Windows Forms: Adding Margins to FloatingText ViewMode
When using any other view mode than the PageView mode, page-oriented features such as margins are not visible. This sample shows how to add TextControl to a container panel to simulate a margin and how to integrate custom scroll bars.

When using any other view mode than the PageView mode, page-oriented features such as margins are not visible. This sample shows how to add TextControl to a container panel to simulate a margin and how to integrate custom scroll bars.
FloatingText ViewMode
The following screenshot shows a Text
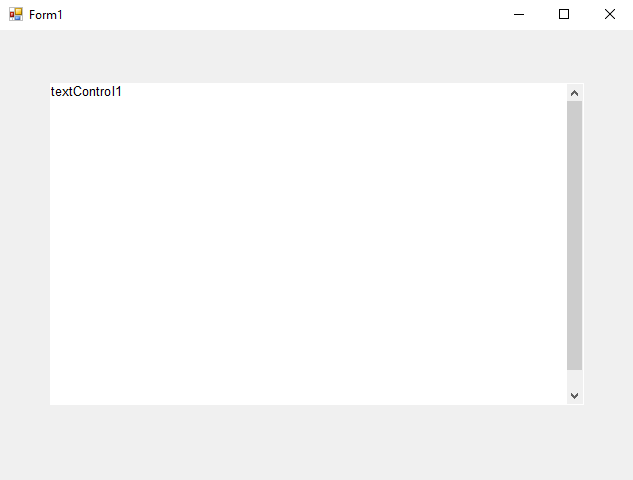
According to the documentation, this view mode has specific settings and limitations:
FloatingText
This view mode provides a vertical scrollbar to enable unlimited text content. The maximum horizontal text extent is the horizontal size of the control. The values of the PageSize and PageMargins properties are ignored. Headers and footers are not displayed.
As you can see in the screenshot, the text is directly aligned with the border of the control. But in some applications, a border or a margin should be displayed when using this view mode.
Adding a Panel
An obvious idea is to place the TextControl into a panel with the same background color like the page color and a specific padding enabled:
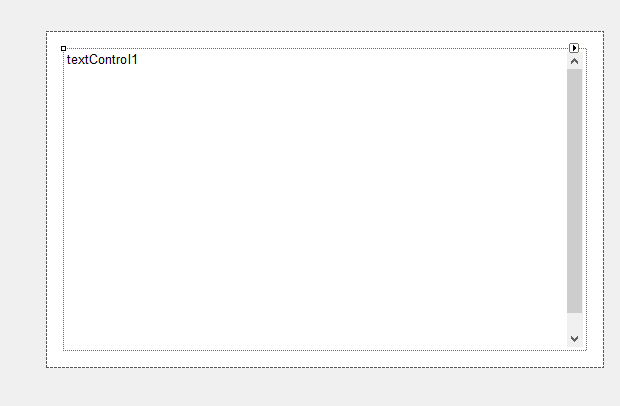
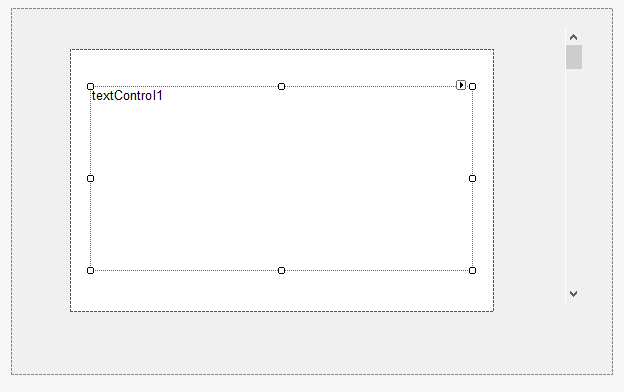
Now, there is a visible margin, but the scrollbar is inside the new padding as well. In order avoid that, a custom scrollbar must be implemented. The following screenshot shows the custom control that consists of two panels, a vertical scrollbar and a TextControl.
When docked and used on a form, you can see a working scrollbar and a visible margin when using the FloatingText view mode:
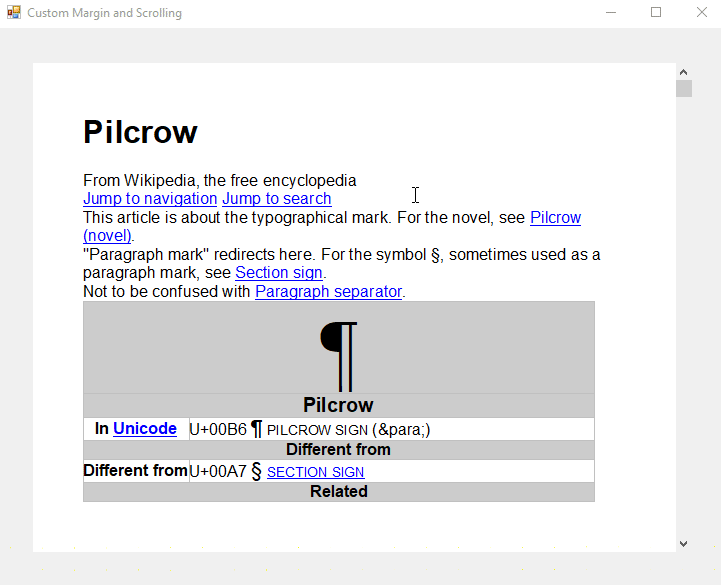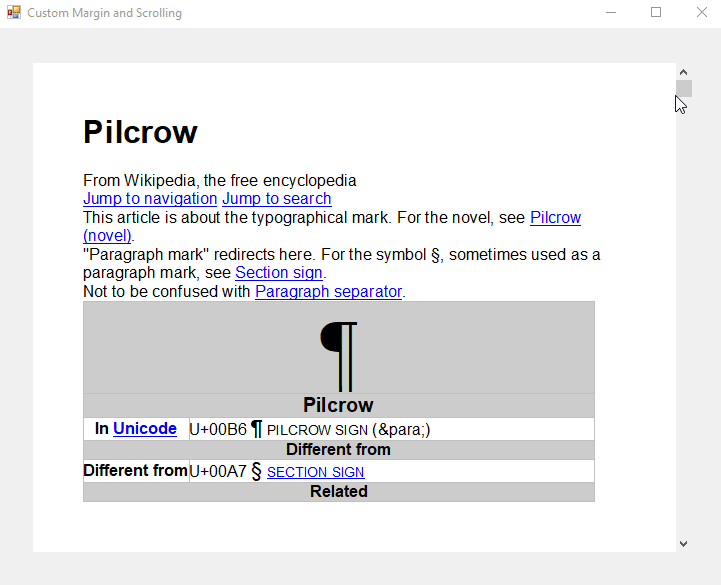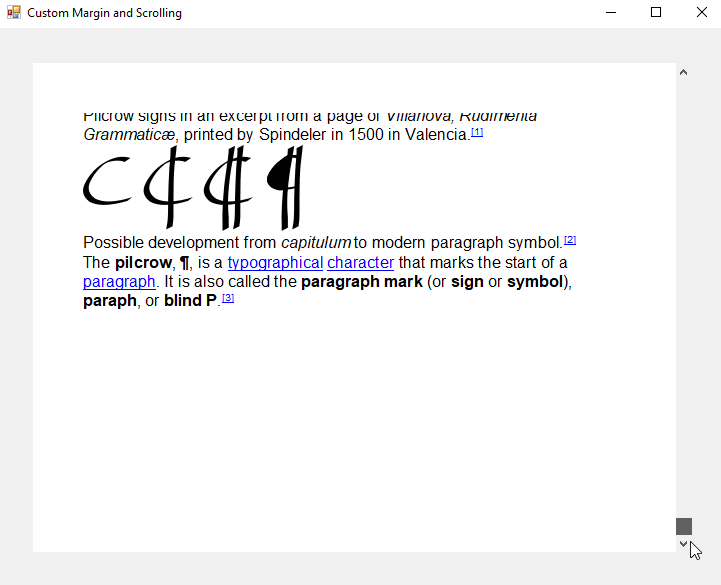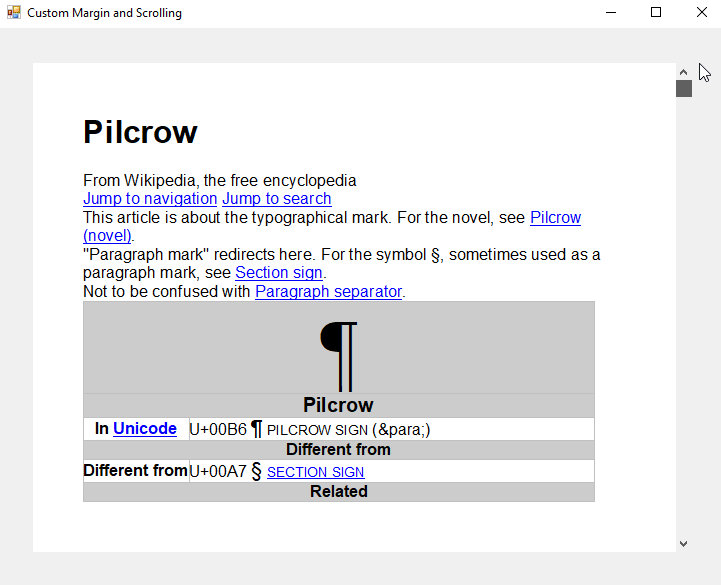
The following code is mirroring the maximum scrollbar value of the custom scrollbar with the Scroll
private bool scrolling = false;
private void setScrollOffset() {
// remember old scroll location
var oldScrollLocation = textControl1.ScrollLocation;
// scroll to bottom to get max value
textControl1.ScrollLocation = new Point(0, int.MaxValue);
int scrollY = textControl1.ScrollLocation.Y;
// mirror the max value in custom scroll bar
vScrollBar1.Maximum = scrollY;
// restore scroll location
textControl1.ScrollLocation = oldScrollLocation;
}
private void textControl1_Changed(object sender, EventArgs e) {
setScrollOffset();
}
private void textControl1_VScroll(object sender, EventArgs e) {
if (scrolling == true)
return;
// set the scroll location
if (textControl1.ScrollLocation.Y <= vScrollBar1.Maximum) {
vScrollBar1.Value = textControl1.ScrollLocation.Y;
vScrollBar1.SmallChange = 300; // fine tune speed here
vScrollBar1.LargeChange = 300;
}
}
private void vScrollBar1_Scroll(object sender, ScrollEventArgs e) {
// mirror the scroll location
scrolling = true;
textControl1.ScrollLocation = new Point(0, e.NewValue);
scrolling = false;
}Feel free to test this on your own by downloading the sample from our GitHub repository.
Also See
This post references the following in the documentation:
- TXText
Control. Text Control Class - TXText
Control. Text Control. Scroll Location Property - TXText
Control. Text Control. View Mode Property
![]()
Download and Fork This Sample on GitHub
We proudly host our sample code on github.com/TextControl.
Please fork and contribute.
Requirements for this sample
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms 30.0
- Visual Studio 2022
Windows Forms
Text Control combines the power of a reporting tool and an easy-to-use WYSIWYG word processor - fully programmable and embeddable in your Windows Forms application. TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms is a royalty-free, fully programmable rich edit control that offers developers a broad range of word processing features in a reusable component for Visual Studio.

