TX Spell .NET is a very powerful spell checking engine with a tight integration into the document editors from Text Control including ASP.NET, Angular and Windows Forms. It provides fully-featured UI elements including dialog boxes and context menus when connected to a Text Control instance.
Non-Visual Spell Engine
But the product also includes the non-visual component TXSpell 
╰ Proofing Namespace
╰ TXSpell Class
The TXSpell class provides properties and methods with spell checking features. that can be used for background processing. This sample shows how to use this class to create a spell checking Web API using ASP.NET Core.
Implementing the Web API Controller
The sample implements the Web API controller SpellController:
| [Route("api/[controller]")] | |
| [ApiController] | |
| public class SpellController : ControllerBase | |
| { | |
| } |
This controller implements 4 endpoints:
- Check
- CreateSuggestions
- CreateSynonyms
- DetectLanguageScopes
The following code shows the implementation of the Check method that accepts the Text to be checked and an optional language identifier:
| [HttpGet] | |
| [Route("Check")] | |
| public List<IncorrectWordModel> Check(string text, string language = "en_US") | |
| { | |
| if (text == null) | |
| return null; | |
| // create a new spell checking engine | |
| TXTextControl.Proofing.TXSpell spell = new TXTextControl.Proofing.TXSpell(); | |
| spell.Create(); | |
| TXTextControl.Proofing.OpenOfficeDictionary dict = | |
| new OpenOfficeDictionary(@"Dictionaries\en_US.dic"); | |
| spell.Dictionaries.Add(dict); | |
| spell.Check(text, new System.Globalization.CultureInfo(language)); | |
| List<IncorrectWordModel> lIncorrectWords = new List<IncorrectWordModel>(); | |
| var incorrectWords = spell.IncorrectWords; | |
| if (incorrectWords == null) | |
| return null; | |
| foreach (IncorrectWord word in incorrectWords) | |
| { | |
| lIncorrectWords.Add(new IncorrectWordModel() | |
| { | |
| Text = word.Text, | |
| Index = word.Index, | |
| IsDuplicate = word.IsDuplicate, | |
| Length = word.Length, | |
| Start = word.Start | |
| }); | |
| } | |
| return lIncorrectWords; | |
| } |
In the method Check, a new instance of the spell checker is created and a dictionary is loaded and added to the available dictionaries using the Dictionaries.
╰ Proofing Namespace
╰ DictionaryCollection Class
╰ Add Method
Adds objects of the type Dictionary to the collection and validates them for spell checking and suggestion operations. method.
The given Text is checked using the Check 
╰ Proofing Namespace
╰ TXSpell Class
╰ Check Method
Checks text for spelling errors and fills the IncorrectWordCollection at TXSpell.IncorrectWords with all incorrect words. method and the results are returned as a list of IncorrectWords.
Calling from JavaScript
On the JavaScript side, the endpoint is called using a jQuery ajax call:
| async function check(text, language = "en_US") { | |
| var serviceURL = "api/spell/check?text=" + text + "&language=" + language; | |
| return await callEndpoint(serviceURL); | |
| } |
| async function callEndpoint(serviceURL) { | |
| return new Promise(resolve => { | |
| $.ajax({ | |
| type: "GET", | |
| url: serviceURL, | |
| contentType: 'application/json', | |
| success: successFunc, | |
| error: errorFunc | |
| }); | |
| function successFunc(data, status) { | |
| resolve(data); | |
| } | |
| function errorFunc(data) { | |
| throw "Request failed. Please try again later."; | |
| } | |
| }); | |
| } |
The spell checking functions are encapsulated in a private scope and exposed as properties in the TXSpell JavaScript object. This way, the check method can be called like this in the sample:
| async function checkText() { | |
| // call the check method | |
| var results = await TXSpell.check(document.getElementById('textbox').textContent); | |
| // check console for details | |
| console.log(results); | |
| var consoleText = ""; | |
| // loop through the results and return the text | |
| results.forEach(function (element) { | |
| consoleText += "<p>Misspelled: <strong>" + element.text + "</strong></p>"; | |
| }); | |
| document.getElementById('results').innerHTML = consoleText; | |
| } |
On a button click, the function checkText is called:
| <input value="Check" type="button" onclick="checkText()" /> |
Demo Screenshots
The following screenshot shows the sample after the Check button has been clicked:
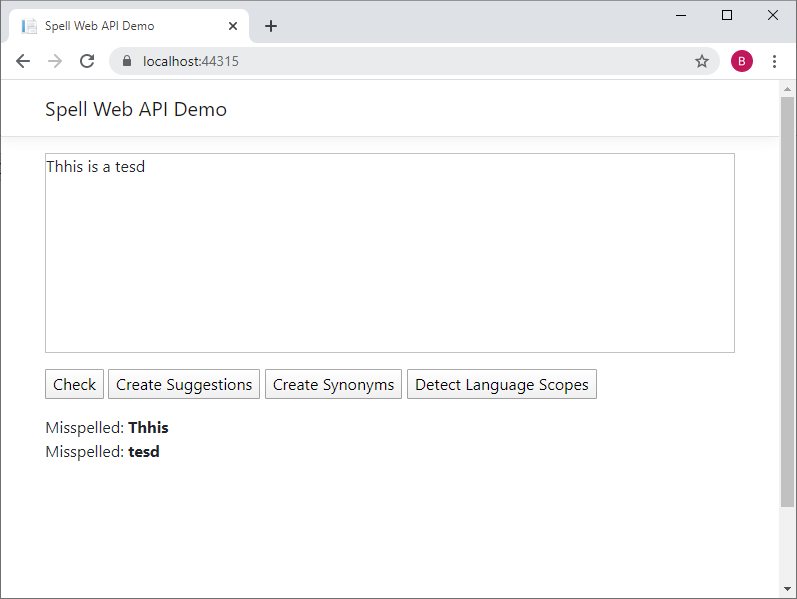
Create Suggestions:
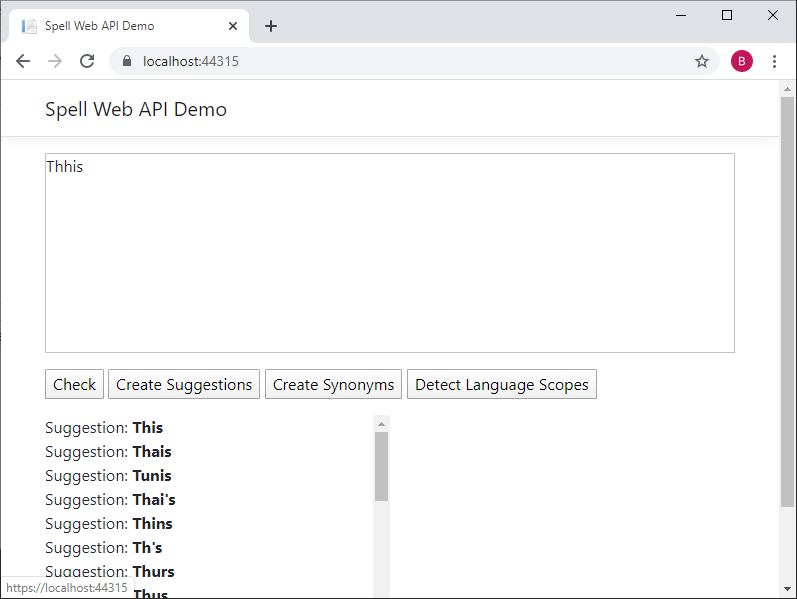
Create Synonyms:
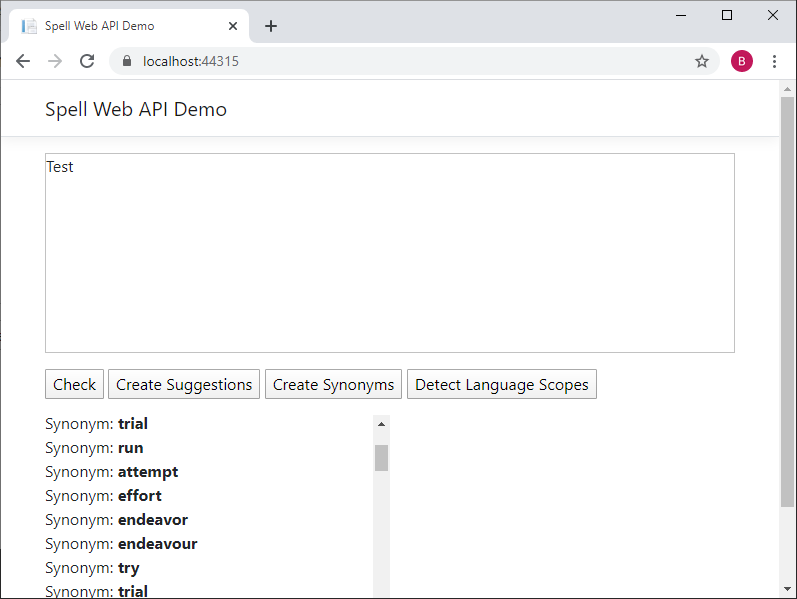
Detect Languages:
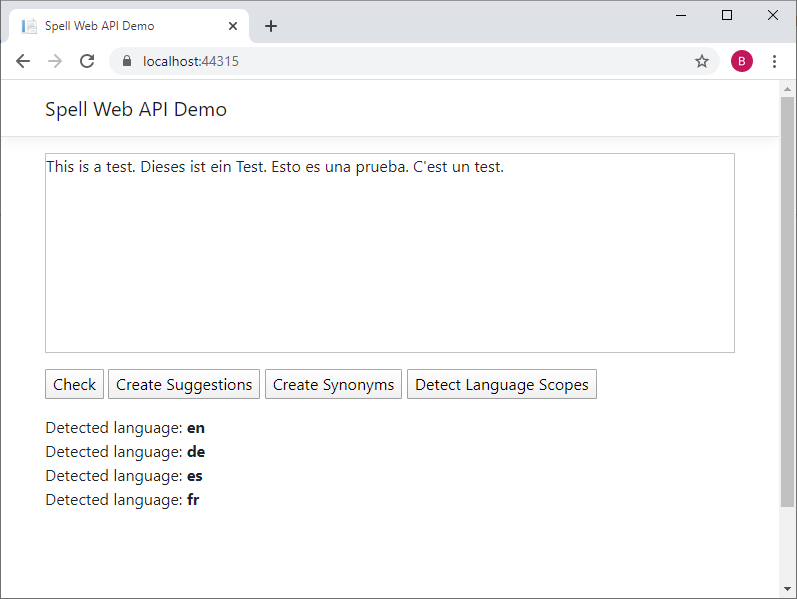
Download the sample project and test this on your own.






