Create Word Document with .NET C#
This article provides a guide on using TX Text Control to create MS Word DOCX and DOC documents in .NET applications, such as ASP.NET Core and Windows applications. It covers steps to set up a console project in Visual Studio, install the required NuGet package, and write C# code to generate Word documents complete with paragraphs, tables, headers, and footers.

Creating Office Open XML (DOCX) documents in .NET applications is a common requirement and can be very complex when using the Open XML SDK. TX Text Control provides a high-level API for creating and manipulating DOCX documents in .NET applications. The library supports all the features of the DOCX format, including tables, headers and footers, and images.
With TX Text Control, you can generate MS Word document files in any .NET application, whether it's ASP.NET Core, a console app, or a Windows application.
Creating the Application
To demonstrate how easy this is with the TX Text Control library, we will use a .NET console application.
Make sure that you downloaded the latest version of Visual Studio 2022 that comes with the .NET 8 SDK.
Prerequisites
The following tutorial requires a trial version of TX Text Control .NET Server.
-
In Visual Studio 2022, create a new project by choosing Create a new project.
-
Select Console App as the project template and confirm with Next.
-
Choose a name for your project and confirm with Next.
-
In the next dialog, choose .NET 8 (Long-term support) as the Framework and confirm with Create.
Adding the NuGet Package
-
In the Solution Explorer, select your created project and choose Manage NuGet Packages... from the Project main menu.
Select Text Control Offline Packages from the Package source drop-down.
Install the latest versions of the following package:
- TXTextControl.TextControl.ASP.SDK
Creating a Word Document
-
Open the Program.cs file and add the following code:
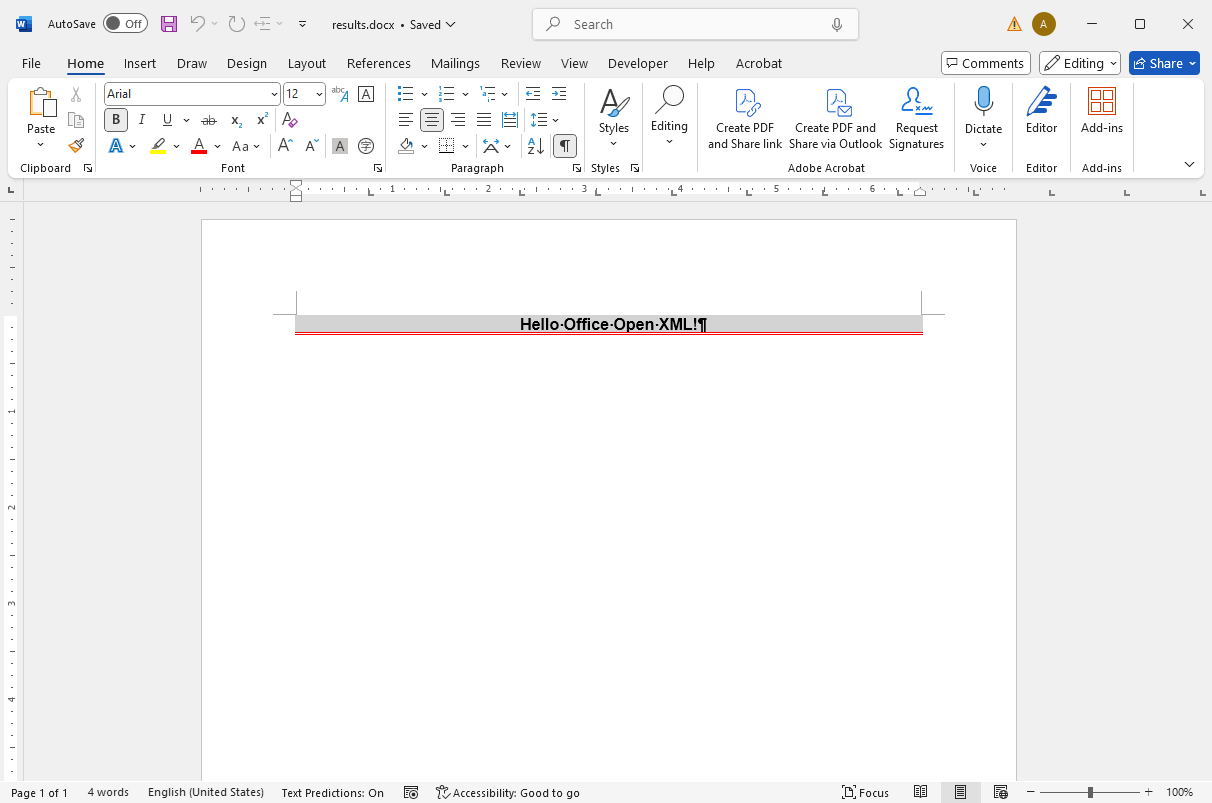
using TXTextControl; using (TXTextControl.ServerTextControl tx = new TXTextControl.ServerTextControl()) { tx.Create(); // Add a paragraph to the document TXTextControl.Selection selection = new TXTextControl.Selection(0, 0); selection.Text = "Hello Office Open XML!"; // Set the paragraph format selection.ParagraphFormat = new ParagraphFormat() { Alignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center, BackColor = System.Drawing.Color.LightGray, Frame = Frame.BottomLine, FrameLineColor = System.Drawing.Color.Red, FrameStyle = FrameStyle.Double, FrameLineWidth = 10 }; // Set the font format selection.FontSize = 240; // 240 twips = 12 pt selection.FontName = "Arial"; selection.Bold = true; // Apply the changes to the document tx.Selection = selection; // Save the document tx.Save("results.docx", TXTextControl.StreamType.WordprocessingML); }
This generates a new document and inserts a paragraph with defined formatting, such as borders, alignment, and character styling. The document is then saved as a DOCX file.
To create the document in the legacy DOC format, you can use the Stream
tx.Save("results.doc", TXTextControl.StreamType.MSWord);Adding Tables
Inserting tables into a document is as straightforward as adding text. The following code snippet demonstrates how to create a table, format cells, and apply borders and background colors for a customized appearance.
using TXTextControl;
using (TXTextControl.ServerTextControl tx = new TXTextControl.ServerTextControl())
{
tx.Create();
tx.Tables.Add(5, 5, 10);
// Set the table border style
Table table = tx.Tables.GetItem(10);
// Set the table border style
TableCellFormat cellFormat = new TableCellFormat()
{
BottomBorderWidth = 1,
BottomBorderColor = System.Drawing.Color.Red,
TopBorderWidth = 1,
TopBorderColor = System.Drawing.Color.Red,
LeftBorderWidth = 1,
LeftBorderColor = System.Drawing.Color.Red,
RightBorderWidth = 1,
RightBorderColor = System.Drawing.Color.Red,
BottomTextDistance = 80,
TopTextDistance = 80,
LeftTextDistance = 120,
RightTextDistance = 120
};
// Loop through all cells and set the cell format
foreach (TableCell cell in table.Cells)
{
cell.CellFormat = cellFormat;
cell.Text = $"Cell: {cell.Row}/{cell.Column}";
}
// Highlight the first column and row
TableCellFormat highlightCellFormat = new TableCellFormat()
{
BackColor = System.Drawing.Color.LightGray
};
table.Columns.GetItem(1).CellFormat = highlightCellFormat;
table.Rows.GetItem(1).CellFormat = highlightCellFormat;
// Save the document
tx.Save("results.docx", TXTextControl.StreamType.WordprocessingML);
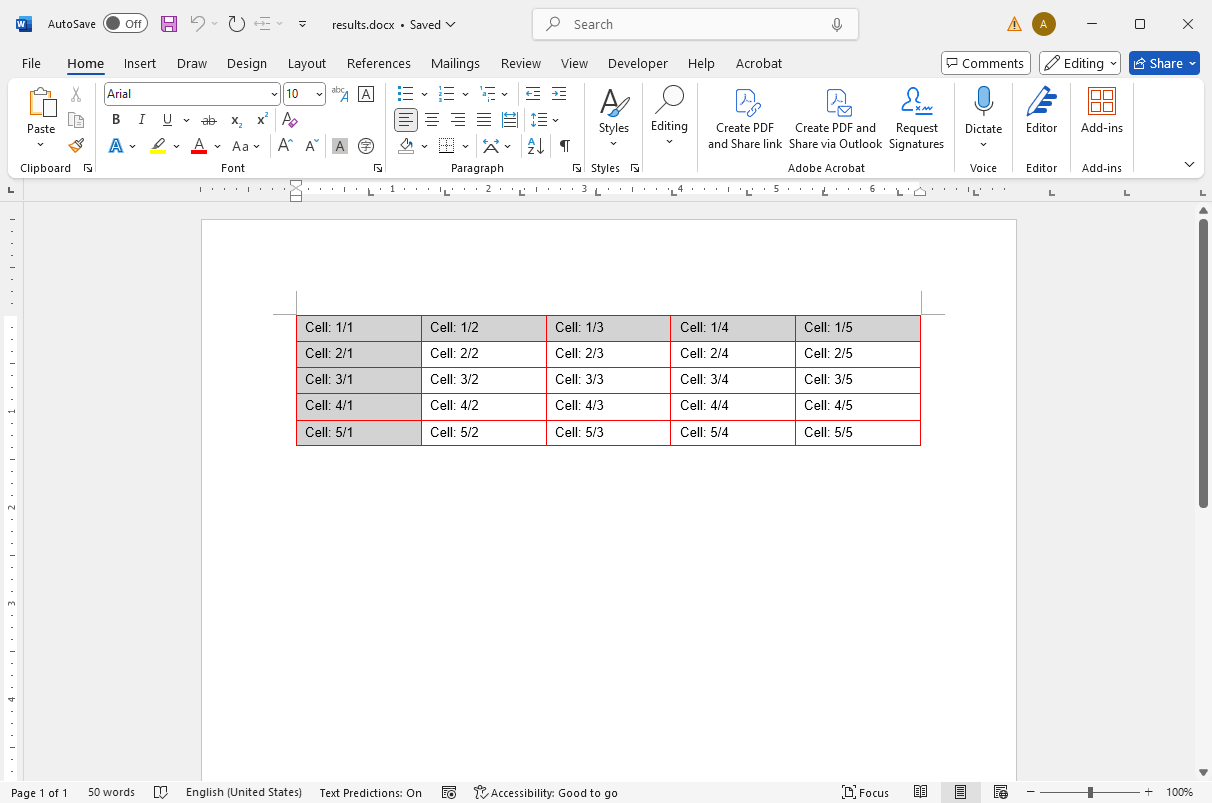
}When opened in MS Word, the DOCX document looks like this:
Adding Headers and Footers
You can add headers and footers to a document through the Headers
Headers and footers are designated areas at the top (header) and bottom (footer) of each page within a document. They typically contain information like page numbers, titles, dates, logos, or other consistent elements that repeat across the document to enhance structure and readability.
using TXTextControl;
using (ServerTextControl tx = new ServerTextControl())
{
tx.Create();
// Add a header
tx.Sections.GetItem().HeadersAndFooters.Add(HeaderFooterType.Header);
// Get the header/footer object
HeaderFooter headerFooter = tx.Sections.GetItem().HeadersAndFooters.GetItem(HeaderFooterType.Header);
// Add an image to the header
Image image = new Image("tx_logo.svg", 0);
headerFooter.Images.Add(image, HorizontalAlignment.Right, 1, ImageInsertionMode.AboveTheText);
// Add a text to the header
headerFooter.Selection.Text = "Header Text\r\n\r\n";
// Add a page number field to the header
headerFooter.Selection.Text = "Page ";
headerFooter.PageNumberFields.Add(new PageNumberField());
headerFooter.Selection.Text = " of ";
headerFooter.PageNumberFields.Add(new PageNumberField() { ShowNumberOfPages = true });
// Add a new page
tx.Selection.Text = "\f";
// Save the document
tx.Save("results.docx", StreamType.WordprocessingML);
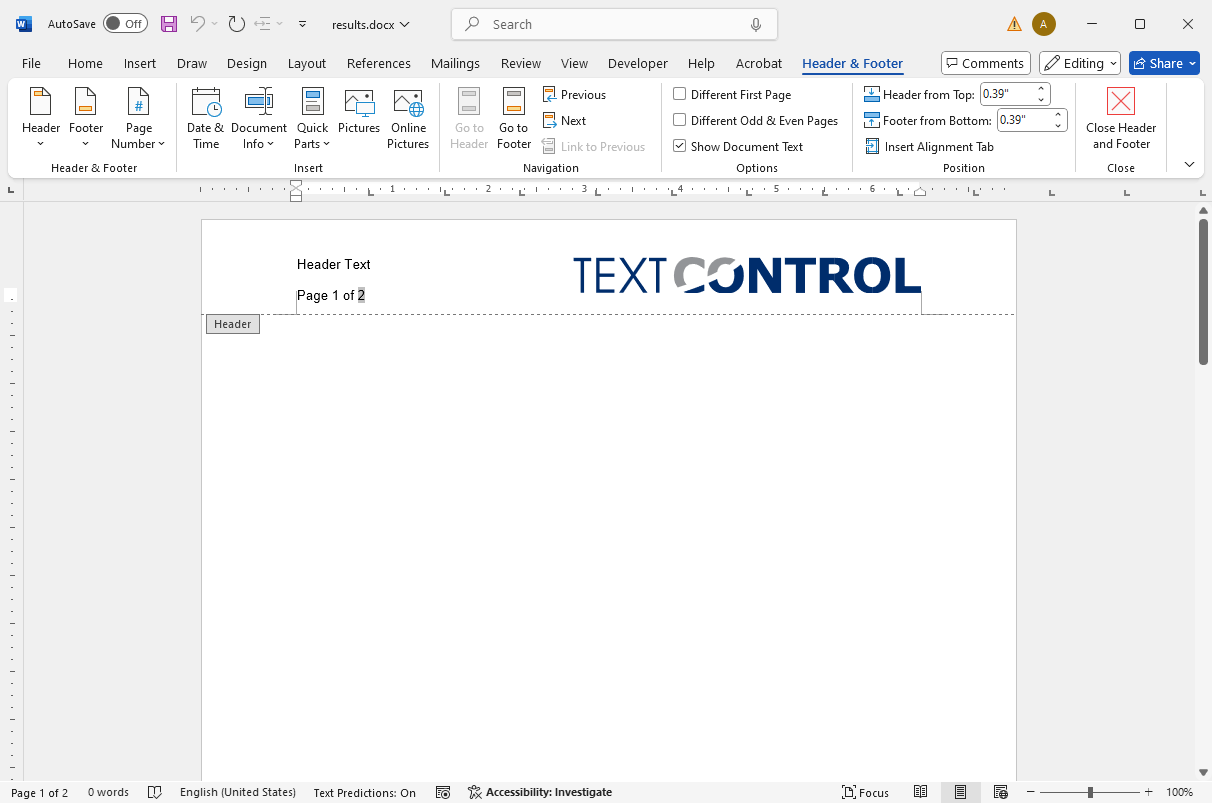
}When you open the Word document in Microsoft Office, it looks like this:
Meta Data and Document Properties
Document properties, often referred to as metadata, are details about the document that describe or identify it. This can include information such as the document title, author name, modification date, subject, and specific keywords to identify or categorize the content.
In TX Text Control, metadata can be added using the Save
TXTextControl.SaveSettings saveSettings =
new TXTextControl.SaveSettings() {
Author = "Susan Paul",
CreationDate = DateTime.Now,
CreatorApplication = "TX Text Control",
DocumentKeywords = new string[] { "Summary", "Report" },
DocumentSubject = "Detailed summary report 2022",
DocumentTitle = "Sales Report 2022"
};
textControl1.Save("output.docx",
TXTextControl.StreamType.WordprocessingML, saveSettings);Custom properties allow you to store extra information within a document, which stays embedded and is visible to any MS Word user who opens it. Various property management servers offer data tracking features, enabling users to search, sort, and monitor documents based on these embedded document properties.
The following code is an example of how to add new custom properties to an MS Word document:
TXTextControl.UserDefinedPropertyDictionary userSettings =
new TXTextControl.UserDefinedPropertyDictionary();
userSettings.Add("CustomPropertyString", "Custom property string");
userSettings.Add("CustomPropertyInt32", 123);
userSettings.Add("CustomPropertyBoolTrue", true);
userSettings.Add("CustomPropertyBoolFalse", false);
userSettings.Add("CustomPropertyDouble", 123.232);
TXTextControl.SaveSettings saveSettings = new TXTextControl.SaveSettings() {
UserDefinedDocumentProperties = userSettings
};
textControl1.Save("output.docx",
TXTextControl.StreamType.WordprocessingML,
saveSettings);When you open the Advanced Properties dialog box in MS Word, you see a list of these key/value pairs:
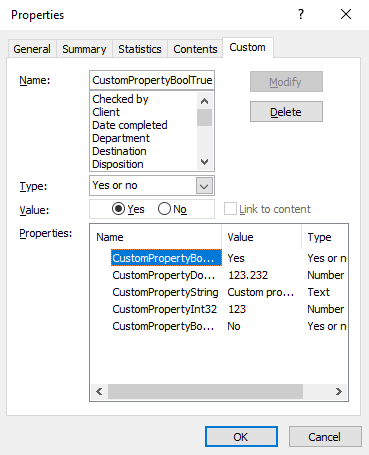
Conclusion
TX Text Control provides developers with a powerful, high-level API to create and manipulate DOCX documents seamlessly within .NET applications. It provides comprehensive support for all DOCX features, including tables, headers and footers, images, and more. TX Text Control makes it easy to create dynamic, professional-looking documents. Imagine effortlessly creating MS Word files directly from any .NET environment, whether it's ASP.NET Core, console applications, or Windows applications. Take advantage of the flexibility and efficiency of TX Text Control to transform the way you work with documents and add value to your applications.
ASP.NET
Integrate document processing into your applications to create documents such as PDFs and MS Word documents, including client-side document editing, viewing, and electronic signatures.
- Angular
- Blazor
- React
- JavaScript
- ASP.NET MVC, ASP.NET Core, and WebForms
Related Posts
How to Import and Read Form Fields from DOCX Documents in .NET on Linux
Learn how to import and read form fields from DOCX documents in .NET on Linux using TX Text Control. This article provides a step-by-step guide to help you get started with form fields in TX Text…
How to Programmatically Create MS Word DOCX Documents with .NET C# on Linux
Learn how to programmatically create MS Word DOCX documents using .NET C# on Linux with TX Text Control. This tutorial covers the necessary steps to set up your environment and create a simple…
Edit MS Word DOCX Files in .NET C# and ASP.NET Core
This article shows how to edit MS Word DOCX files in .NET C# and ASP.NET Core using the TX Text Control Document Editor and also how to manipulate documents without a user interface using the…
How to Extend the Default Style Mapping when Converting DOCX to Markdown in…
Learn how to customize the default style mapping when converting DOCX documents to Markdown format using Text Control's .NET C# libraries. This article provides step-by-step instructions and code…
DOCX Meets Markdown: Preparing Enterprise Documents for AI
Discover why Markdown is a game-changer for document creation in the age of AI. Explore how this lightweight markup language can enhance collaboration, version control, and integration with AI…






