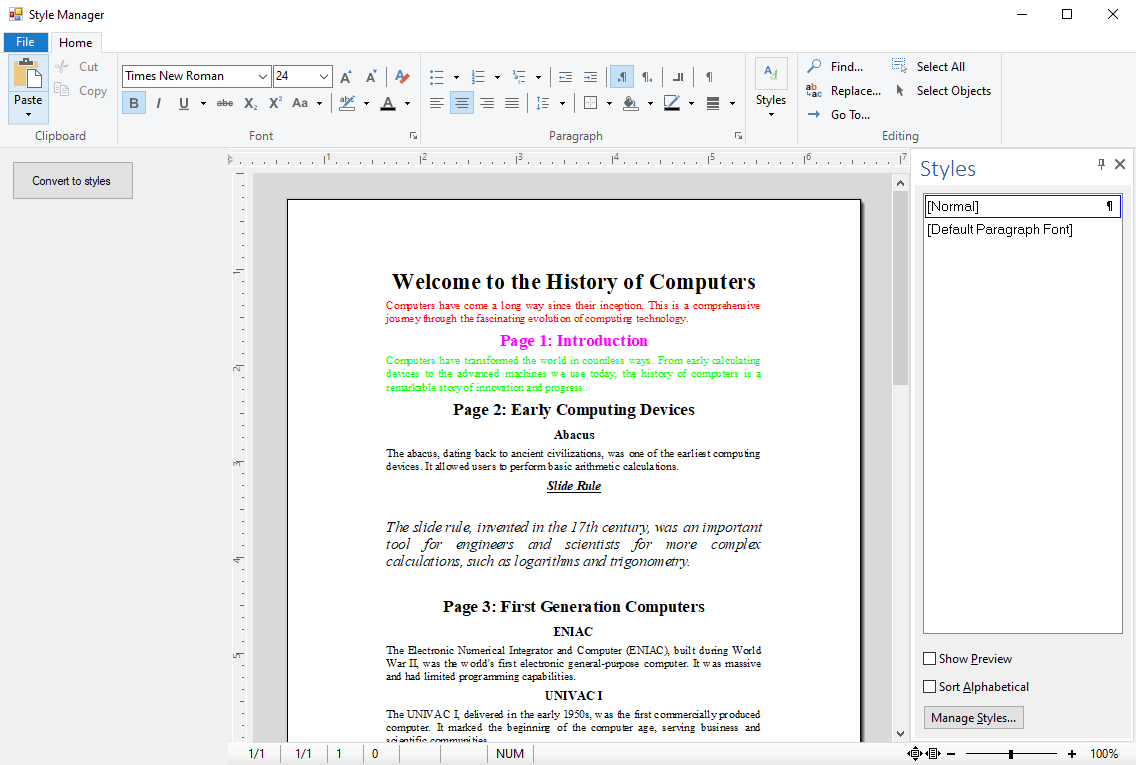
Consider the document shown in the following screenshot. The paragraphs are formatted. However, as shown, no styles are applied.
The sample contains the StyleManager class, which parses the paragraphs for common paragraph and character formatting. If a new format is detected, a new style will be created and applied to the document. If formatting is detected that already exists as a style, that style is applied.
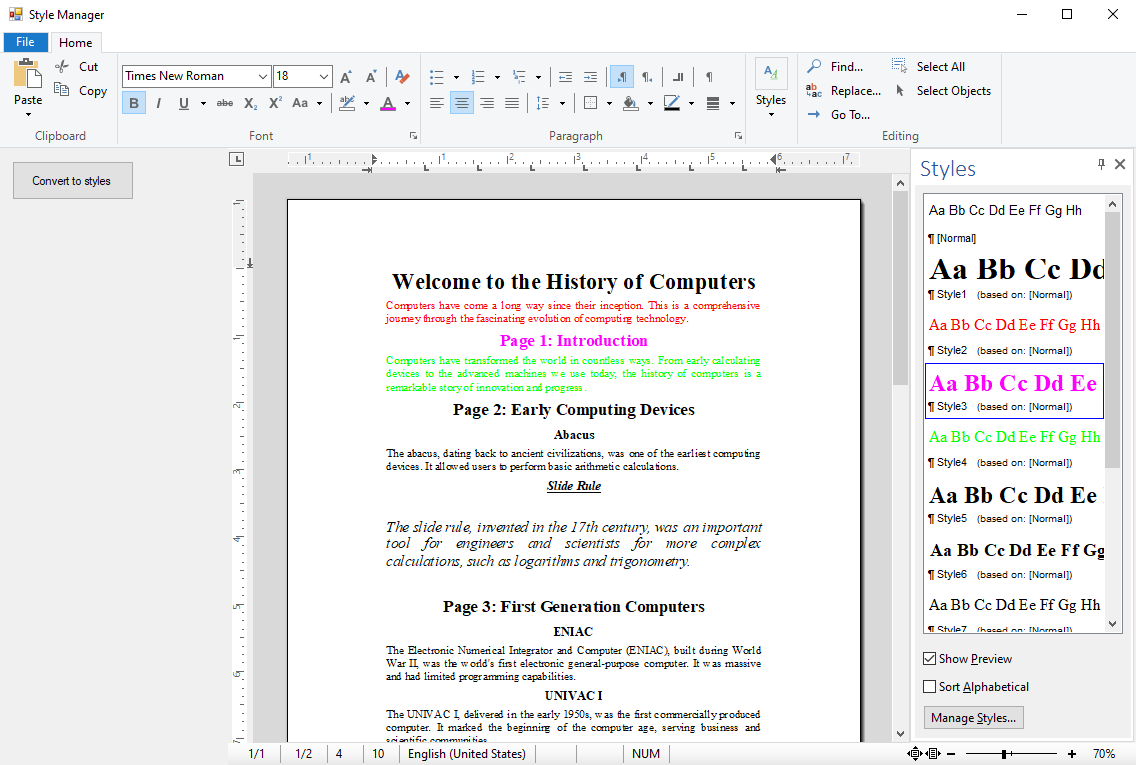
The following screenshot shows the same document with style sheets created for each of the unique paragraph styles.
These styles can then be applied to other paragraphs in the document to maintain a consistent layout throughout the document.
StyleManager Class
For your reference, the complete code of the StyleManager class is shown below. We will discuss its specific functions in more detail later on. If you want to use this code for ASP.NET (Core), you can easily replace TextControl with Server
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using TXTextControl;
// **************************************************************
// * *
// * This example demonstrates how to extract styles from *
// * paragraphs and how to apply them to other paragraphs. *
// * *
// **************************************************************
public class StyleManager
{
// The TextControl instance to work with
private TextControl _textControl;
// A list of properties to compare
private string[] _positiveListParagraphFormat = { "Alignment", "ForeColor", "BottomDistance", "TopDistance", "LeftIndent", "RightIndent" };
private string[] _positiveListCharacterFormat = { "Bold", "Italic", "FontName", "FontSize", "ForeColor", "Strikeout", "Underline" };
// A counter to create unique style names
private int styleNameCounter;
public string[] PositiveListParagraphFormat { get => _positiveListParagraphFormat; set => _positiveListParagraphFormat = value; }
public string[] PositiveListCharacterFormat { get => _positiveListCharacterFormat; set => _positiveListCharacterFormat = value; }
// The constructor requires a TextControl instance
public StyleManager(TextControl control)
{
_textControl = control;
styleNameCounter = 1;
}
// This method applies the styles to all paragraphs
public void ApplyStyles()
{
foreach (Paragraph paragraph in _textControl.Paragraphs)
{
if (IsCommonFormatting(paragraph))
{
var style = FindOrCreateStyle(paragraph);
paragraph.FormattingStyle = style.Name;
}
}
}
// This method creates a new style or returns an existing one
private ParagraphStyle FindOrCreateStyle(Paragraph paragraph)
{
var existingStyle = FindStyle(paragraph);
if (existingStyle == null)
{
existingStyle = CreateStyle(paragraph);
}
return existingStyle;
}
// This method searches for an existing style
private ParagraphStyle FindStyle(Paragraph paragraph)
{
foreach (ParagraphStyle paragraphStyle in _textControl.ParagraphStyles)
{
// compare paragraph format
if (IsParagraphFormatEqual(paragraph.Format, paragraphStyle.ParagraphFormat))
{
// compare character format
if (IsCharacterFormatEqual(paragraph, paragraphStyle))
{
return paragraphStyle;
}
}
}
return null;
}
// This method creates a new style
private ParagraphStyle CreateStyle(Paragraph paragraph)
{
ParagraphStyle paragraphStyle = new ParagraphStyle("Style" + styleNameCounter, "[Normal]");
CopyCharacterFormat(paragraph, paragraphStyle);
CopyParagraphFormat(paragraph.Format, paragraphStyle.ParagraphFormat);
// add the style to the collection
_textControl.ParagraphStyles.Add(paragraphStyle);
styleNameCounter++; // increase the counter
return paragraphStyle; // return the new style
}
// This method compares the character format of a paragraph with a style using Reflection
private bool IsCharacterFormatEqual(Paragraph paragraph, ParagraphStyle paragraphStyle)
{
paragraph.Select();
var selection = _textControl.Selection;
foreach (var property in typeof(Selection).GetProperties())
{
if (!_positiveListCharacterFormat.Contains(property.Name))
{
continue;
}
object value1 = property.GetValue(selection);
var paragraphStyleProperty = typeof(ParagraphStyle).GetProperty(property.Name)?.GetValue(paragraphStyle);
// compare the values
if (!object.Equals(value1, paragraphStyleProperty))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// This method compares the paragraph format of a paragraph with a style using Reflection
private bool IsParagraphFormatEqual(ParagraphFormat format1, ParagraphFormat format2)
{
foreach (var property in typeof(ParagraphFormat).GetProperties())
{
if (_positiveListParagraphFormat.Contains(property.Name))
{
object value1 = property.GetValue(format1);
object value2 = property.GetValue(format2);
if (!object.Equals(value1, value2))
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
// This method copies the character format of a paragraph to a style using Reflection
private void CopyCharacterFormat(Paragraph paragraph, ParagraphStyle style)
{
paragraph.Select();
var selection = _textControl.Selection;
var styleType = style.GetType();
foreach (var property in styleType.GetProperties())
{
var selectionProperty = typeof(Selection).GetProperty(property.Name);
if (selectionProperty != null && selectionProperty.PropertyType == property.PropertyType)
{
property.SetValue(style, selectionProperty.GetValue(selection));
}
}
}
// This method copies the paragraph format of a paragraph to a style using Reflection
private void CopyParagraphFormat(ParagraphFormat source, ParagraphFormat destination)
{
foreach (var property in typeof(ParagraphFormat).GetProperties())
{
object value = property.GetValue(source);
if (value != null && _positiveListParagraphFormat.Contains(property.Name))
{
property.SetValue(destination, value);
}
}
}
// This method checks if the paragraph has common formatting
private bool IsCommonFormatting(Paragraph paragraph)
{
paragraph.Select();
return _textControl.Selection.IsCommonValueSelected(Selection.Attribute.All);
}
}The use is very simple.
StyleManager styleManager = new StyleManager(textControl1);
styleManager.ApplyStyles();If you only want to check for certain formatting properties, you can define them beforehand.
StyleManager styleManager = new StyleManager(textControl1);
styleManager.PositiveListCharacterFormat = new string[] { "Bold", "Italic", "FontName" };
styleManager.ApplyStyles();Code in Detail
Basically, the algorithm loops through all the paragraphs and checks if the character formatting of the paragraphs is the same.
private bool IsCommonFormatting(Paragraph paragraph)
{
paragraph.Select();
return _textControl.Selection.IsCommonValueSelected(Selection.Attribute.All);
}It then checks to see if it should create a new style or if the style already exists. The interesting methods are IsParagraphFormatEqual and IsCharacterFormatEqual, which compare the formatting properties of the current paragraph and the styles.
private bool IsCharacterFormatEqual(Paragraph paragraph, ParagraphStyle paragraphStyle)
{
paragraph.Select();
var selection = _textControl.Selection;
foreach (var property in typeof(Selection).GetProperties())
{
if (!_positiveListCharacterFormat.Contains(property.Name))
{
continue;
}
object value1 = property.GetValue(selection);
var paragraphStyleProperty = typeof(ParagraphStyle).GetProperty(property.Name)?.GetValue(paragraphStyle);
// compare the values
if (!object.Equals(value1, paragraphStyleProperty))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}private bool IsParagraphFormatEqual(ParagraphFormat format1, ParagraphFormat format2)
{
foreach (var property in typeof(ParagraphFormat).GetProperties())
{
if (_positiveListParagraphFormat.Contains(property.Name))
{
object value1 = property.GetValue(format1);
object value2 = property.GetValue(format2);
if (!object.Equals(value1, value2))
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}The formatting properties are copied to the newly created style using the CopyCharacterFormat and CopyParagraphFormat methods. As an example, the code of the CopyParagraphFormat method is shown here:
private void CopyParagraphFormat(ParagraphFormat source, ParagraphFormat destination)
{
foreach (var property in typeof(ParagraphFormat).GetProperties())
{
object value = property.GetValue(source);
if (value != null && _positiveListParagraphFormat.Contains(property.Name))
{
property.SetValue(destination, value);
}
}
}To avoid setting each property name individually, all methods that compare formatting properties or apply properties use Reflection.
Sample Application
The sample application is available for download from our GitHub repository.
![]()
Download and Fork This Sample on GitHub
We proudly host our sample code on github.com/TextControl.
Please fork and contribute.
Requirements for this sample
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms 32.0
- Visual Studio 2022
ASP.NET
Integrate document processing into your applications to create documents such as PDFs and MS Word documents, including client-side document editing, viewing, and electronic signatures.
- Angular
- Blazor
- React
- JavaScript
- ASP.NET MVC, ASP.NET Core, and WebForms
Related Posts
Sneak Peek 32.0: Modifying the Normal Stylesheet
Stylesheets in TX Text Control provide a powerful tool for maintaining consistency and ensuring that documents look and feel professional. In version 32.0 it will be possible to manipulate the…
TX Text Control 34.0 SP1 is Now Available: What's New in the Latest Version
TX Text Control 34.0 Service Pack 1 is now available, offering important updates and bug fixes for all platforms. If you use TX Text Control in your document processing applications, this service…
Introducing TX Text Control 34.0: Your Next Leap in Document Processing.
We are happy to announce the release of TX Text Control 34.0. This version is packed with new features and enhancements that will elevate your document processing experience. This version…
Sneak Peek: TX Text Control 34.0 Coming November 2025
We are excited to announce the upcoming release of TX Text Control 34.0, scheduled for November 2025. This update brings a host of new features and improvements to enhance your document processing…
TX Text Control 33.0 SP3 is Now Available: What's New in the Latest Version
TX Text Control 33.0 Service Pack 3 is now available, offering important updates and bug fixes for all platforms. If you use TX Text Control in your document processing applications, this service…