DS Server: Announcing Distributed OAuth Authentication for Scalable Applications
In the next update, DS Server provides support for a distributed OAuth authentication for scalable applications. This article gives an overview of this new feature and the advantages.

DS Server comes with a fully-featured, included OAuth authentication server that enables users to add Security Profiles to access the document services using access tokens or by using the Client ID and Client Secret directly. But what if multiple instances of DS Server are used for load balancing or when your backends are distributed across multiple regions, countries and continents?
In the current version, all security profiles must be cloned on all instances of DS Server, so that each request is able to authenticate the user. This implied another problem: During the OAuth process, an access token is provided. If this access token is then used on another server, this instance doesn't know this token and the request will be denied.
Distributed Authentication
The solution to this problem is a new feature of DS Server that allows each instance of DS Server to accept authentication requests from other DS Server instances. The following illustration shows a typical request flow:
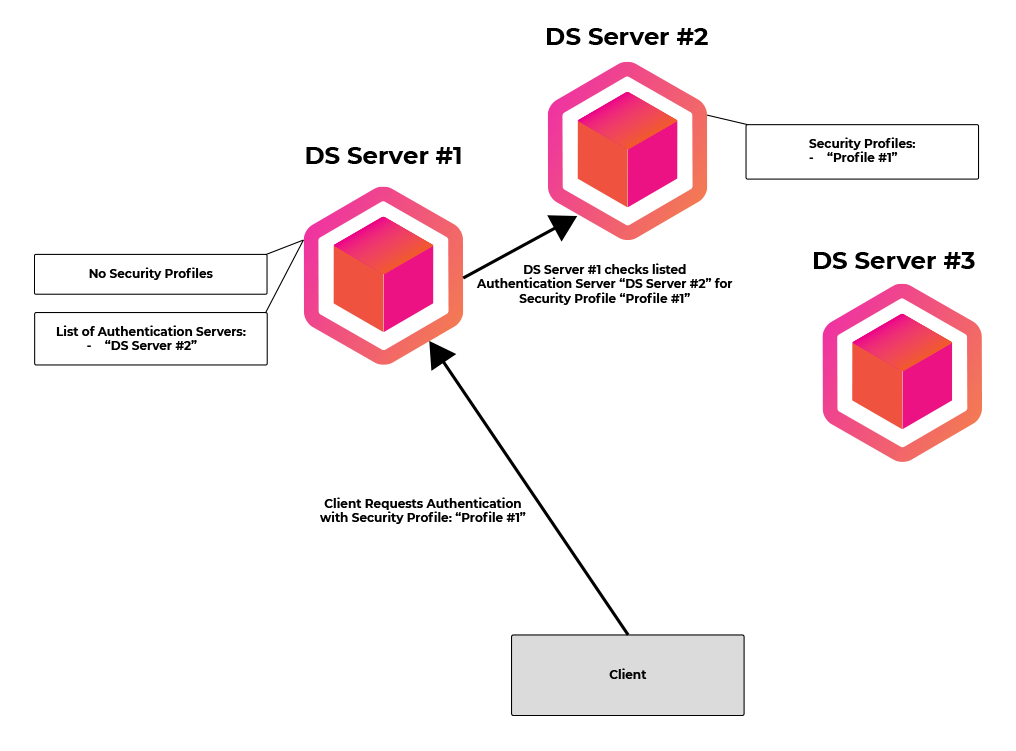
The instance DS Server #1 doesn't have any security profiles, but lists DS Server #2 as an Authentication Server. When a request is coming to instance DS Server #1 based on a specific user profiles (Profile #1), DS Server #1 is asking DS Server #2, if the authentication is valid. If yes, the request is accepted and processed on DS Server #1.
The actual server load is happing on DS Server #1 and based on your used load balancing distribution algorithm, the load can be balanced accordingly.
Central Authentication Server
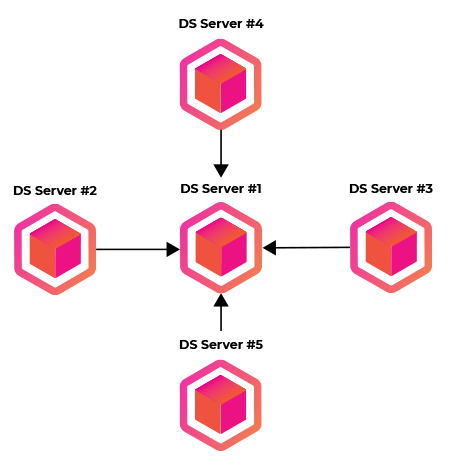
This structure allows different server setups and the deployment can be tailored to the exact requirements when it comes to scalability. The following diagram shows a central server that takes care of all authentication requests. DS Server #1 is the only server with security profiles and is handling all requests for connected servers.
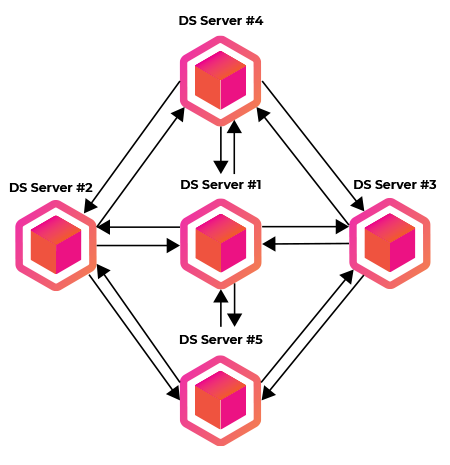
Distributed Authentication Servers
In this case, all instances (or some) are able to authenticate each request. This allows a better redundancy and authentication requests can be processed even if a central server is not available or accessible.
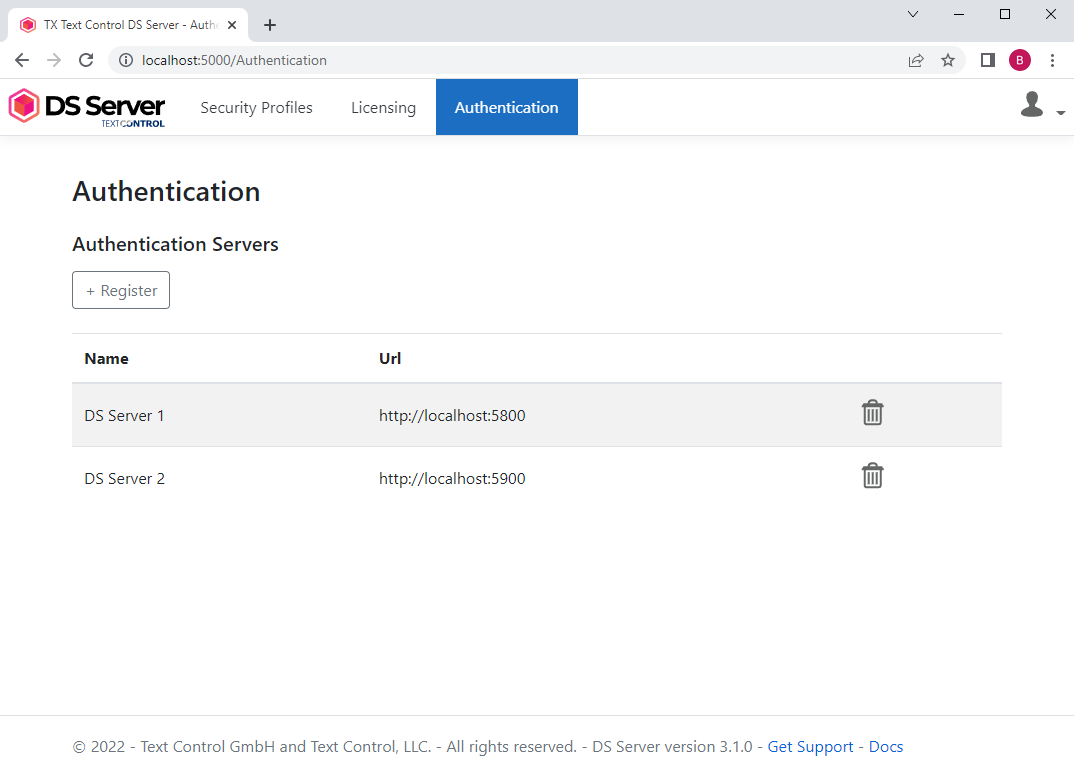
Portal Interface
The portal and the Web API have been extended to add authentication server URLs. The following screenshot shows the new portal section Authentication where 2 servers have been added:
Stay tuned for more features of DS Server 3.1.0.
ASP.NET
Integrate document processing into your applications to create documents such as PDFs and MS Word documents, including client-side document editing, viewing, and electronic signatures.
- Angular
- Blazor
- React
- JavaScript
- ASP.NET MVC, ASP.NET Core, and WebForms
Related Posts
Extending DS Server with Custom Digital Signature APIs
In this article, we will explore how to extend the functionality of DS Server by integrating custom digital signature APIs. We will cover the necessary steps to create a plugin that allows DS…
Meet Text Control at DDC 2025 in Cologne
Join us at the .NET Developer Conference (DDC) 2025 in Cologne from November 24-27. Visit our booth to explore the latest in document generation and reporting with Text Control's DS Server and…
Building an Ecosystem around DS Server: Join Us as a Plug-in Pioneer
DS Server 4.1.0 introduces a plug-in architecture that transforms the platform into an extensible ecosystem. Text Control invites developers, ISVs, and domain experts to co-innovate, build the…
Getting Started Video Tutorial: Using DS Server with Docker
This video tutorial demonstrates how to quickly set up a Docker container with your own on-premises DS Server backend. You'll learn how to spin up the container in just seconds and configure it to…
Unleash Document Automation Superpowers at NDC Oslo 2025
Join us at NDC Oslo 2025 to discover how to supercharge your document automation with the latest features and best practices. At our booth, you can explore the latest advances in document…






