Using TX Spell .NET in ASP.NET
TX Spell .NET ships with a non-visual TXSpell class that enables server-side spell checking in ASP.NET web applications and Windows services. This post shows how to validate user input using a CustomValidator control, detect misspelled words, and display correction suggestions.


 Both versions of TX Spell .NET (Windows Forms and WPF) ship with a non-visual component: TXTextControl.Proofing.TXSpell. This class can be used for ASP.NET Web Services, Web Applications or even Windows Services.
Both versions of TX Spell .NET (Windows Forms and WPF) ship with a non-visual component: TXTextControl.Proofing.TXSpell. This class can be used for ASP.NET Web Services, Web Applications or even Windows Services.
In order to create an instance of this pure spell checking engine, the following code is required:
TXTextControl.Proofing.TXSpell txSpell1 = new TXTextControl.Proofing.TXSpell();
txSpell1.Create();The Create method initializes the resources of a newly instantiated TXSpell object.
After an instance has been created, the Check method can be called to check the spelling of single words, a paragraph or a whole text. In this sample application, the content of an ASP.NET TextBox should be validated using the ServerValidate event of a CustomValidator. Using this validator object is a very smart way to validate user input and to display custom error messages when the input could not be validated. The following code is used to validate the content using TX Spell .NET:
protected void CustomValidator1_ServerValidate
(object source, ServerValidateEventArgs args)
{
TXTextControl.Proofing.TXSpell txSpell1 =
new TXTextControl.Proofing.TXSpell();
txSpell1.Create();
txSpell1.Check(args.Value);
if (txSpell1.IncorrectWords.Count == 0)
args.IsValid = true;
else
{
args.IsValid = false;
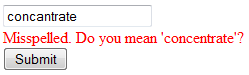
string sErrorMessage = "Misspelled.";
txSpell1.CreateSuggestions(args.Value);
if (txSpell1.Suggestions.Count > 0)
sErrorMessage += " Do you mean \'" +
txSpell1.Suggestions[0].Text + "\'?";
CustomValidator1.ErrorMessage = sErrorMessage;
}
}In a first step, the input string is checked for spelling errors. If the word is misspelled, TX Spell .NET is used to create proper suggestions that are suggested to the user in the custom validation error message.
This is just one way of using TX Spell .NET in a Web Application. How would you make use of it? Request a sample.
![]()
Download and Fork This Sample on GitHub
We proudly host our sample code on github.com/TextControl.
Please fork and contribute.
Requirements for this sample
- Visual Studio 2017 or better
- TX Text Control .NET Server (trial sufficient)
Related Posts
Create a Table of Contents in Windows Forms using C#
This article explains how to create a table of contents in Windows Forms using the ribbon or programmatically. Creating a table of contents is required to organize large documents.
Official TX Text Control .NET Sample Applications Are Now Hosted on GitHub
This article gives a quick overview of the new repositories, their structure and our plans for the future.
ASP.NETJavaScriptDocument Editor
Detect Toggle Button Changes Using a MutationObserver
This article shows how to detect changes of toggle buttons in the ribbon of the web editor using a MutationObserver. The state of a toggle button in the ribbon visualizes the state of a certain…
Two Ways to Restart Numbered Lists in TX Text Control
In TX Text Control, numbered lists are continued by default and need to be reset when required. There is more than one way if you want to restart numbered lists in a document. In this article, two…
Zoom Tricks: Disabling CTRL + MOUSE WHEEL and More
This article shows how to disable CTRL + MOUSE WHEEL, implement zooming with keyboard and reset the zoom factor to its default value.

