Your Requirements - Our Features
MS Word
Add MS Word Look and Feel to your Applications
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms provides comprehensive, MS Word-compatible text formatting, powerful mail merge features and all word processing key concepts such as table support, images, headers and footers and page sections.
Reporting
Combine Word Processing and Powerful Reporting
Text Control Reporting combines the power of a reporting tool and an easy-to-use WYSIWYG word processor - fully programmable and embeddable in your Windows Forms application.
Core Processing
Most Advanced Feature-Set in Rich Text Controls
Integrate professional word processing features into your Windows Forms applications such as headers and footers, page sections, background images, protected sections, hyphenation and many more.
Browser
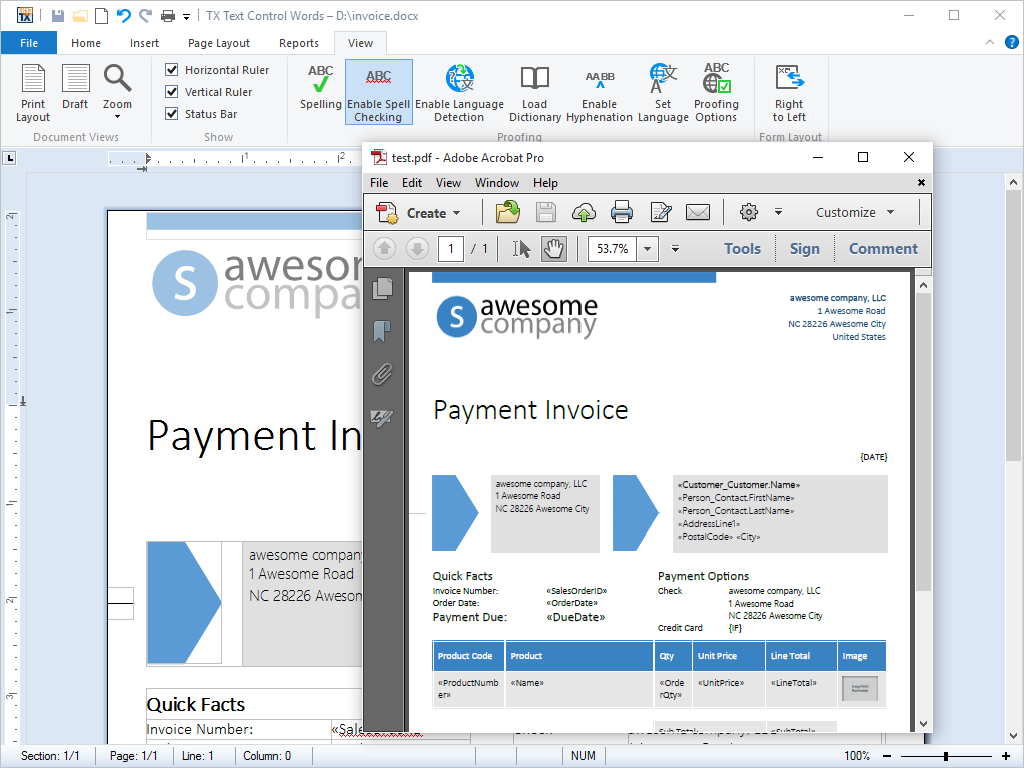
Create, Import and Edit Adobe PDF and PDF/A
Using TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms, you can create Adobe PDF and PDF/A documents including document access security settings and digital signatures. Additionally, "digitally born" PDF documents can be imported, viewed, edited and converted.
Features in Detail
- Common Word Processing Features This category lists typical word processing features that can be found in professional word processors such as MS Word.
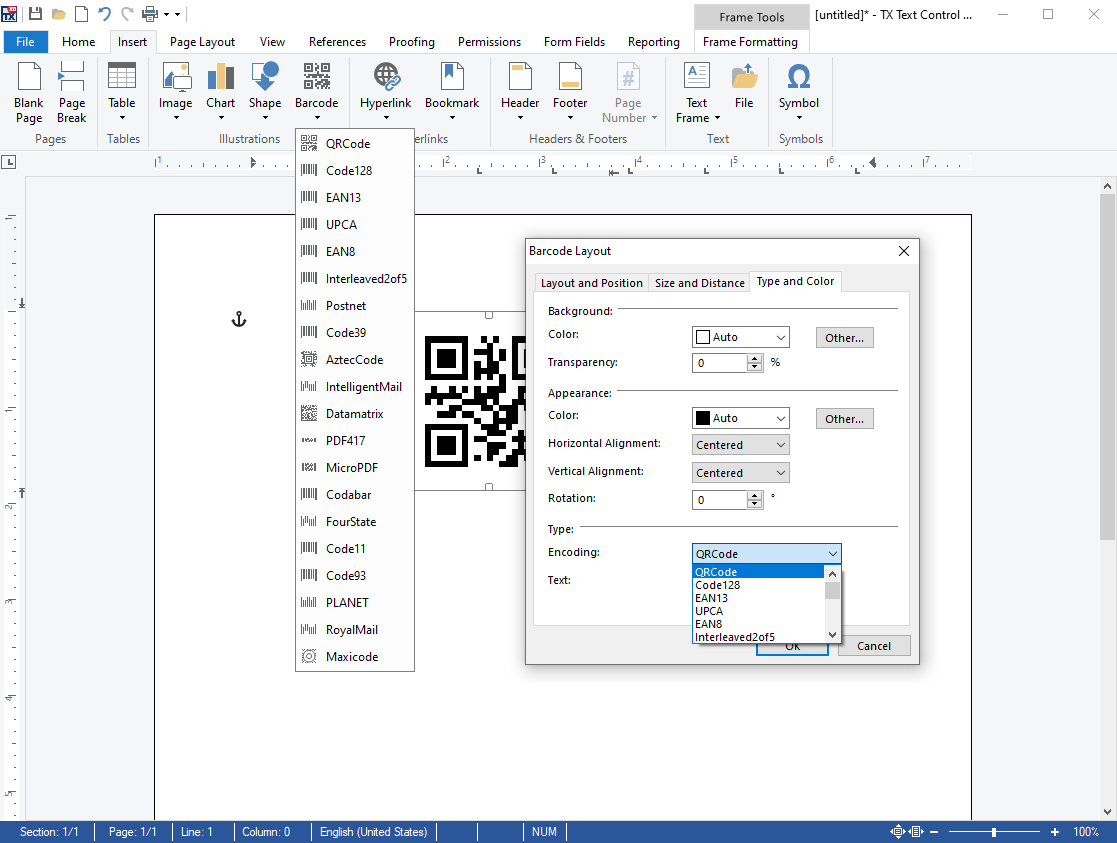
- 1D and 2D Barcode Support Barcode support is directly integrated into TX Text Control without the dependency on optional products.
In today's processes, barcodes are included everywhere: Invoices, delivery notes or boarding passes. Barcodes are used to store digital data on paper that can be acquired easily for further processing using laser-based scanners, cameras or mobile phones.
Barcodes can close the gap between online business processes and the paper oriented world. Consider a QR Code on an electricity bill. The QR Code contains a direct payment URL with parameters containing customer details, the invoice number, the amount or simply a generated ID for this specific transaction for an easy payment experience.
Using TX Text Control, you can add fast and accurate 1D and 2D barcodes to your .NET based applications. Integrate barcodes into reports, invoices and mail merge templates. Generated barcodes are optimized for printing and on-screen scanning.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
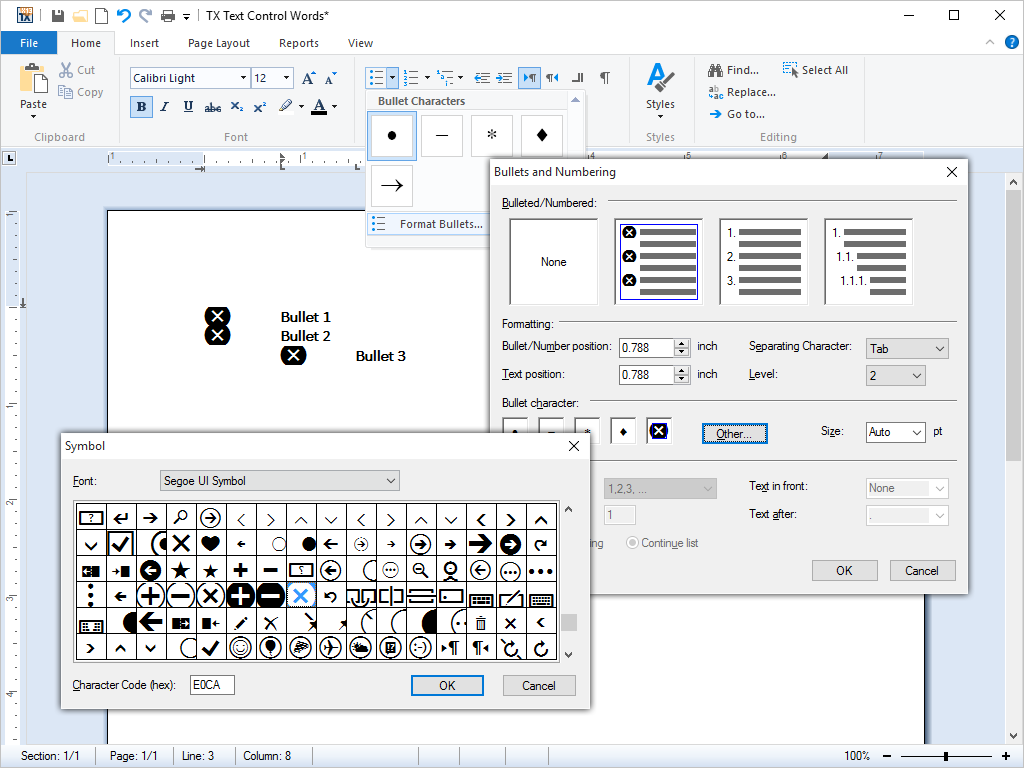
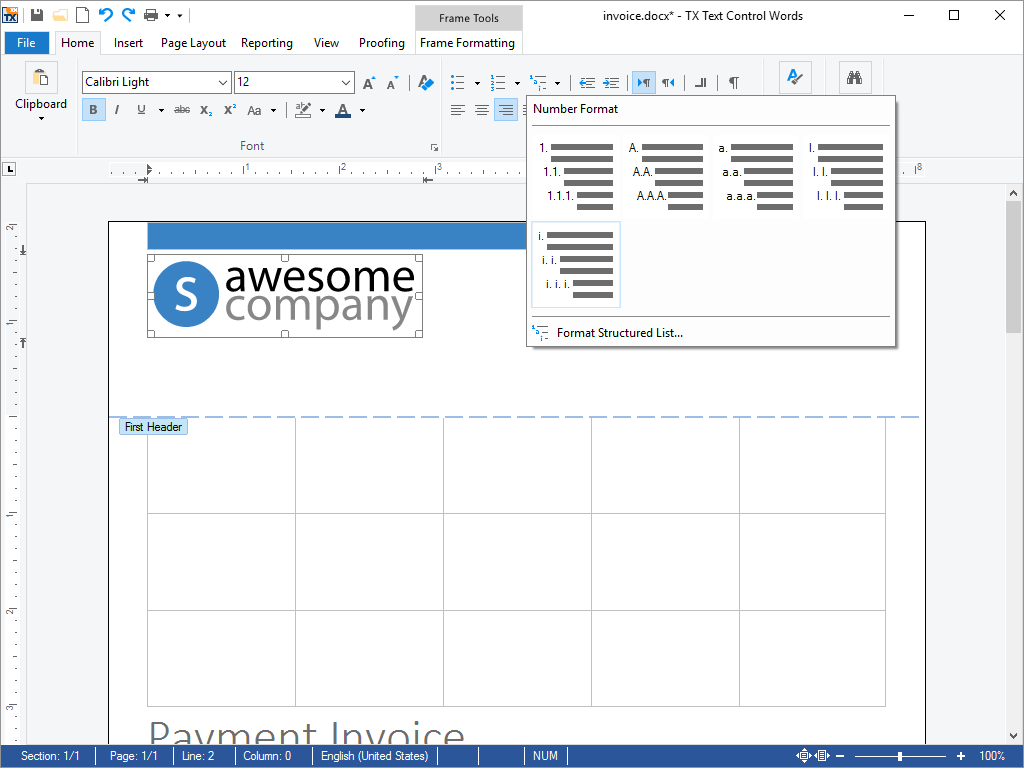
- Bullets and Numbered Lists Every aspect of bullets and numbered lists can be influenced from program code. Lists can be incremented and numbered automatically.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms provides comprehensive support for bullets and numbered lists. Typical applications areas include the creation of documents containing meeting minutes, reading lists or to do lists.
Virtually every conceivable attribute of the bullets and numbered lists can be user defined, including the type and shape of bullet directly from program code.
Numbered lists and bullets may contain any of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms vast formatting options.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Character and Paragraph Formatting Rich character and paragraph formatting is standard in all editions. All formatting options expected from a word processor are available.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms offers all the formatting control over character and paragraph presentation and that you would expect from a fully fledged word processing package.
Applications created with TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms provide rich character formatting options, including font size, font family, character style, foreground and background colors etc.
All formatting options can be combined with one another, making the possible formatting options almost infinite.
Flexible paragraph formatting such as indentation, many types of tabs, variable line and paragraph spacing, and paragraph frames offer a variety of formatting opportunities.
The following paragraph styles are available:
Keep with next: By selecting this option, an end-user can force TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms to place the current paragraph and the preceding paragraph on the same page.
Keep lines together: If the end-user selects this attribute, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms places all lines of the current paragraph on the same page. TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms does not break this paragraph, but keeps it intact.
Page break before: If the end-user selects this attribute, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms places the current paragraph at the top of a new page.
Widow and orphan control: Widow and orphan control options can be set by developers and end-users. The number of lines that are considered to constitute a widow or orphan can be specified.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms offers end-users access to all formatting options directly from the shipped dialog box.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Clipboard Operations All clipboard operations are built in and require no programming effort. ASCII, HTML and RTF are used for maximum interoperability.
Typical clipboard operations, such as 'Cut', 'Copy' and 'Paste' are built into TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms and require no further programming effort.
In addition to plain text and HTML, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms automatically uses RTF as a clipboard format to exchange formatted text and images with other Windows applications.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms provides programmers an easy way to change the default behavior for pasting data from the clipboard. TextControl.GetClipboardFormats returns an array of formats, currently stored in the clipboard and which can be pasted into TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms.
Developers can easily make clipboard operations available to the end-user via menu points and directly from keyboard shortcuts.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
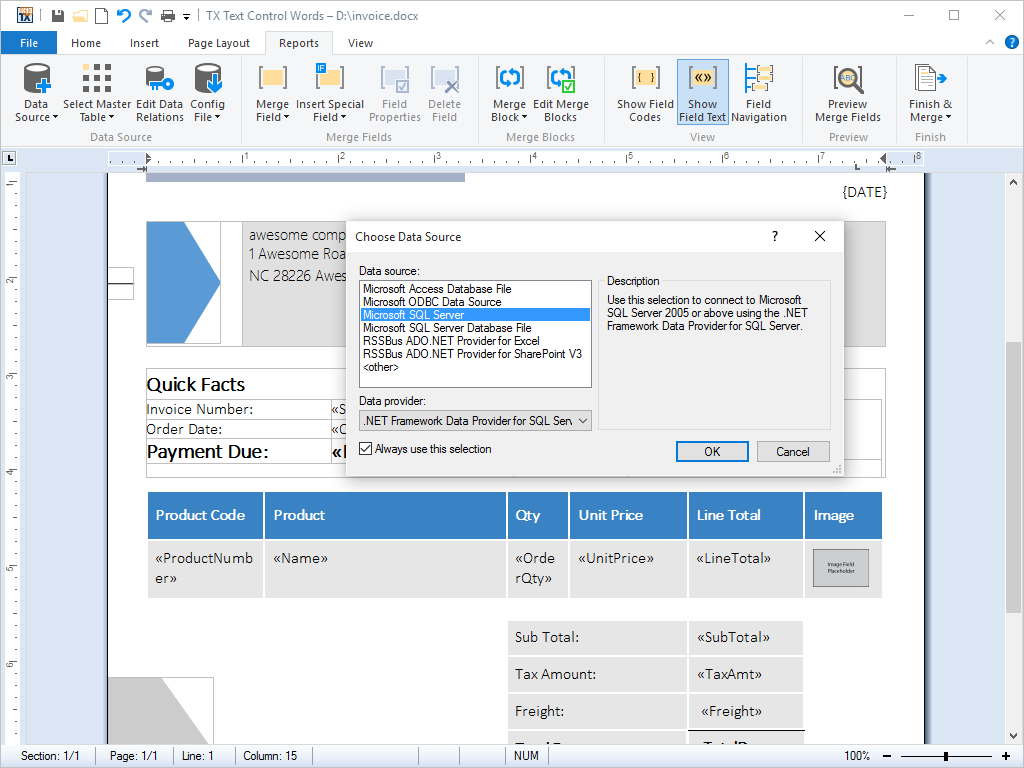
- Loading from and Saving to Databases Read from and write to databases, independent of the type of database or interface, using all formats supported by TX Text Control.
Using a fully abstracted database layer, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms can load and save plain text and formatted blocks of text from and to all databases.
Additionally, fully formatted documents, including pages containing graphics, tables, header, footers and any other rich formatting that TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms offers can be stored to and retrieved from databases.
Typical applications include mail merge, report generation and any other scenario in which documents are stored in a central database and edited on a client - such as content management systems or intranet based word processing programs.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Integrated Dialog Boxes All editions ship with multiple end-user dialog boxes. Dialog boxes can also be accessed from program code and are fully localizable.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms ships with many integrated dialog boxes for most functions, including dialog boxes for paragraph settings, text formatting, table formatting, stylesheet formatting, bullets and numbered and many more.
In addition to English, all dialog boxes are shipped in French, Spanish, Italian and German. Furthermore, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms based applications can be localized into any further language using the shipped resource kit. Localizing into a new language is simply a matter of translating a resource file.
While these dialog boxes provide a standardized interface for the end-user, all of the functionality that can be addressed using a point and click interface is also available to the developer from program code.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
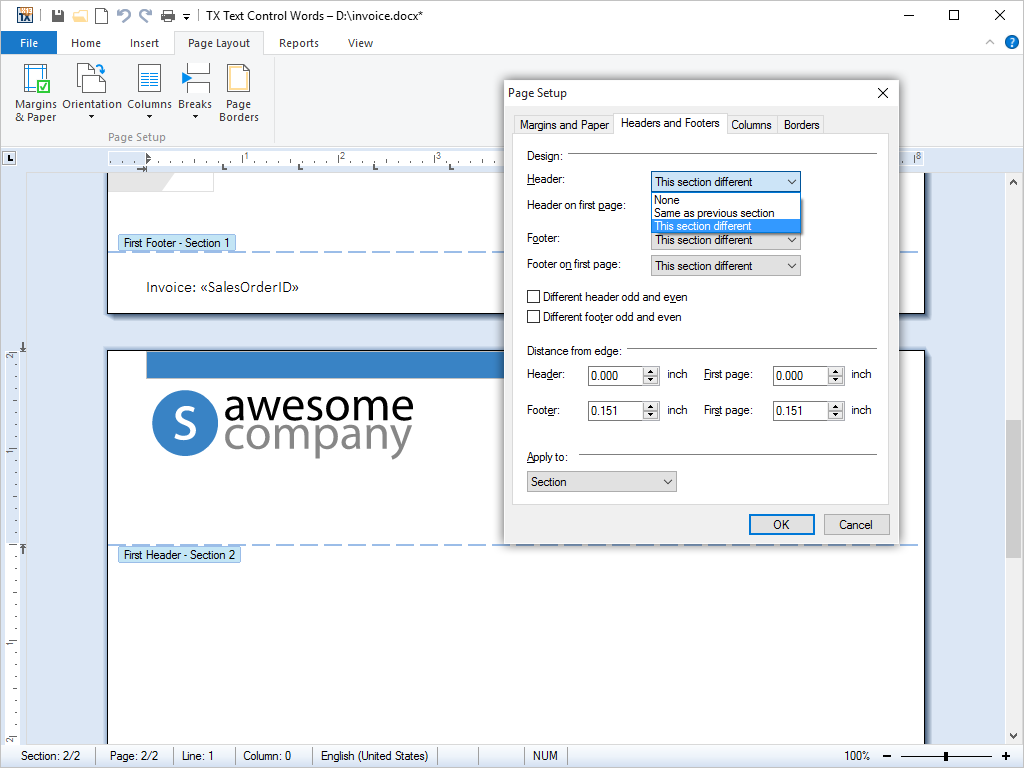
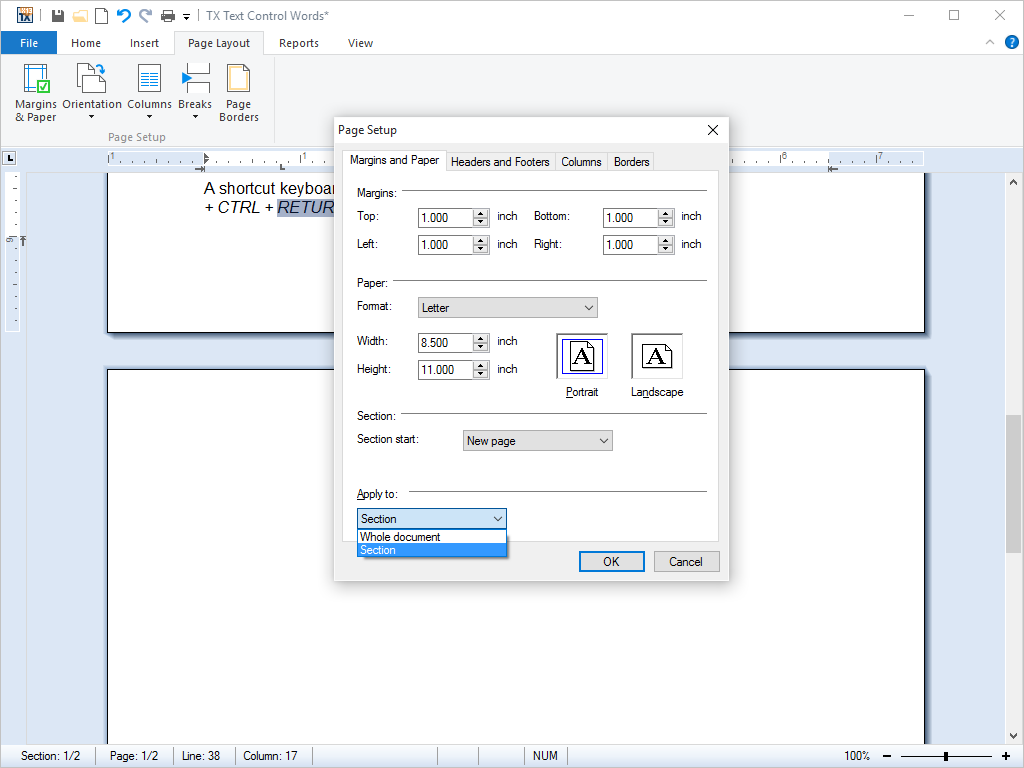
- Document Sections Documents can be divided into an unlimited number of different sections, each one of which may be individually formatted.
The document sections feature of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms allows documents to be divided into an unlimited number of different parts. Each part, or section, can be formatted independently of all other sections in the document.
The following document configurations and formatting options are now possible:
Multiple page orientations: The orientation of a page in each section can be specified. This enables one document to contain pages with varying orientations.
Multiple headers and footers formatting: The formatting of headers and footers can be specified on a per-section basis. This allows the headers and footers in each section in a document to be formatted independently from the headers and footers in all other sections.
Multiple page sizes and margin settings: The dimensions of a specific page can be set independently of the dimensions on all other pages in a document. Similarly, the margins of a specific page can be set independently to the margins of all other pages.
Section dialog box: TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms ships with a dialog box that the entire document or individual sections to be formatted.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Footnotes Insert MS Word compatible footnotes into documents.
Footnotes are a word processing feature that allows users to insert additional information at the bottom of pages. Without interrupting the flow of the main text, these notes provide additional details or citations.
Legal software, one of our main industries where TX Text Control is used, is another area where footnotes are popular. Legal footnotes are especially useful for explaining complex terms or legal citations.
The ribbon interface provides all the necessary buttons to insert, delete and manipulate footnotes. The start number and format can also be adjusted.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
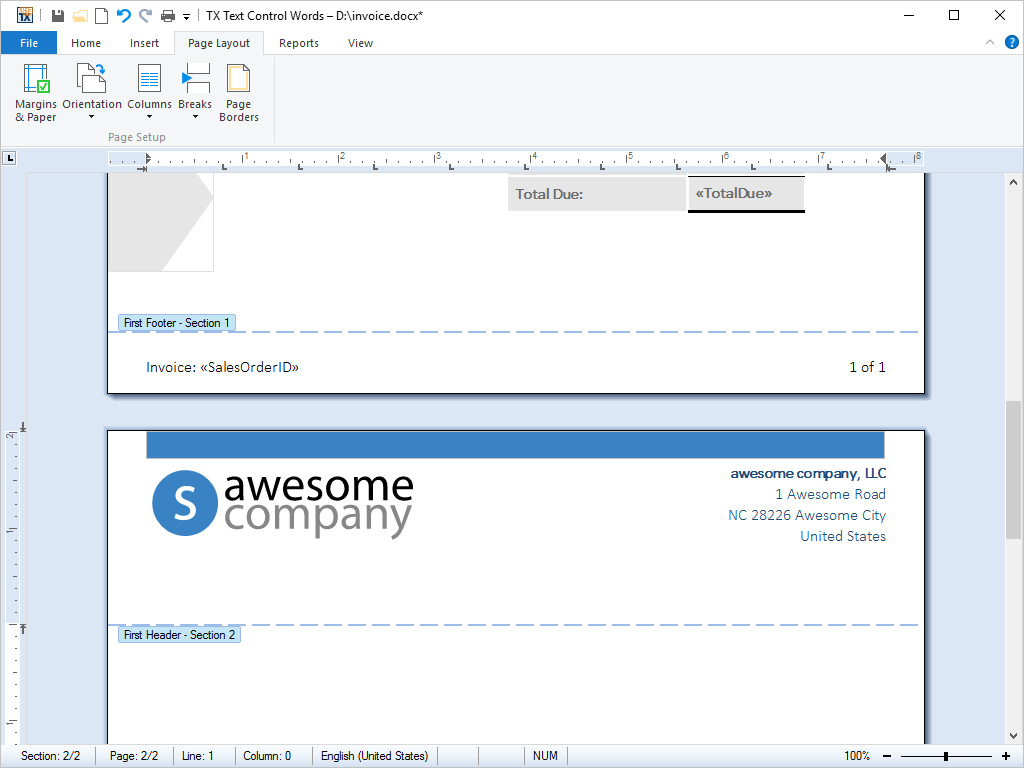
- Headers and Footers Headers and footers are accessible from program code and are loaded from and saved to MS Word or RTF files.
A header or footer is text or other information such as graphics or tables that is stored at the top or bottom of the page throughout a TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms document. End-users can use the same header and footer throughout a document or change the header and footer for part of the document.
For example, end-users can add their corporate logo to the first page header, and then include the document's file name in the header for subsequent pages.
All of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's vast array of character formatting can be applied to the text that appears in a header or footer from program code.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
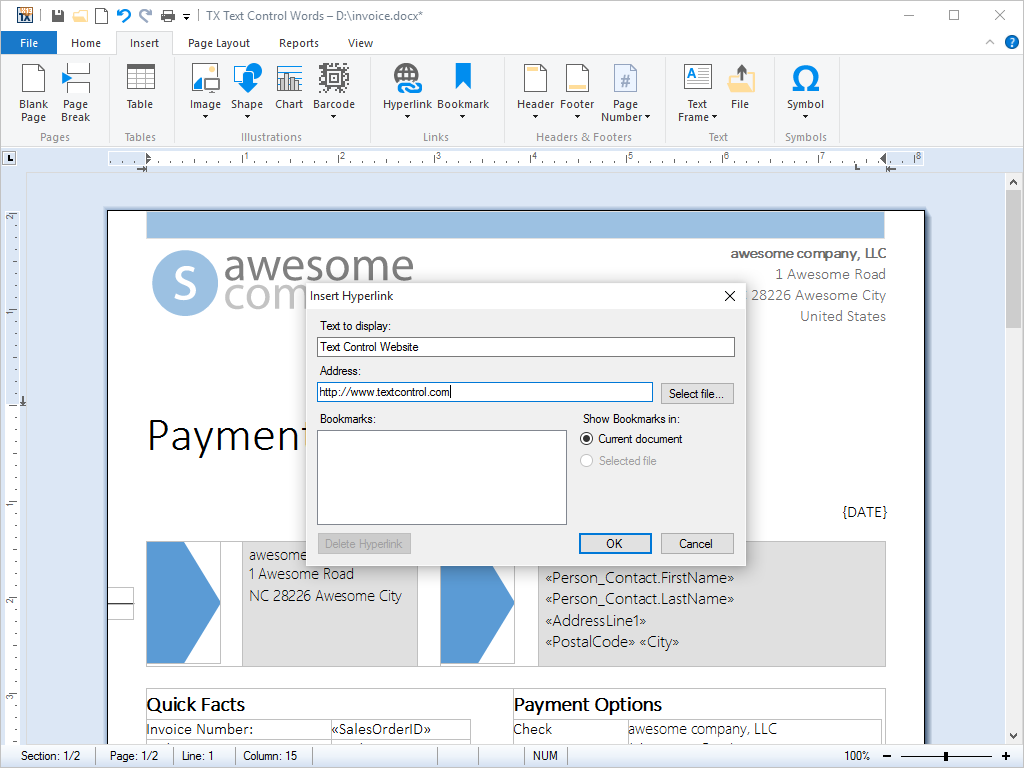
- Hypertext Links Hyperlinks can be defined within a TX Text Control document, loaded from and saved to HTML files.
Hypertext links are elements within a word processing document that link to another place in the same document or to an entirely different document.
Using the hypertext support, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms can be deployed to create hypertext systems that are particularly useful for organizing and editing large databases of textual information.
Files containing hypertext, such as HTML can be loaded and edited in TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms. Likewise, documents in which hypertext links are defined can be exported to HTML and published directly on the Internet or sent as HTML formatted e-mail.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
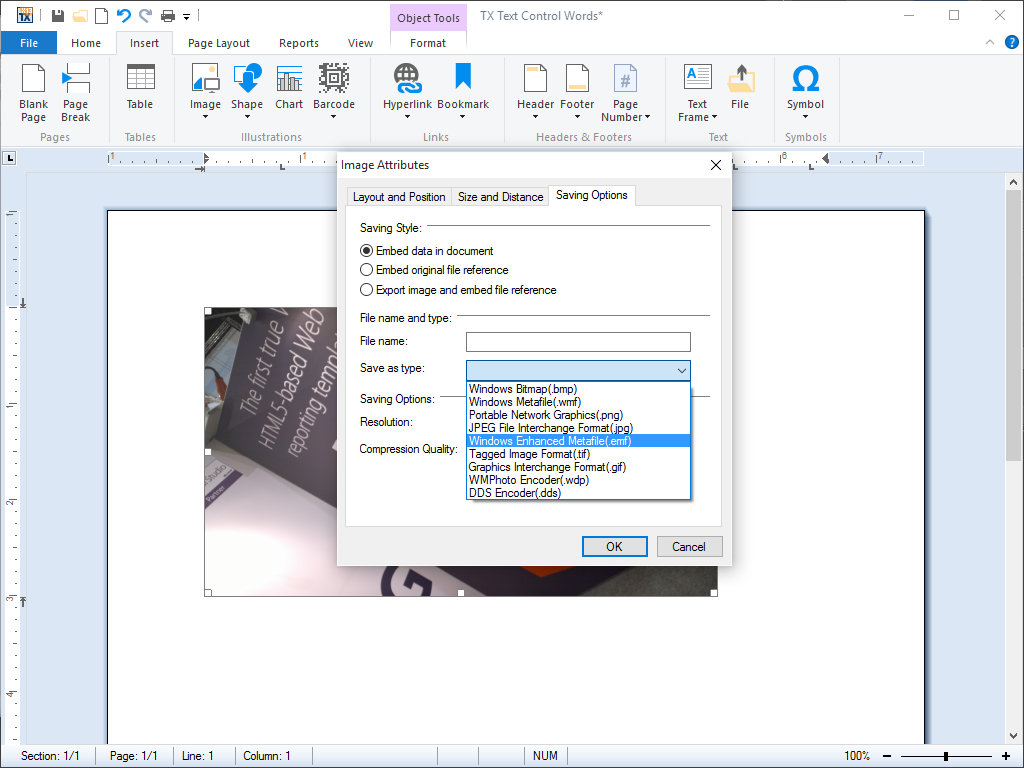
- Image Formats Most popular image file formats are supported. Amongst others: TIFF, WMF, BMP, JPEG, PNG, GIF.
The choice of image file format is very dependent upon the application and the type of image data that is to be saved.
To address the widest possible range of applications, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms supports the following file formats:
Tagged Image File Format (TIFF)
TIFF is a standardized file format for exchanging bitmapped and grayscale images among applications.
Windows Meta File (WMF)
WMF is a vector graphics format for Windows-compatible computers originally designed for word processing clip art.
Bitmap (BMP)
BMP is a standardized file format used to transfer graphic images within Windows applications, designed for maximum compatibility amongst applications.
Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG)
JPEG is a graphical format widely used in WWW pages. JPEG is a compressed format which can result in significantly reduced file sizes for photographs and other images with continuous color changes.
Graphics Interchange Format (GIF)
GIF is the most common format for graphic images on the Internet. It is a highly compressed format that is used to display 2-dimensional raster images. It is especially suited to images containing large areas of the same color.
Portable Network Graphics (PNG)
PNG is a standard file format approved by the World Wide Web consortium to replace the GIF file format. PNG is patent and license-free.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
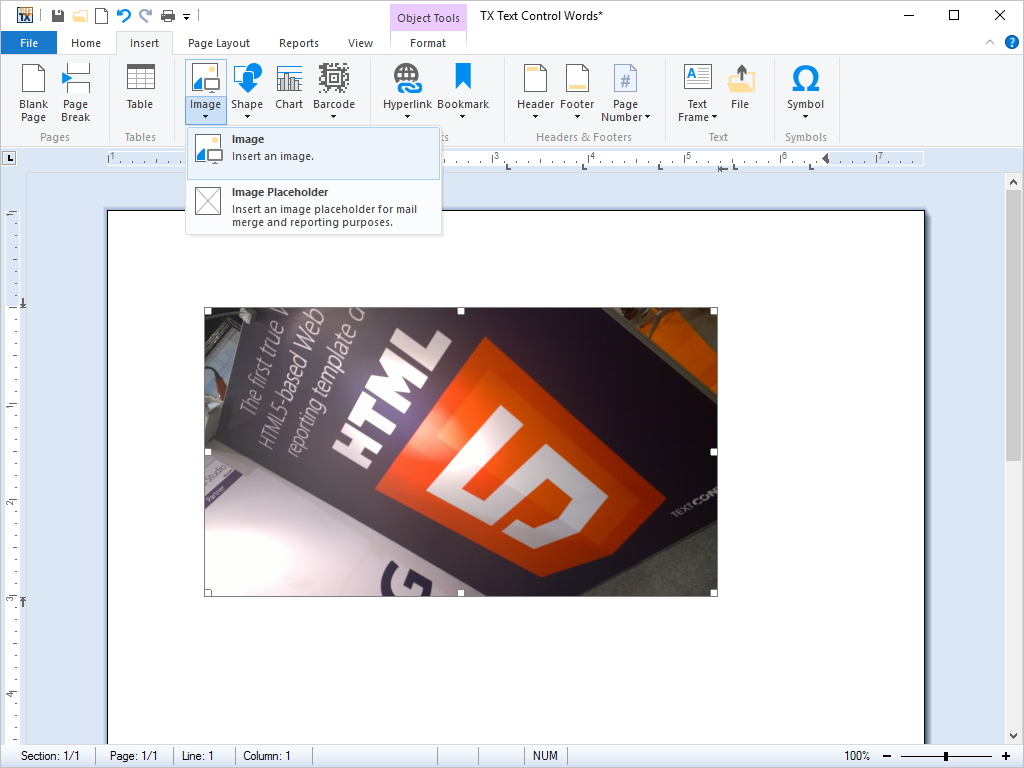
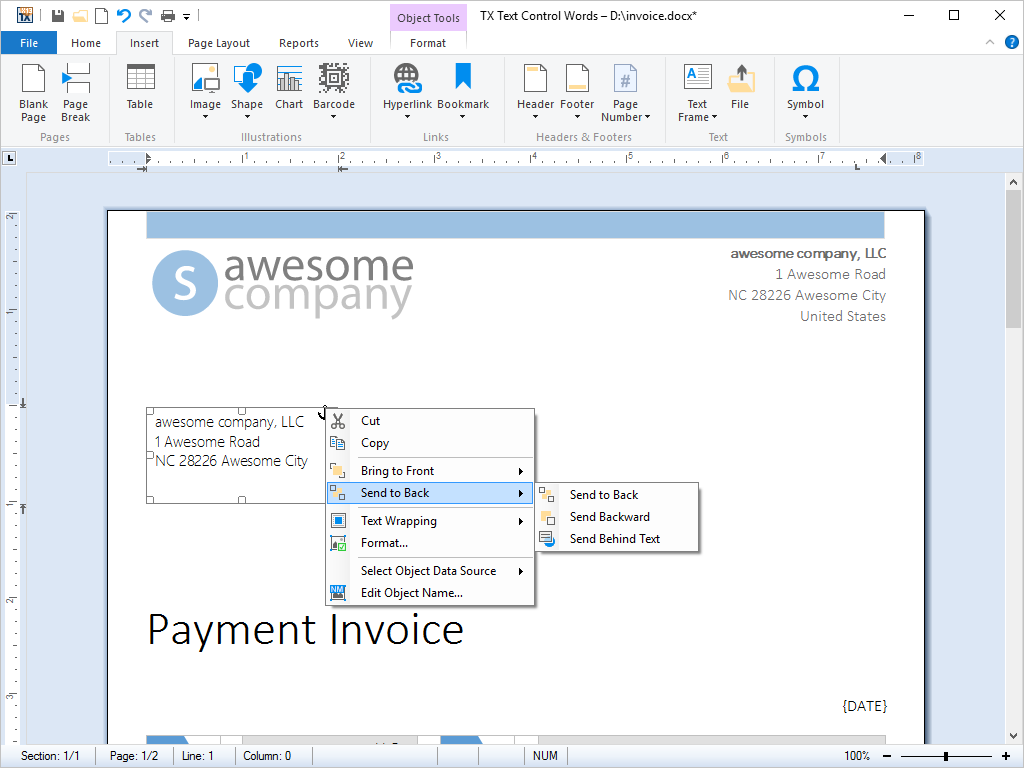
- Images Images can be positioned as characters or given a specific page position. Text flow around images can be set directly from program code. Images are scalable.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms is especially powerful for importing images into word processing documents and supports a wide range of image file formats. There are basically three different approaches to image import:
Import as a character
Images that are positioned as a character are treated as any textual character in a line of text. They flow with the other text in a sentence.
Import to fixed position
Images that are inserted at a fixed position are stationary in the word processing document. TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms automatically flows text around fixed images. End-users can, however, move these images around the page with a traditional drag-and-drop approach.
Anchored to a paragraph
Images can be inserted and attached (anchored) to a specific paragraph. Whenever the paragraph moves down a page - for example, when more text is added before it - the inserted image remains geometrically relative to the paragraph to which it is attached, and thus moves down the page with the rest of the paragraph.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms offers end-users a dialog box, in which the behavior of the text flow can be determined. Additionally, images can be rescaled within in the word processing document.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
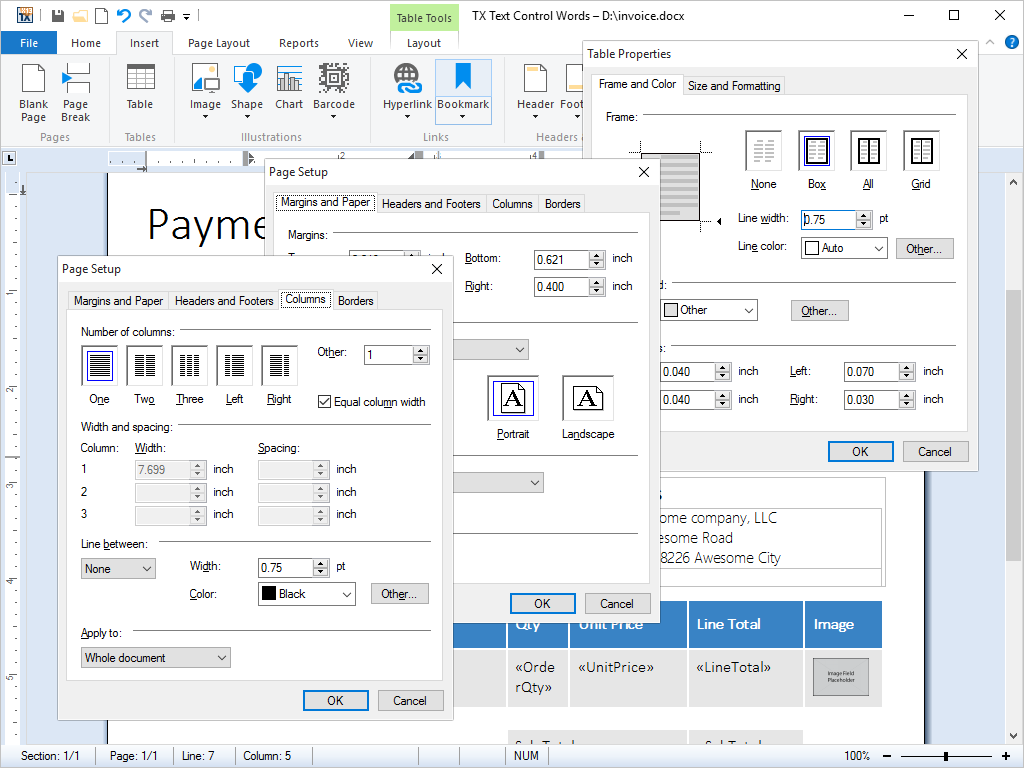
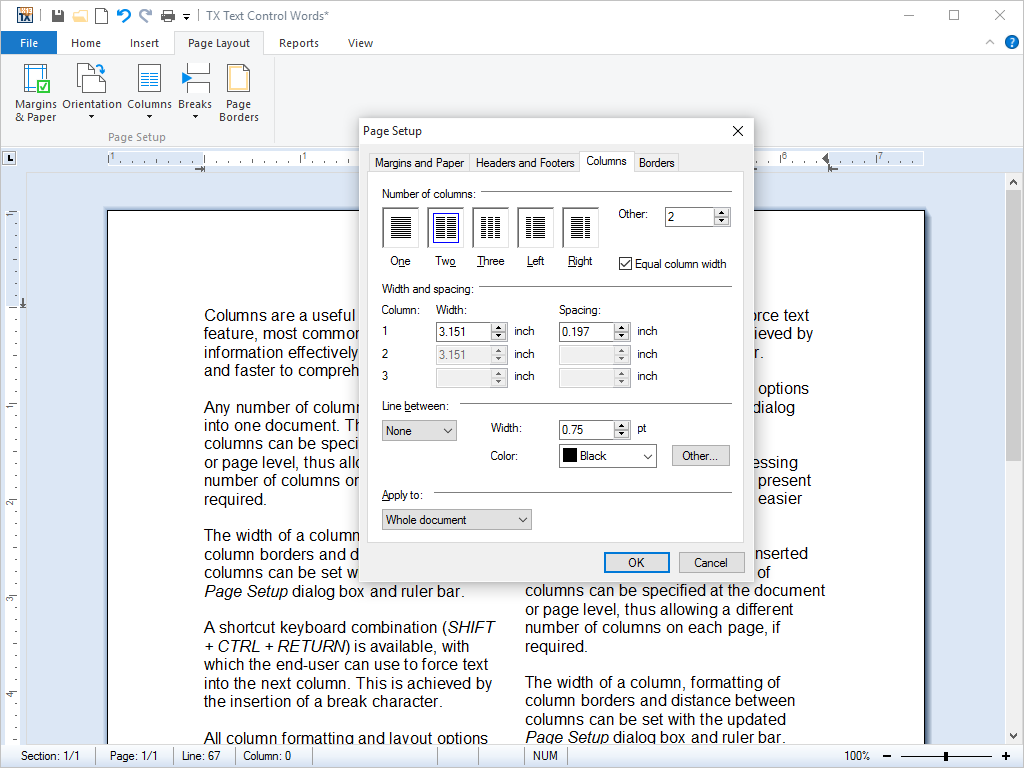
- Page Columns Any number of columns can be inserted into one document. All aspects of the columns can be set with the shipped dialog box and from program code.
Columns are a useful word processing feature, most commonly used to present information effectively, making it easier and faster to comprehend.
Any number of columns can be inserted into one document. The number of columns can be specified at the document or page level, thus allowing a different number of columns on each page, if required.
The width of a column, formatting of column borders and distance between columns can be set with the updated Page Setup dialog box and ruler bar.
A shortcut keyboard combination (SHIFT + CTRL + RETURN) is available, with which the end-user can use to force text into the next column. This is achieved by the insertion of a break character.
All column formatting and layout options are available in the Page Setup dialog box.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Page and Document Settings Developers can access and define document settings, such as page size, orientation, margins and default printer amongst others from program code.
Page settings define the on-screen display of a document, which includes scrollbar settings and page display. Document settings include page size, orientation, and margins, as well as the default printer for which the document is formatted.
All page and document settings can be set and accessed from program code.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
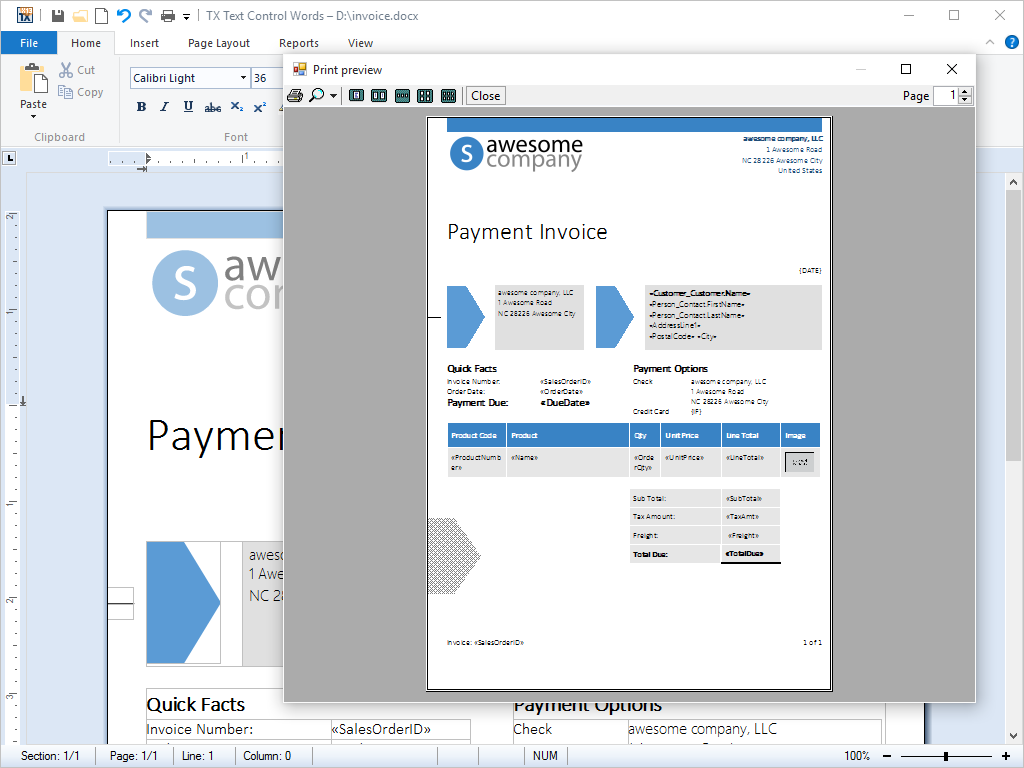
- Print and Print Preview Printing and print preview are available in all editions. A single function call is required to print documents, complete with graphics, tables, page numbers etc.
Printing is traditionally a complex task in Microsoft Windows. Using TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms, however, only a single call is required to print multi-page documents, complete with graphics, tables, headers and footers.
For developers with extreme printing demands, advanced printing functions are available to implement features such as printing multiple controls, or even mixing TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms with other objects on a single printed page.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms also offers end-users a print preview. The print preview windows shows the page exactly as it will appear on paper. End-users are, therefore, able to check whether they have the desired formatting and layout before they commit their document to the printer.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
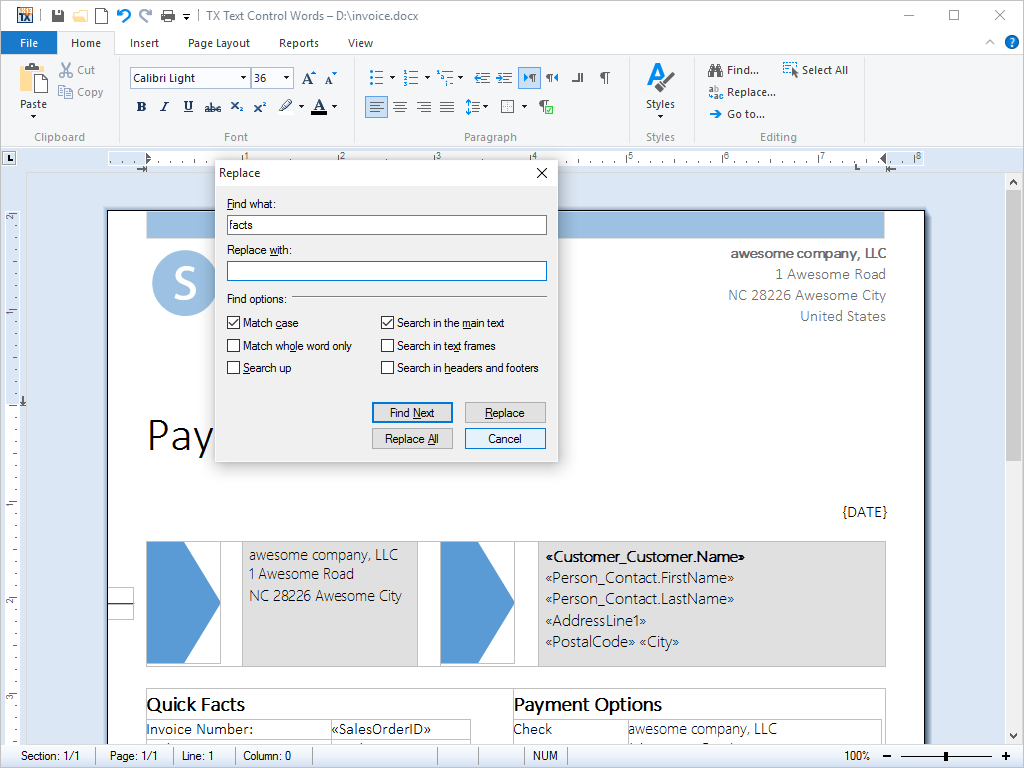
- Search and Replace Search and replace functions are available from built-in dialog boxes and programmatically, so that can be used without end-user interaction.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms can locate anywhere in a document: any text, any collection of characters, one or more words, whole sentences and page breaks. Once the text has been found, it can be replaced as necessary.
For the end-user, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms presents an easy to understand, standardized search and replace dialog box.
Developers are offered a rich set of functions to access TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms search and replace functions directly from program code.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
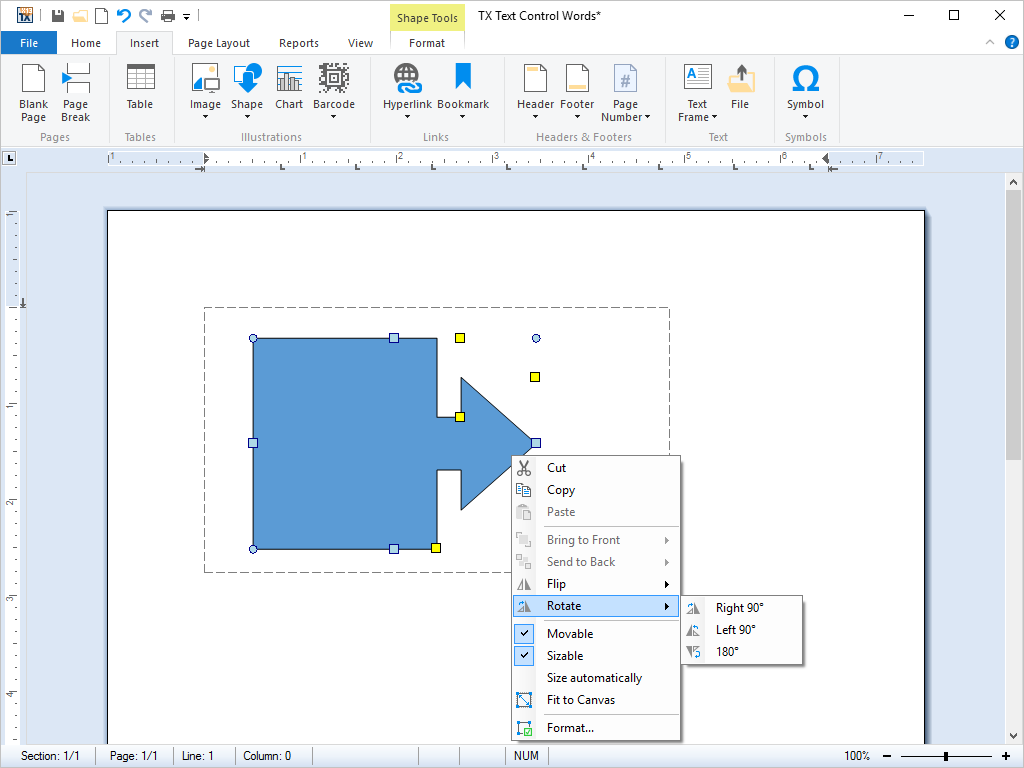
- Drawings and Shapes MS Word compatible drawings and shapes can be inserted and edited.
MS Word compatible drawings and shapes can be inserted and edited. Shapes can be added as single objects into TX Text Control and can be completely edited using the ribbon interface, a ready-to-use dialog box and programmatically using the TX Text Control API.
When activating drawing objects, a fully featured editor is available to modify the shape. Shape objects can be also grouped in a Drawing Canvas and modified as a group. All shape types are compatible to MS Word and can be imported and exported from and to supported formats.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
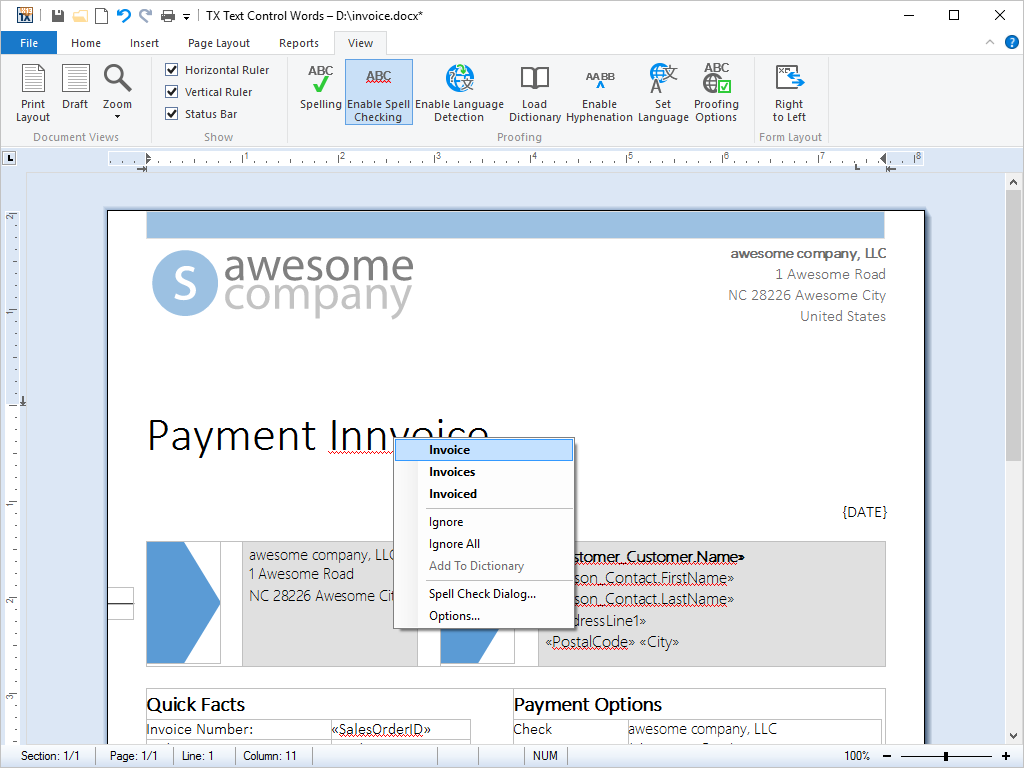
- Spell Checking With TX Spell .NET you can add extremely fast, highly reliable and very accurate spell checking to your applications.
Using TX Spell .NET you can add extremely fast, highly reliable and very accurate spell checking to your TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms based applications.
- Built-in support for Hunspell dictionaries.
- American English shipped as standard.
- Other dictionaries are freely available.
- Spell check multi-lingual documents.
- Build user dictionaries.
- Really easy-to-use API.
- Spell-as-you-type.
Words that are not in the selected or user dictionaries are underlined using wavy red lines. TX Spell .NET persistently checks spelling as you type, word by word and as you copy and paste.
Right-clicking on a spelling mistake presents a context menu with suggestions and options to Ignore All or Add to user dictionary.
TX Spell .NET is sold separately and 100% compatible to TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express (partially)
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional (partially)
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise (partially)
- Built-in support for Hunspell dictionaries.
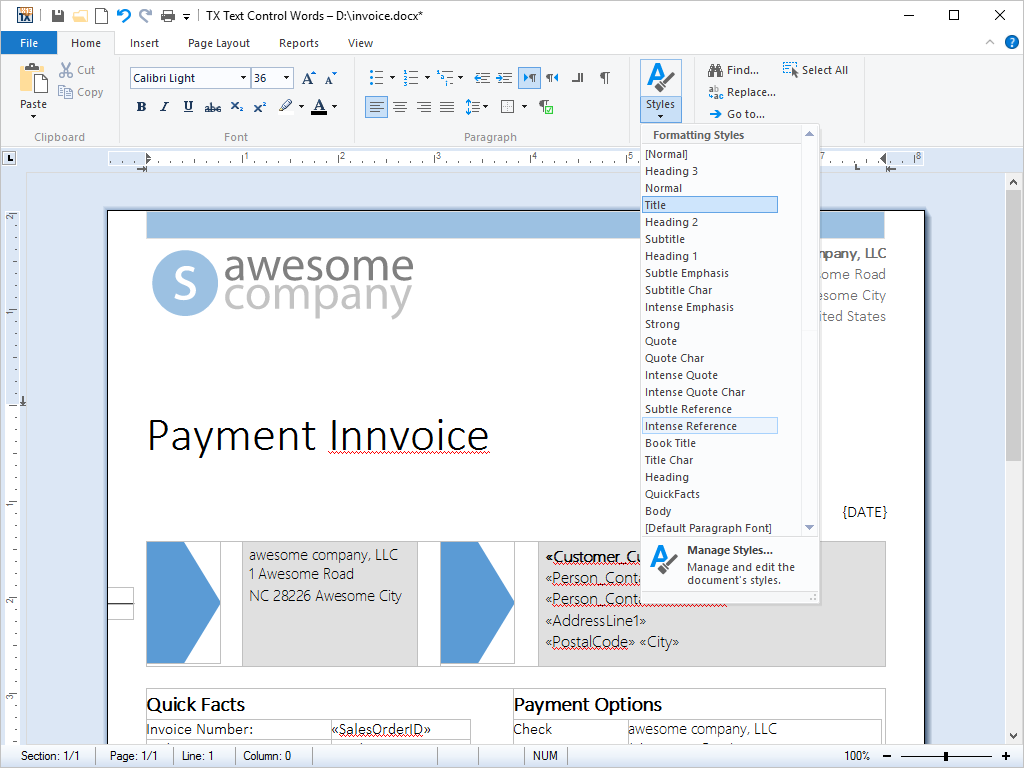
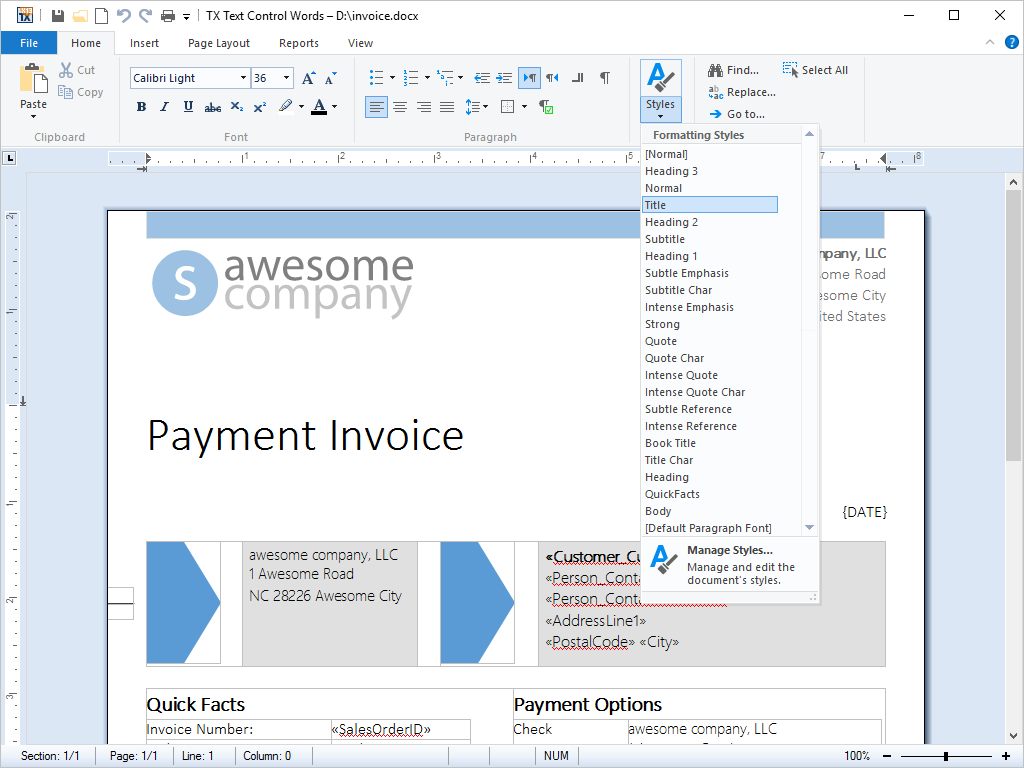
- Stylesheet Formatting Complete separation of content and formatting is offered with this feature. Stylesheets, defining the look and feel of a document, can be accessed and defined from program code.
Stylesheets are a feature common to all large word processing packages. Imagine a large corpus of word processing documents, in which all the captions are formatted in 12pt Times Bold. Due to a relaunched brand, a developer is given the task of changing the font to 14pt Arial.
Without stylesheets, this task would be a chore: In order to change the font, every caption would need to be programmatically selected and edited. With stylesheets, the task can be completed with a few lines of code.
Stylesheets become even more important when several authors are working on the same set of documents, preventing every chapter from being formatted in a slightly different way.
All of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's stylesheet formatting options can be accessed from program code.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms' supports both paragraph and character based styles, as well as multiple style inheritance. The stylesheets are compatible with MS Word, and can be used with RTF and DOC files.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express (partially)
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional (partially)
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
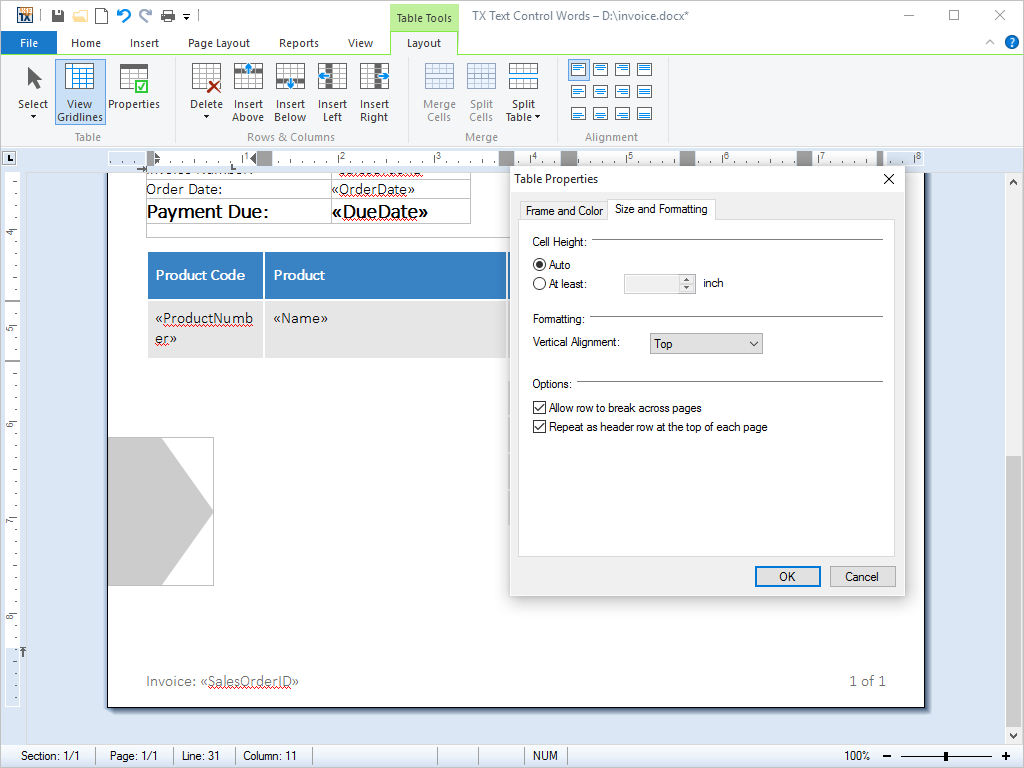
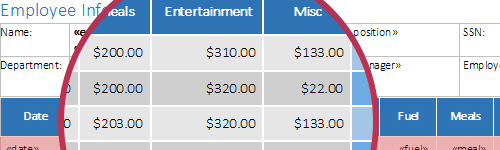
- Table Headers Any row in a table can be automatically added to the top of each table, right after a page break has occurred.
Tables are often used to display large amounts of data, for example in a sales report. As the maximum length of a table on any one page can only be the maximum height of the page (minus margins and headers and footers), it is necessary to divide the table every time a page break occurs.
Any row in a table can be automatically added to the top of each table, right after a page break has occurred. This ensures that tables always have a table header on every page, regardless of how long they may become.
The screenshots to the right, illustrates how the first row of the table is being repeated at the top of each successive page.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
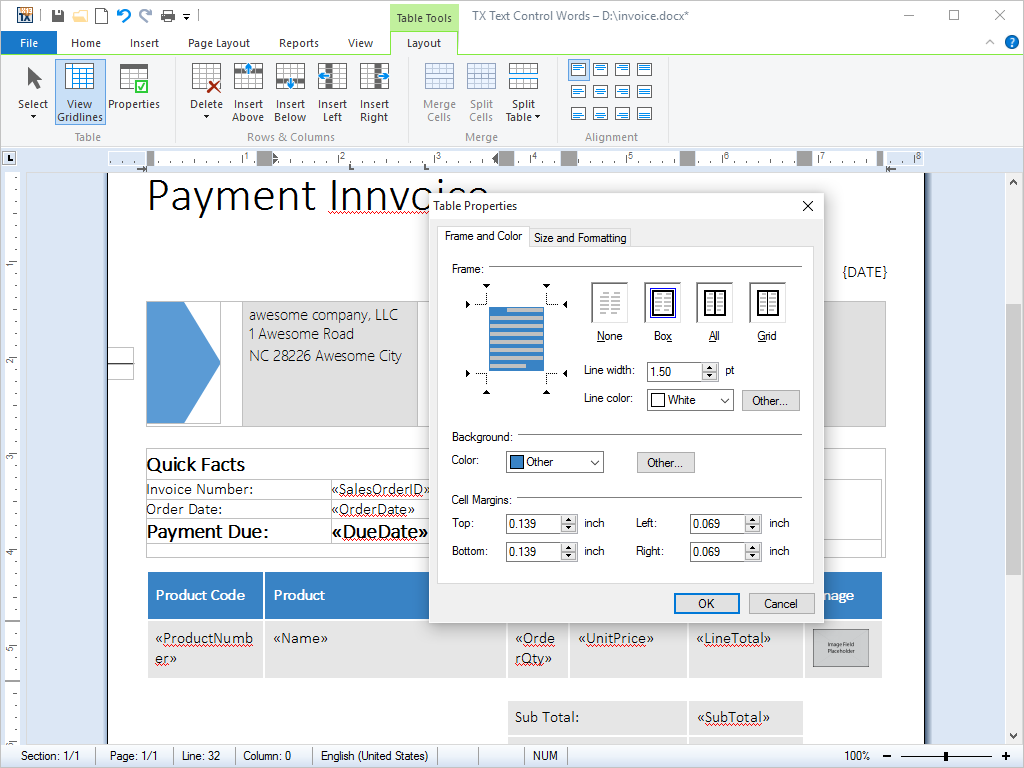
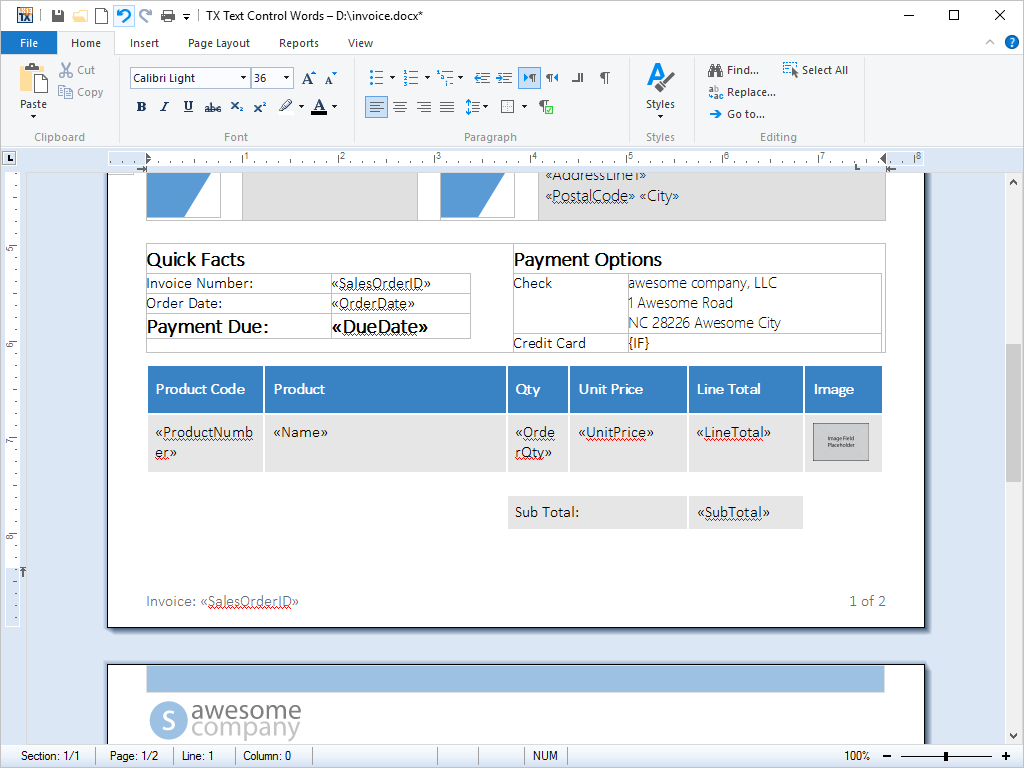
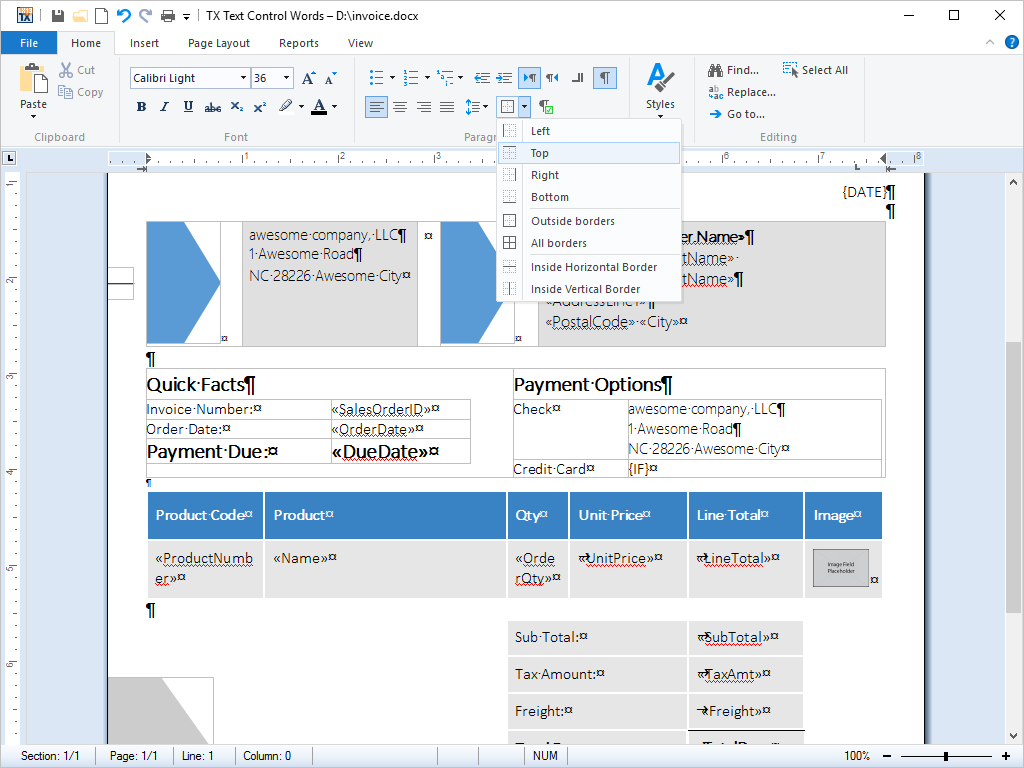
- Tables Tables can be inserted into documents. Cell contents can contain virtually any kind of formatting. Borders and shading can be set for individual cells.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms provides a rich set of formatting options for tables, cells and text contained within table cells.
Tables can be inserted into documents or other tables using the integrated dialog box or directly from program code. Frames and shading can be applied to cells and the cell contents can be formatted using any of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's formatting options.
Selecting a font face, setting an indent or setting line spacing, for example, for text within a table cell is performed exactly the same as for text elsewhere in a document.
Cells can contain singular words or figures, entire paragraphs, graphics and even tables. Their height and width can be set independently from one another, either from program code or using the integrated dialog box.
Table cells can be accessed in a grid-like manner, enabling developers to fill in their contents from a database and perform calculations on the contents of rows and columns.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Text Frames Freely placeable and programmable text frames can be inserted and positioned as a character or geometrically relative to a paragraph or a page.
Text frames are rectangles that can be filled with any kind of text, tables or other data objects that TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms supports. Text frames may be edited just like any other text in a document.
Label Printing
Using TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's precise text frame positioning, end users can simply create and populate a page of labels automatically. The content of the label may consist of fully formatted text, complete with images, bar codes and logos. The resulting document can be printed to standardized printer labels and / or badges.
Mail Merge
Similarly, mail merge applications can benefit from TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's text frames. Marked text fields in a text frame can be accessed independently from other fields in the current document. This enables end users to merge all fields in a specific text frame without having to iterate through all fields in the document.
All text frame settings can be accessed directly from program code or via TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's integrated dialog boxes. The behavior of text frames can be changed after inserting them into the current document. Their position, style, alignment, size or background color may be adjusted using the dialog box. This is illustrated in the animated screenshot.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Multi-Level Undo / Redo Programmers can add multiple levels of undo and redo to their applications, providing end-users an easy path to correct mistakes they may make.
Multi-level undo / redo is one of the most basic features of a fully-fledged word processing application. TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms records every step taken when an end-user edits a word processing document.
At any time, end-users may undo the editing steps that they have taken or redo what they have undone.
Programmers can implement multi-level undo / redo that can be accessed from the menu using the mouse or directly via the keyboard using a shortcut.
- Zooming End-users can zoom in and out in steps of 1 percent - from 10 percent up to 400 percent. All word processing functions are available at all zoom levels.
End-users can zoom in and out of their documents in steps of 1 percent, with a zoom factor from 10 percent to 400 percent. The zoom factor can be automatically set to view the whole page or the page width.
All of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's rich set of word processing features - including text input - are available at all zoom levels.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- 1D and 2D Barcode Support Barcode support is directly integrated into TX Text Control without the dependency on optional products.
- Advanced Programming Capabilities This category lists advanced an unique features such as mail merge.
- 64 Bit Version 64 bit processors can handle much more memory and larger files than their 32 bit pendants.
64 bit processors can handle much more memory and larger files than their 32 bit pendants.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms can address this much larger memory space, thus enabling developers to build high-performance word processing applications.
Typically, word processing applications which are built with TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms can open and save much larger files than was previously possible with the 32 bit versions of TX Text Control.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
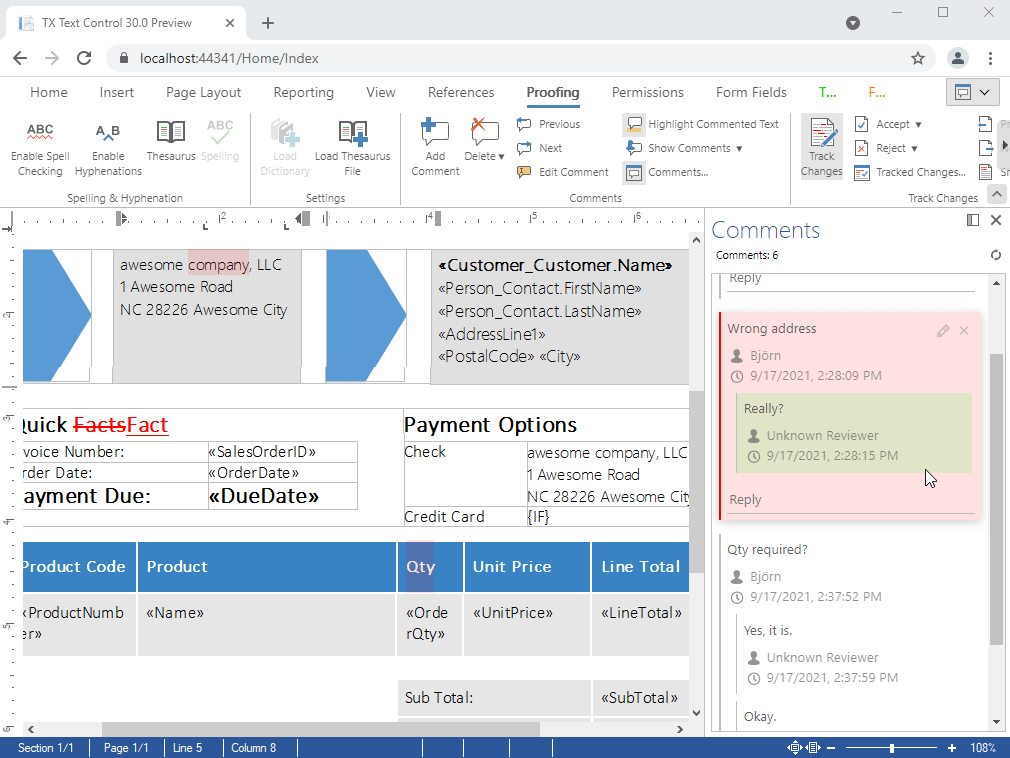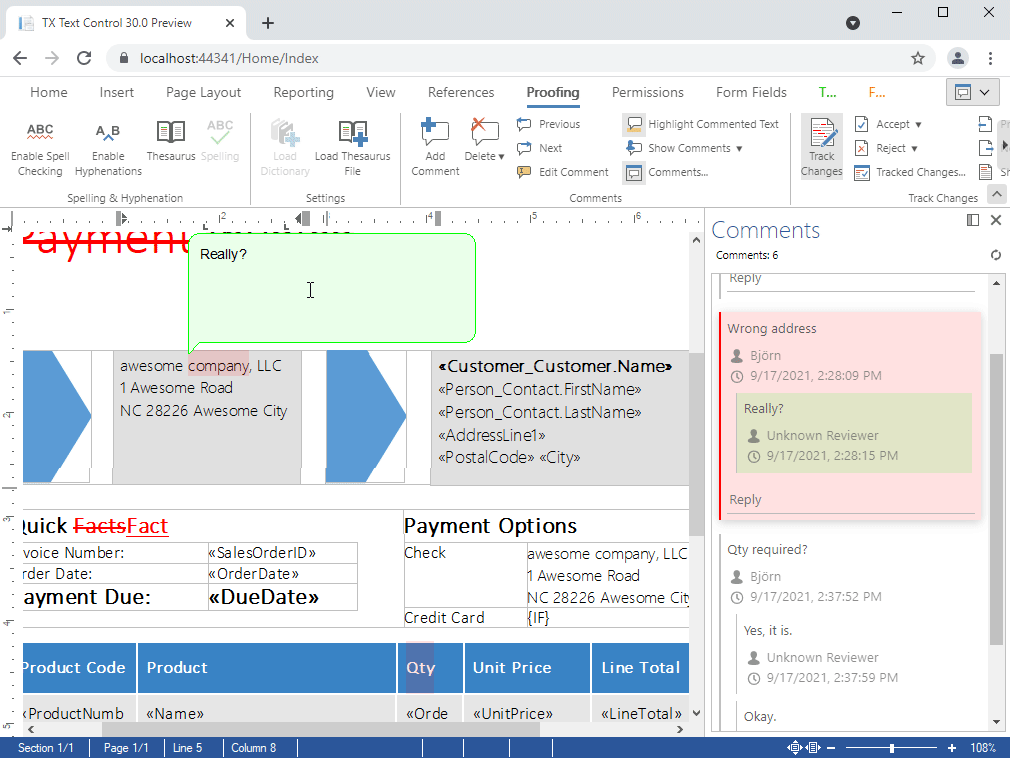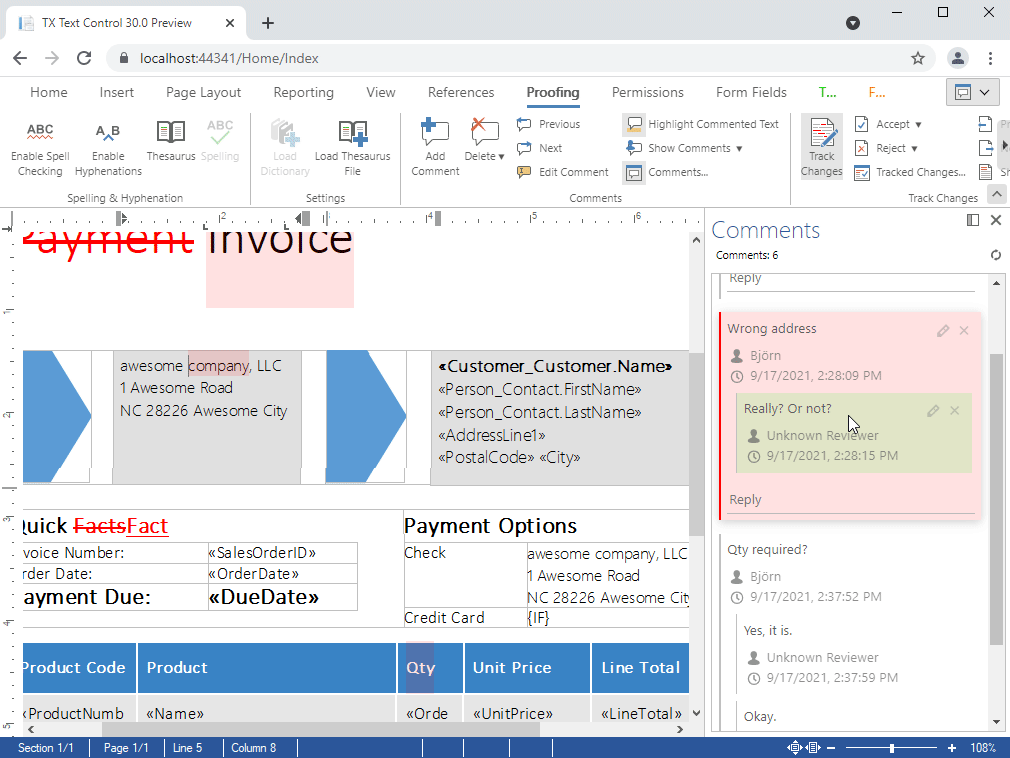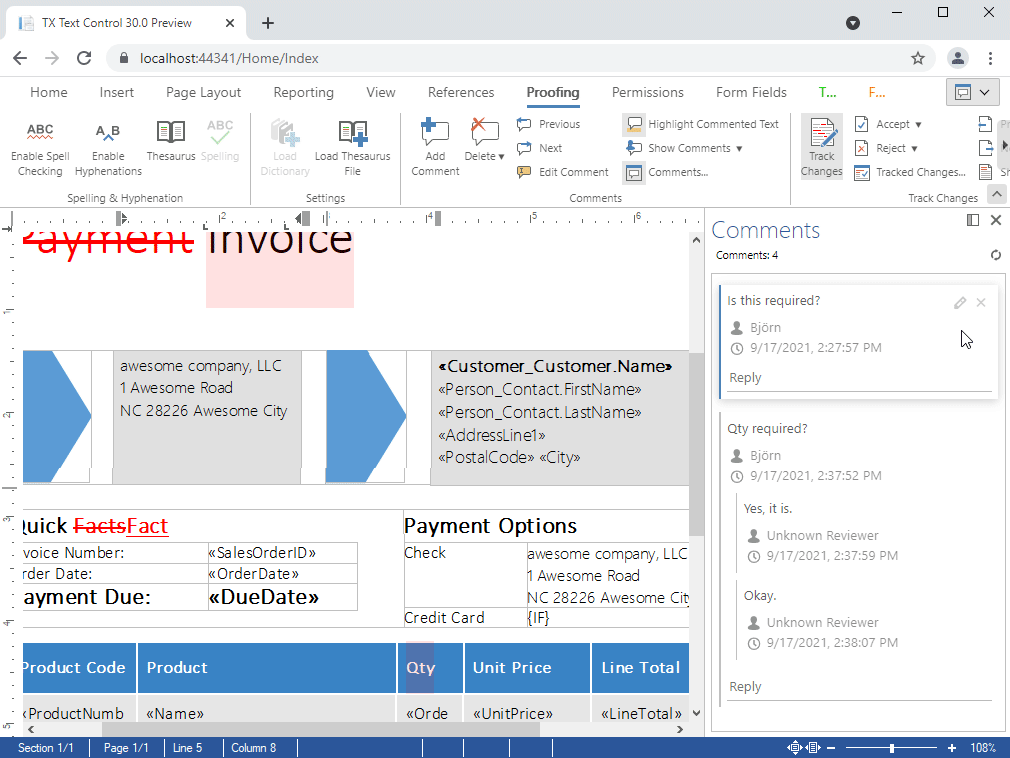
- Comments Enable professional, MS Word compatible collaboration features in your applications. Different authors can add comments to all text ranges and attach MS Word compatible comments to tracked changes. Comments can be imported and exported from and to MS Word formats including Office Open XML, DOC and RTF.
Enable professional, MS Word compatible collaboration features in your applications.
Different authors can add comments to all text ranges and attach MS Word compatible comments to tracked changes. Comments can be imported and exported from and to MS Word formats including Office Open XML, DOC and RTF.
- Visual sidebar to edit comments and replies
- Fully featured ribbon group for comments
- Add comments from context menu and ribbon bar
- Link comments to tracked changes
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Control Settings Control settings are available to set border styles, pagination, scrollbar and many more document appearance and behavior characteristics.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms provides a number of options to define the appearance and behavior of word processing documents. These characteristics can be set using the rich selection of control settings.
Appearance control settings include view modes (normal and page), document background color, where scrollbars should be positioned and whether scrollbars and control characters should be visible.
Behavioral control settings include edit mode - i.e. defining whether text is read-only, can be selected or is editable - and tab behavior. For example, the behavior of the tab key can be toggled between inserting a tab character and moving the focus of the caret to the next control in the predefined tab order.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Data Binding Interface controls, such as buttons or dropdown menus of a Ribbon bar can be easily connected to TX Text Control without writing one single line of code.
Interface controls, such as buttons or dropdown menus of a Ribbon bar can be easily connected to TX Text Control without writing one single line of C# or VB.NET code. The connection can be completely done in XAML, making such bindings quick, flexible and easy to implement.
Consider the following example:
A ToggleButton should visualize, whether the character formatting at the current input position is bold or not and it should change this state when the button is clicked. In this case, the target of the data binding is the IsChecked property of the ToggleButton. The source is the Bold property of the new TX Text Control WPF.InputFormat class. This class represents all formatting attributes at the current text input position. The properties of this class are updated automatically when the input position changes.
The following XAML code shows the ToggleButton and it's binding:
<ToggleButton Name="tbtnBold" Content="Bold" Focusable="False" IsChecked="{Binding ElementName=textControl1, Path=InputFormat.Bold, Mode=TwoWay}" />In the Binding statement the Mode attribute has been set to TwoWay. This attribute specifies how the data flows between the source and the target. The following methods are available:
- OneWay:
The data flows from the source to target each time a change is made on the source. - TwoWay:
The data flows from the source to target and vice versa each time a change is made on the source or target. - OneTime:
The data flows from the source to target when the application is started. - OneWayToSource:
The data flows from the target to source each time a change is made on the target.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- OneWay:
- Data Source Manager The DataSourceManager encapsulates the complete handling, logic and ready-to-use dialog boxes for the reporting template creation task.
The DataSourceManager encapsulates the complete handling, logic and ready-to-use dialog boxes for the reporting template creation task.
The DataSourceManager provides all information required to create a fully-featured template designer. Like with MailMerge, a data source can be loaded from a DataSet, DataTable, Json, an object or XML. In this sample, a simple .NET class is used as a data source.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
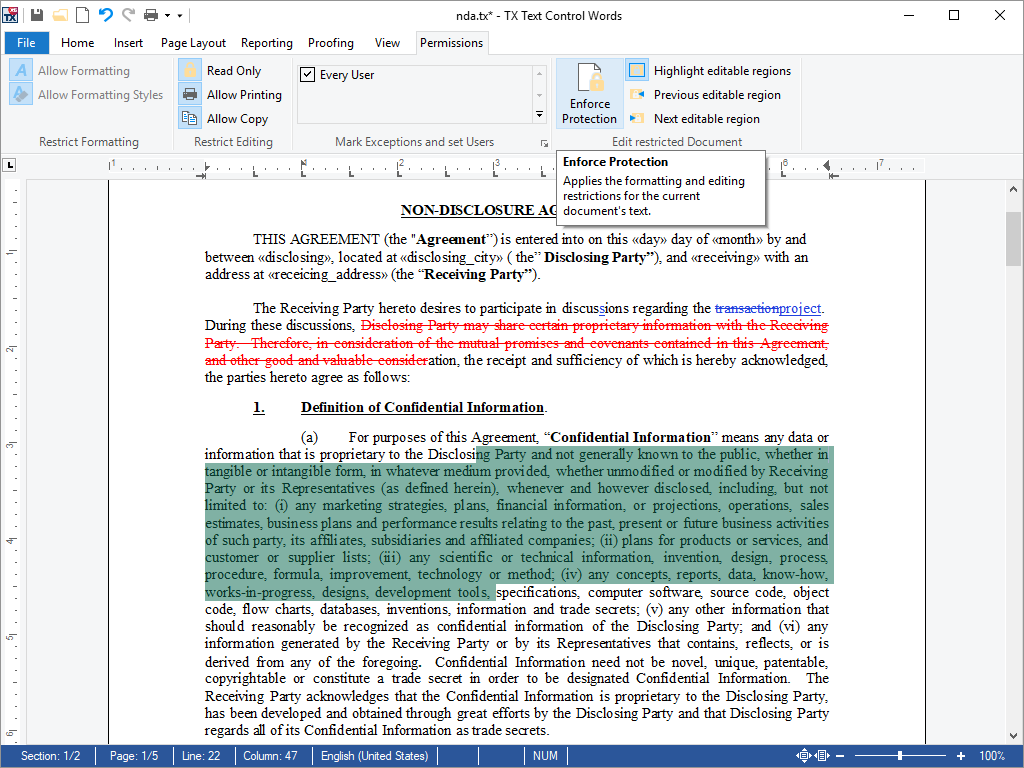
- Document Protection Using TX Text Control, documents can be protected by restricting the formatting and editing of content.
Using TX Text Control, documents can be protected by restricting the formatting and editing of content. When protecting a document, it is possible to define whether the document is completely locked or formatting can be applied.
Editable regions are exceptions within protected documents that can be defined through a start position and a length or through a selection. These regions can be nested and overlap. Each editable region is associated with a user through the UserName property. Only this user can edit the region, when the document has been set to read only.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
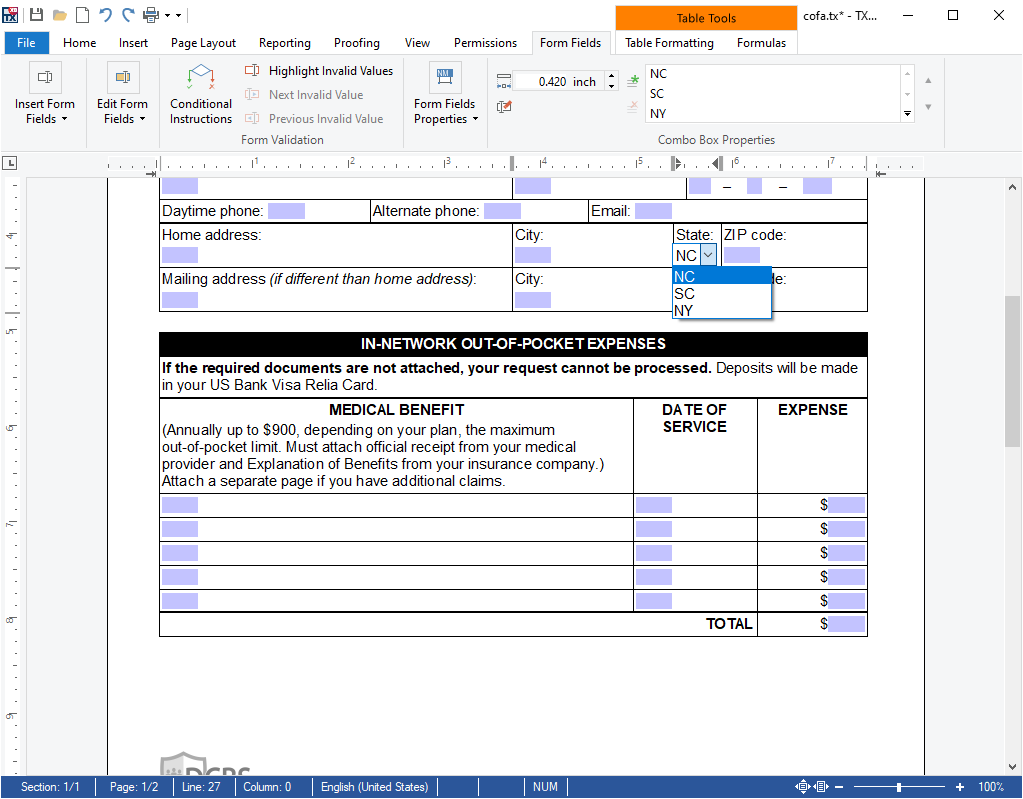
- Form Fields The TX Text Control form field processing functionality enables users to create and deploy forms including MS Word compatible fields such as checkboxes, drop-down boxes and form text fields.
TX Text Control supports form field processing functionality to create and deploy forms including MS Word compatible fields such as checkboxes, drop-down boxes and form text fields. Documents created in MS Word containing legacy form fields and content control form fields can be imported into TX Text Control.
A unique feature of these forms is the option to add conditional instructions to each form field and to connect fields logically. Using instructions, it is possible to add dependencies between fields based on logical operators.
Visually, invalid fields can be highlighted. The instructions are activated automatically when the document is in "read only protection" mode.
Regular Expressions for Syntax Checking
Additionally, it is possible to check the syntax of form fields by adding a regular expression to the conditional instruction.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
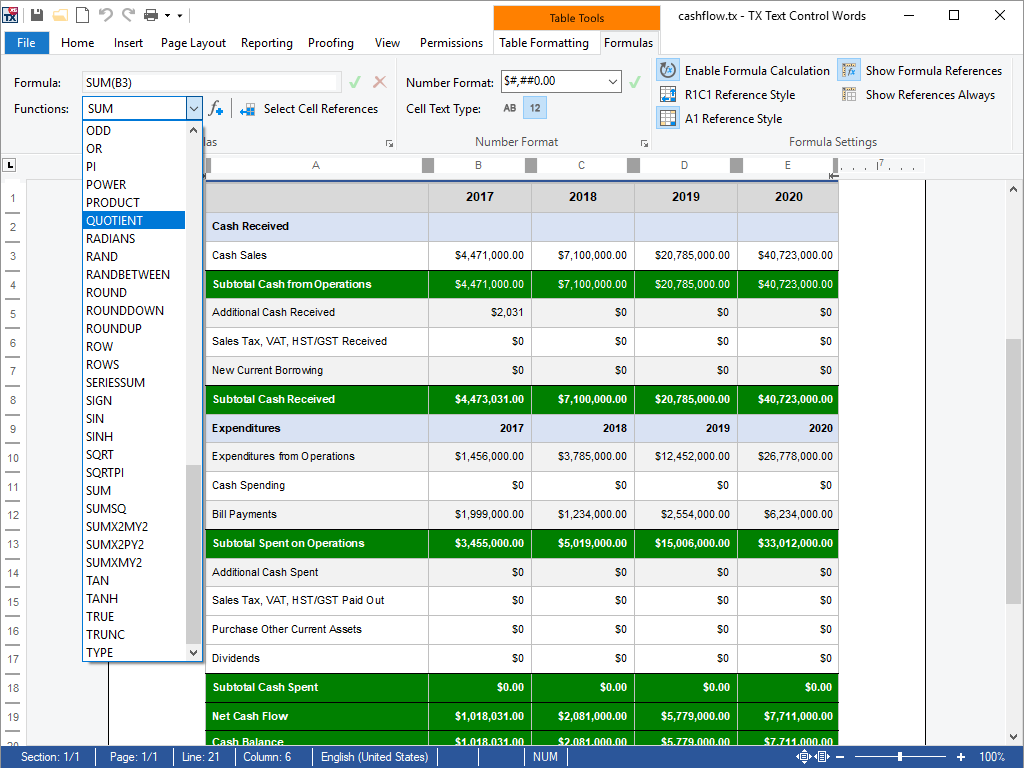
- Excel Formulas Excel compatible formulas can be used in table cells to calculate results based on values and references to other cells in the same table.
Excel compatible formulas can be used in table cells to calculate results based on values and references to other cells in the same table. More than 100 different formulas are supported and can be combined.
Typically, a SUM formula is inserted at the end of a table to create a total sum value. Or a tax value that is calculated based on a tax percentage value and the calculated total sum.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
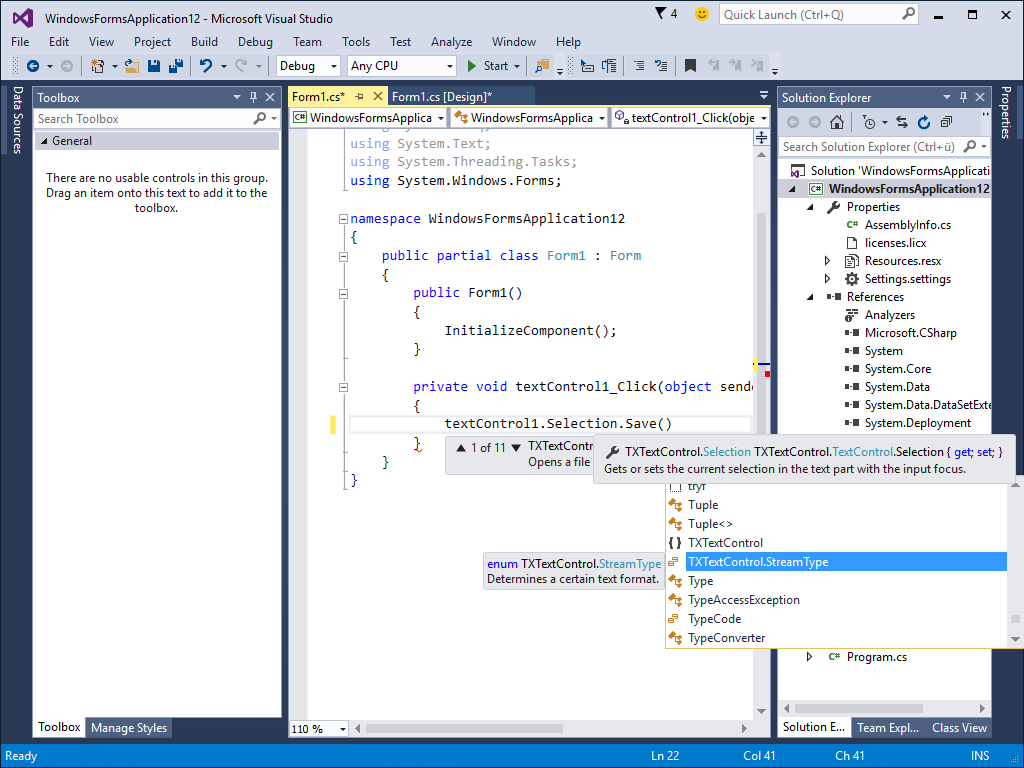
- Line and Character Operations Line operations allows developers to process text line-by-line, access statistics such as number of characters in a line of text or the number of lines in a document.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms offers several line and character operations to be performed from program code.
For example, the number of characters and the number of lines in a document can be counted or the exact position of the caret on a specific line can be retrieved.
Furthermore, the coordinates of a text line or character in relation to the document page can be retrieved.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
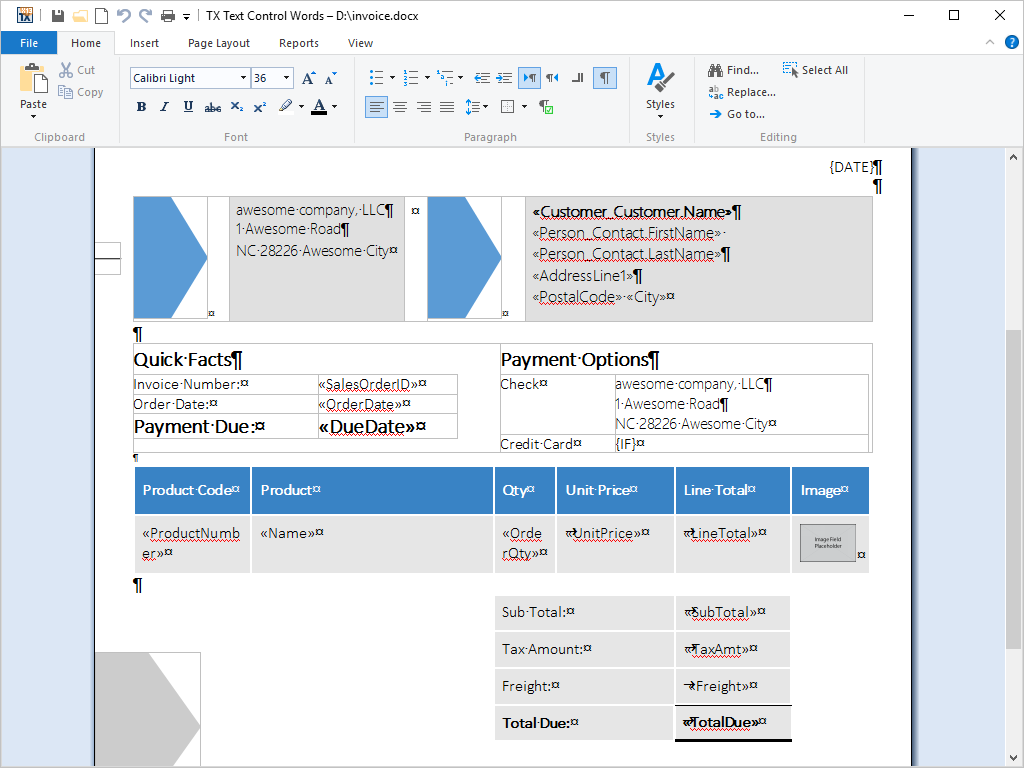
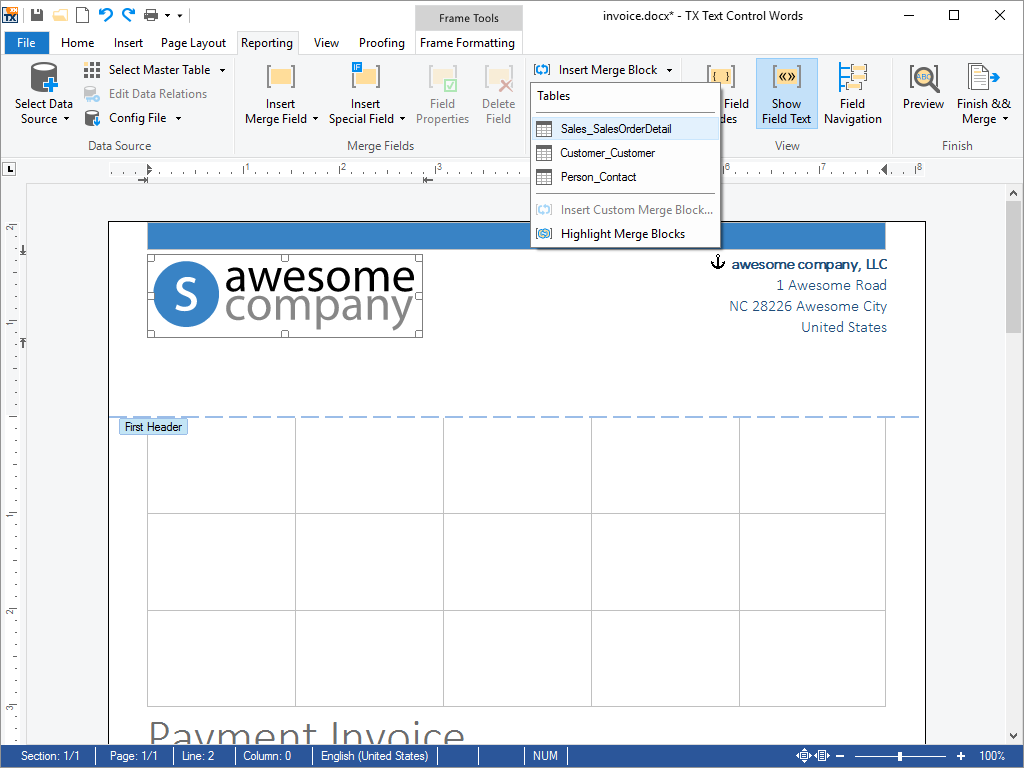
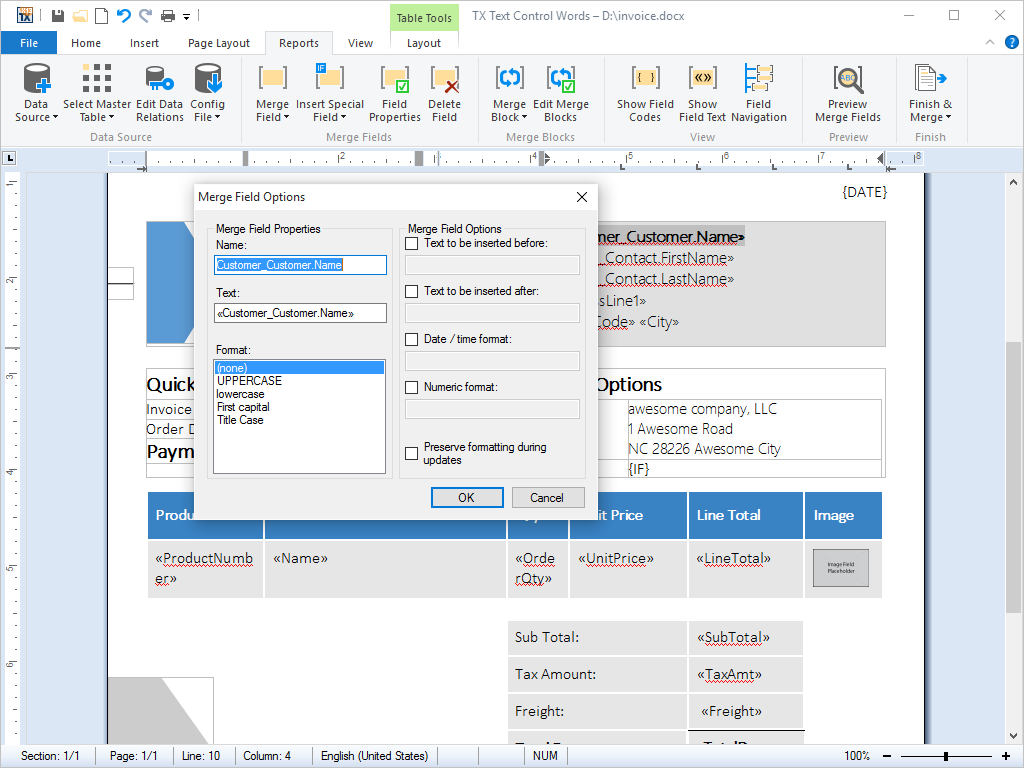
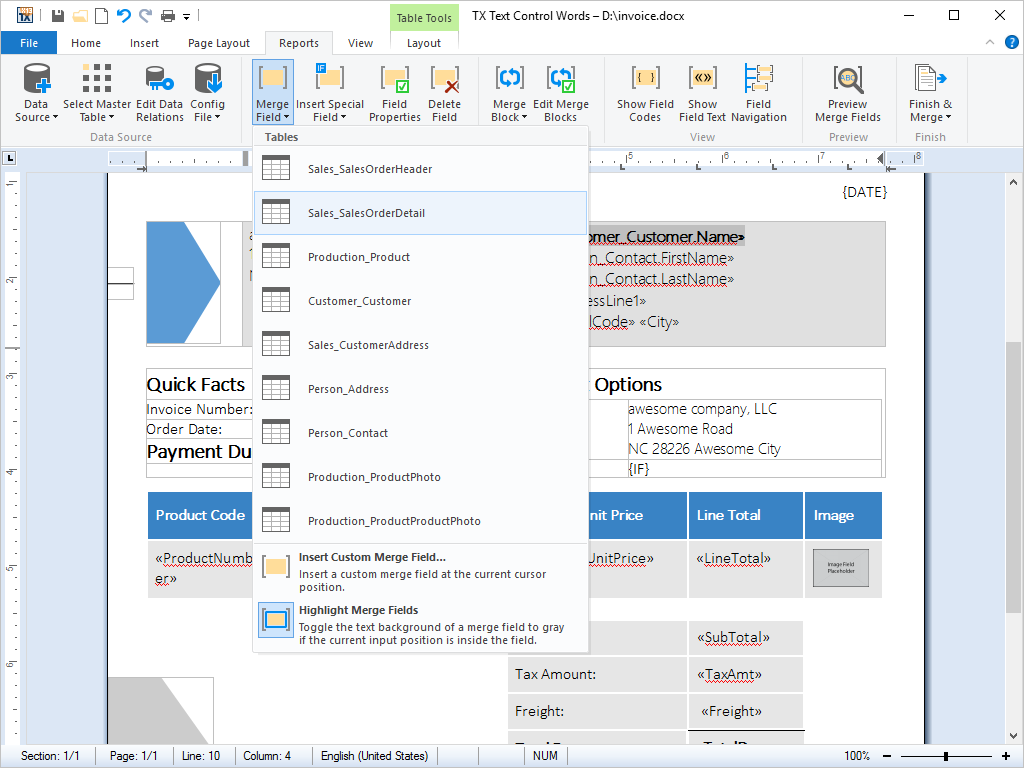
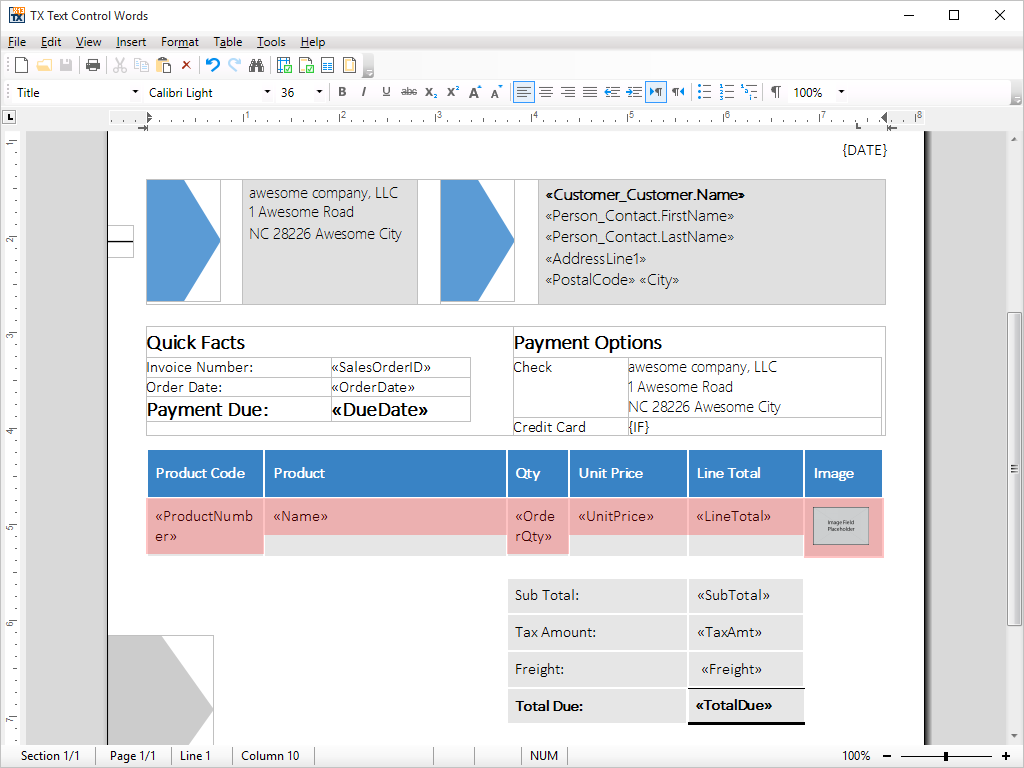
- Marked Text Fields Marked text fields enable developers to build applications such as mail merge, where for example, (formatted) text is retrieved from a database.
Marked text fields, also known as 'macro fields', can be inserted into TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms documents. Typical applications for marked text fields include mail merging, quotation and report generation.
Marked text fields are typically connected to a database, in which plain text or text formatted with any of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms rich formatting options can be loaded. The loaded data populates a previously prepared template, to create a complete word processing document. The finished document can then be printed, faxed or sent as e-mail.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms offers specialized fields for hyperlinks, targets, and page numbers.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
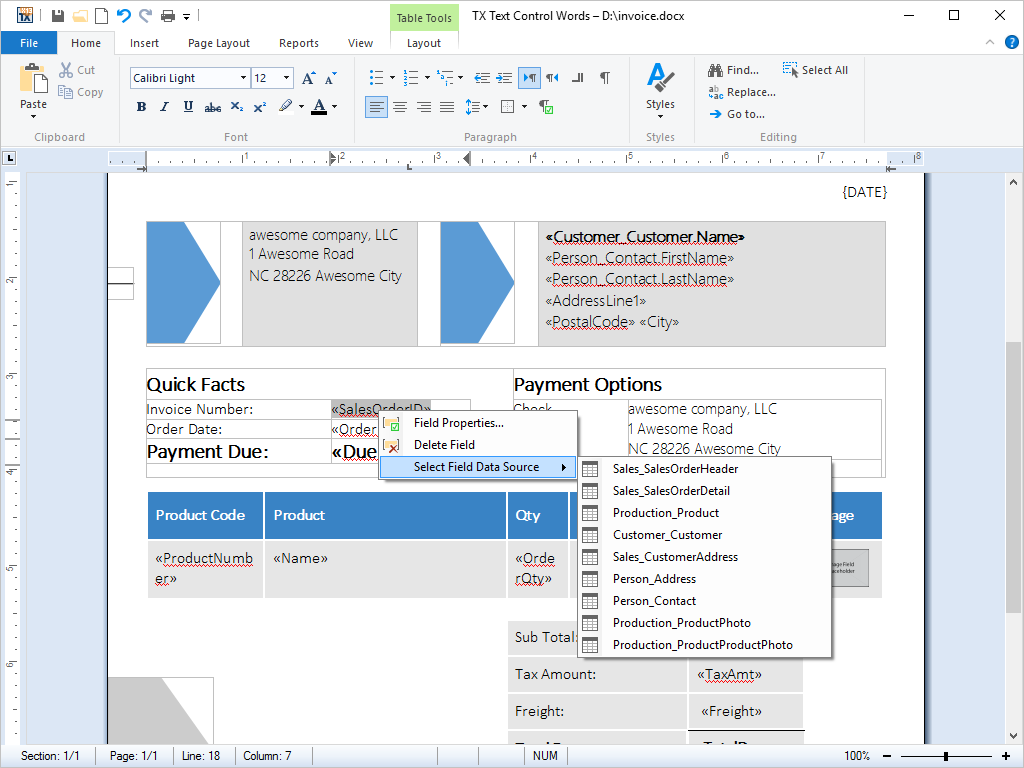
- Microsoft Word Merge Fields Import documents, containing Microsoft Word merge fields into TX Text Control based applications.
Merge fields are special fields that can be inserted into Microsoft Word documents. On demand, they can be dynamically populated with generated data or other information.
As of version 14, word processing documents that contain merge fields can be created in Microsoft Word and then imported into a TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms based application. The merge fields remain in tact and can be post-processed or populated.
Similarly, documents that are created in a TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms based application can be exported and imported into Microsoft Word.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Page Rendering Engine Use the page rendering engine to save a page as a Bitmap (BMP) at screen resolution or as a fully scalable Windows Metafile (WMF).
The page rendering engine allows a graphical representation of a page to be saved as either a Bitmap (BMP) in screen resolution or as an enhanced and fully scalable Windows Metafile (WMF).
Pages exported as Windows Metafiles can be converted into a number of other formats, such as JPG, GIF, PNG, BMP, WMF, EMF, TIFF or ICO.
The layout of the exported page image is exactly the same as that of the printed document or PDF.
A typical application for this new functionality would be to generate thumbnails of all the pages in a document or to display a page-orientated view of a document in a web browser or mobile device.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Programming Paragraphs Programmatically iterate through and process paragraphs in a document. Available in headers and footers, text frames and main text body.
To provide better support to programmatically iterate through and process paragraphs, a Paragraphs collection is available. This collection is available for: i) document's main body ii) headers and footers and iii) text frames.
All formatting attributes can be programmed for each Paragraph, using the ParagraphFormat and ListFormat objects. Additionally, properties are available for: i) first character, ii) first line of a paragraph, iii) number of characters and lines and iv) formatting style.
A Text property and several Save methods can be used to access the paragraph's contents.
The ListNumber and the ListNumberText properties provide further support for numbered lists.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Reporting and Mail Merge Reporting and Mail Merge have become wide-sweeping terms for automated document, report and label creation. Creating invoices, proposals, generated covering letters or shipping labels was never that easy - simply using word processing skills.
Text Control Reporting combines the power of a reporting tool and an easy-to-use word processor - fully programmable and embeddable in your application.
With Text Control Reporting, your users create templates with typical word processing features such as page columns, tables, images and headers and footers. In contrast to complex report designers, users can use their MS Word skills to create beautiful reports - no steep learning curve.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Ribbon Control TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms is shipped with it's own Ribbon control and ready-to-use Ribbon tabs for all typical tasks of TX Text Control.
TX Text Control is shipped with it's own Ribbon control and ready-to-use Ribbon tabs for all typical tasks of TX Text Control.
TX Text Control comes with pre-configured ribbon tabs for document formatting, inserting objects, page layout settings, reporting and mail merge, page view settings and proofing. Additionally, contextual ribbon tabs are available for frame and table formatting tasks.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Stylesheet Programming Developers control stylesheets from program code. They can modify a set of predefined stylesheets within a document template or export these stylesheets separately.
Stylesheets define the layout and formatting of word processing documents. Using stylesheets, document parameters such as the page size, margins, and fonts can be set.
Stylesheets are useful, as they ensure that the style of a document is consistent across all pages in a word processing document and that all documents of a specific type follow a specific style: For example, one stylesheet can be defined for personal documents, another for official letters and a third for reports.
Consequent usage of stylesheets ensures that word processing documents follow corporate identity formatting rules.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms provides a set of methods for manipulating stylesheets. Using these methods, for example, developers can manipulate specialized templates for various types of documents directly from their application code.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms supports both paragraph and character based styles, as well as multiple style inheritance. The stylesheets are compatible with MS Word, and can be used with RTF and DOC files.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
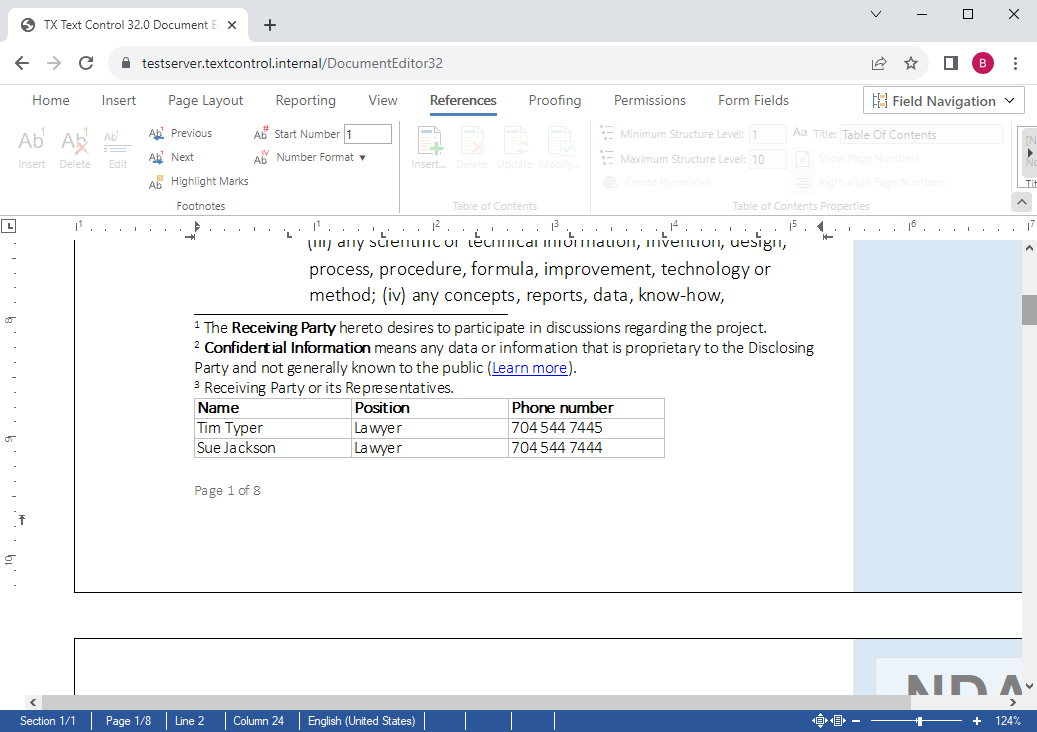
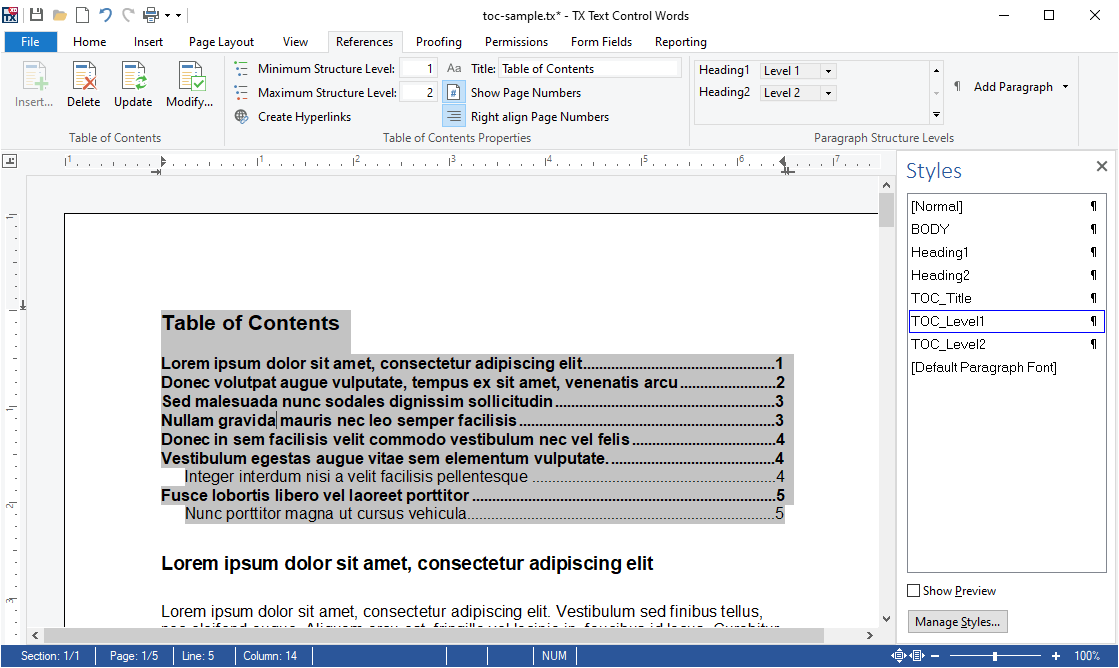
- Table of Contents Using TX Text Control, an MS Word compatible table of contents can be added and modified.
A table of contents is based on used styles (such as headings) in your document. TX Text Control inserts a fully-featured table of contents automatically based on inserted contents and it's paragraph style.
The new ribbon tab References can be used to insert one or more tables of contents at the current input position. A dialog box is used to define the specified levels that should be included into the list. Additionally, you can define whether page numbers and tab leaders are rendered in the list.
For each level of the table of contents, a new style has been added to the list of styles. They can be used to format the table of contents. You can change the complete style of the paragraph including indents, font formatting and distances. After the style has been changed, these changes are applied to the table of contents.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Text Selections and Character Input Two classes to manipulate text. The former enables developers to change font characteristics and the later returns information about the current position of the caret.
Two of the most commonly used classes in TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms are TextSelection and InputPosition. They are used to manipulate text and other elements in word processing documents from program code.
The TextSelection class can be used to select parts of a word processing document and replace them with other text blocks.
Using the InputPosition class, developers can retrieve information about the caret's current line, column and page. Additionally, the caret position can be changed and text can be inserted into any part of the document.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Toolbars Fully configurable status bar, button bar and ruler can be included in applications by simply connecting them to TX Text Control.
Fully configurable ruler bars, status bar and button bar are available out of the box and simply need to be plugged into end-user applications. No further programming effort is required.
The vertical and horizontal ruler bars can be used amongst other things to set page margins, indentations, table sizes, image sizes and text frame sizes.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms offers a number of fully configurable (in terms of functionality and aesthetics) button bar. Button bars with a look at feel of every Windows version from Windows 95 to Windows XP are available and can be set as the end-user application demands.
Each button and combo box has a property, which allows developers to specify whether it should be visible, and where it should be positioned. For example, it is possible to allow end-users access to only stylesheets, but not to any further formatting options. This is particularly useful when XML documents are being edited.
The TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms ruler bar allows tabs to be set and adjusted.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
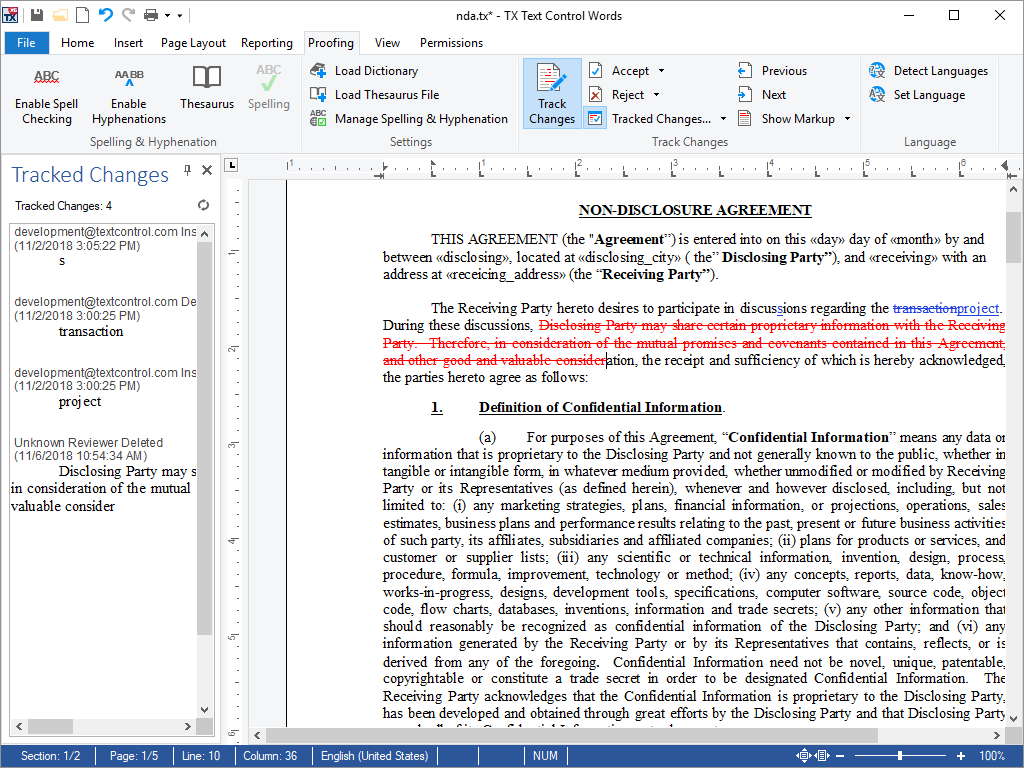
- Track Changes Changes are visually marked in the Text Control editor and also available in the new sidebar Tracked Changes that lists all changes.
This redlining feature is very helpful when working on the same document with multiple authors specifically with legal or healthcare documents where changes need to be tracked and safely logged.
The track changes feature is fully programmable using the TX Text Control API. For each TrackedChange, you can retrieve the timestamp, the kind of the change, position, text, highlight colors and the associated author name.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- XML Programming Developers can access a rich set of properties and methods to manipulate XML documents, while end-users can edit XML in a standardized WYSIWYG environment.
XML is no longer a term used exclusively by technology evangelists. XML is becoming the preferred file format for word processing applications when widespread file interchangeability is demanded.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's XML mode enables non-technical end-users to create valid XML documents. A typical WYSIWYG word processor interface is provided, thus end-users do not need to know anything about XML in order to work with it.
Without really noticing the difference, end-users will instantly produce documents that adhere to corporate identity rules and automatically have all the other advantages of XML.
To the developer, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms offers a rich set of properties and methods for manipulating XML documents and stylesheets from program code.
Many sample applications, illustrating all of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's XML abilities are shipped with the product.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- 64 Bit Version 64 bit processors can handle much more memory and larger files than their 32 bit pendants.
- Localization This category lists localization options.
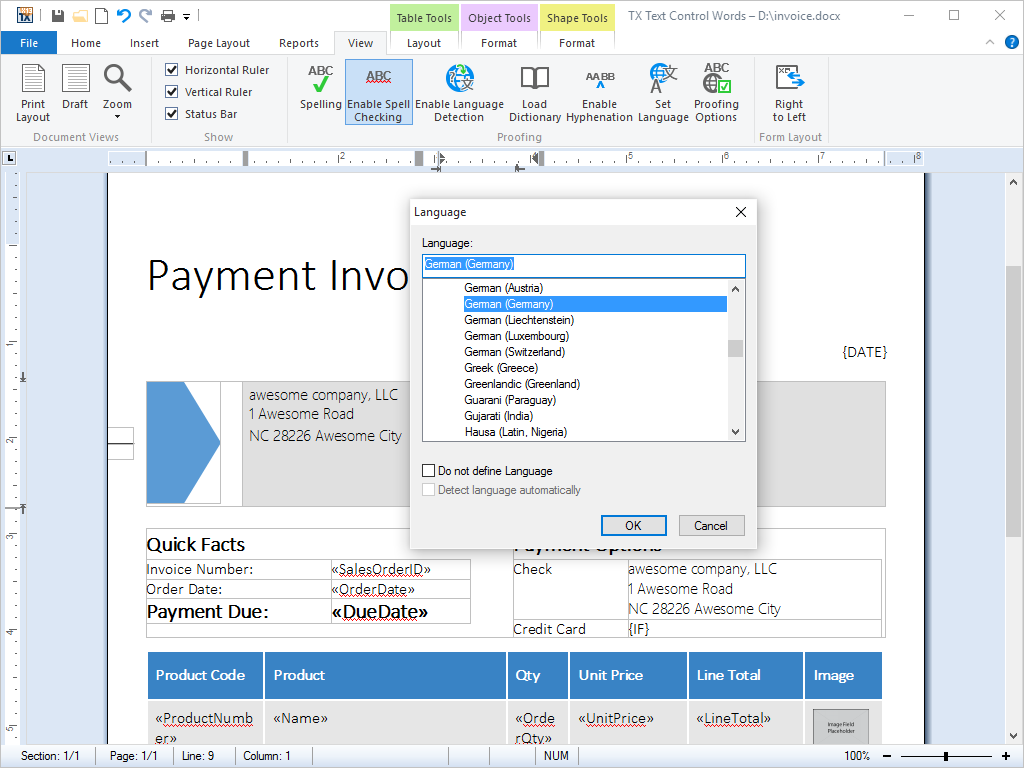
- Multi-Language Support All dialog boxes are shipped in English and German, however, they can be translated into any other language using the included resource files.
Deploying TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms, there is no need to limit applications to one single language: TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms is shipped with dialog boxes that have already been translated into English and German.
Using the included resource files, furthermore, developers can build applications that are fully localized into a wide range of languages.
This has numerous benefits for end-users:
As end-users interact with applications in their primary language, their productivity and satisfaction increase; while at same time, technical support and helpdesk costs decrease, as end-users are able to fully understand the user interface with which they are presented.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
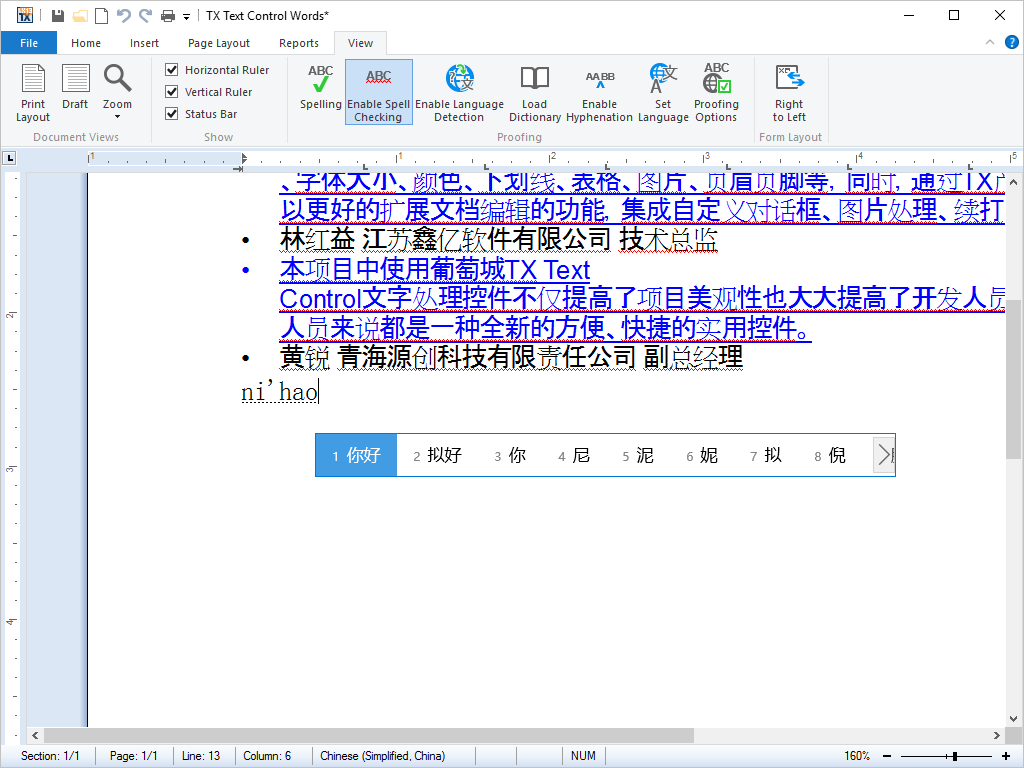
- Unicode TX Text Control offers full Unicode support, thus building applications for eastern languages is as simple as for the English / European languages.
Unicode is a character encoding standard developed by the Unicode Consortium. The aim of the standard is to provide universal way of encoding characters of any language, regardless of the computer system, or platform, being used.
The core of Unicode, known as the Basic Multilingual Plane, contains space for over 65,000 characters. These include some 49,000 characters from the world's languages, include letters from alphabets, ideographs used in writing systems such as Chinese, and other characters such as currency and mathematical symbols.
In addition to these, space is available for custom use, and supplementary code points are available for characters used in languages such as Chinese, where the total number of characters is not quantifiable.
Thanks to TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's Unicode support, applications can be developed in very wide range of languages. Full details of which languages are supported are available on request.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Multi-Language Support All dialog boxes are shipped in English and German, however, they can be translated into any other language using the included resource files.
- Supported Formats This category lists supported industry standard formats.
- Cascading Style Sheet (CSS) TX Text Control uses CSS to render XML files. Different views of a document can be created by simply specifying another CSS file.
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a stylesheet language that allows authors and end-users to attach formatting, such as fonts, spacing and paragraph settings, to structured XML documents.
By separating the presentation formatting of documents from the actual content of documents, CSS simplifies document authoring and maintenance.
Styles can be defined using the shipped dialog box or directly from program code using the rich set of properties and methods that TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms makes available.
Styles that have been defined using TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's style sheets can be exported to a CSS file. The resulting CSS file can be used in other word processing and Internet documents.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Microsoft Office Open XML (DOCX) Load and save documents from and to Microsoft Office Open XML (DOCX) format.
With the 2007 version of Word, Microsoft introduced the DOCX file format, intended as a successor to its binary Microsoft Office file format.
DOCX is a combination of XML architecture and ZIP compression for size reduction, and has become a de facto standard in word processing document formats.
Using the shipped open and save dialog boxes of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms files can be opened and saved in the DOCX file format.
All supported features of TX Text Control can be exported and imported to and from DOCX files.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Document Type Description (DTD) When working with XML, TX Text Control loads the corresponding DTD to ensure the end-user enters only data that is permitted in the DTD.
A Document Type Definition (DTD) is a collection of XML markup declarations that, as a collection, defines the legal structure, elements and attributes that are available for use in a document that complies to the DTD.
When loading an XML file, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms automatically looks for the corresponding DTD on the local file system, from a network path or over the Internet.
Once the XML file is loaded, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms is able to prevent end-user from applying changes that would invalidate the XML contents using the associated DTD.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) HTML documents can be loaded and saved, just as easily as other file formats. Use TX Text Control to create true Intranet and Internet applications.
Originally developed as the authoring language for documents on the Internet, Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is quickly becoming a universal word processing format.
Nowadays, HTML can be viewed on devices ranging from fully fledged desktops, via Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs) to miniature cell phone displays.
Thanks to TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms rich set of properties and methods for the manipulation of HTML, implementing a 'Save to HTML' feature is one line of code. Saving to HTML is just as easy as saving to any of the other file formats that TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms supports.
Furthermore, any file format that can be loaded into TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms can be saved as HTML. Thus, document format conversion applications can be created with ease.
In addition, when text that is formated as HTML is copied into the clipboard, its formatting is retained. On pasting the clipboard back into a word processing document, the text is imported as HTML.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
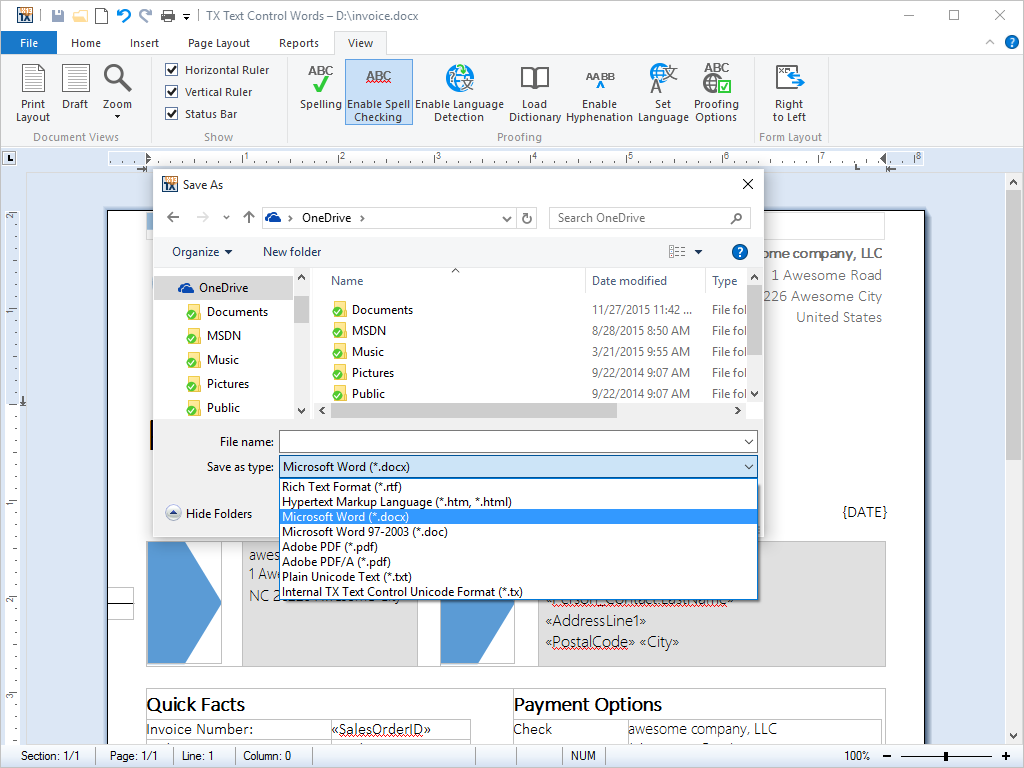
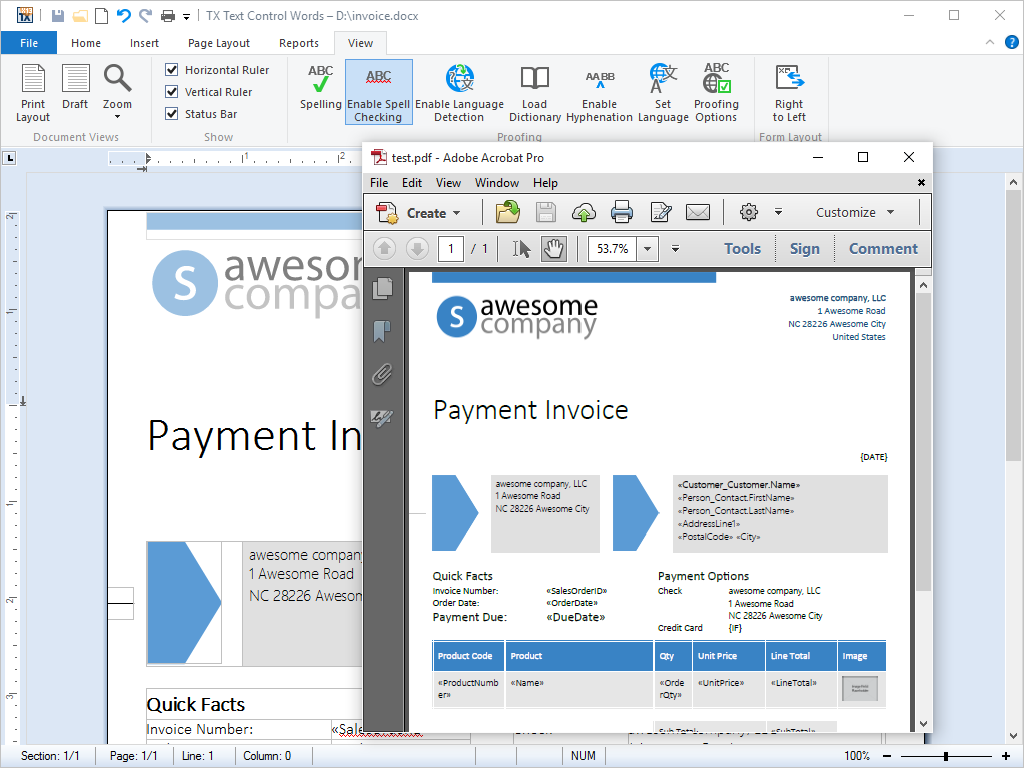
- Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF) Export Export directly to PDF with no further software or third party printer drivers. Exporting to PDF is as easy as saving to DOC, RTF etc.
Portable Document Format (PDF) is a file format originally created by Adobe, to provide a standard form for storing and editing printed publishable documents.
As PDF documents can easily be seen and printed by end-users on a variety of computer and platform types, they are very common deployed on the Internet and are often used as the format of choice when end-users exchange documents via e-mail. PDF files retain the 'look and feel' of the original document with special formatting, graphics, and color intact.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms allows documents to be saved directly to Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF), without the need for any further third party software or cumbersome printer drivers.
Using the traditional approach to PDF creation, it is necessary to print a document to a file and then use a PS to PDF converter (such as Adobe Distiller) to convert the print file to a PDF file. While technologically possible, it is a clumsy solution and taxing on the end-user.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms greatly simplifies the process of creating a PDF file, by offering the end-user a menu entry 'Export as PDF'
Furthermore, as of version 17.0, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms supports digital signatures in Adobe PDF/A documents. Signatures can be created with PFX, DER Cer or Base64 CER certificate files.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF) Import Import PDF documents into TX Text Control and edit them just like all other word processing formats.
Existing PDF documents, for which the original source files no longer exist, can be imported into TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms, upon which they can be edited and saved to any supported file format.
Calculating the layout of a page from an imported PDF, however, is a tricky process: PDF files contain detailed information about the appearance of a page, but not necessarily about the meaning of the characters and images contained within a page.
Furthermore, PDF files do not usually contain any information about the order of text, text flow, nor whether a piece of text is part of a header or table cell. Although recent additions to the PDF specification allow for some of this information to be stored (tagged PDF), this is rarely used.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms extracts and converts all of the text it can find, adds missing spaces and paragraph breaks, and re-sorts the various text blocks and images, so that they appear in their logical order.
The following three parameters are available, which specify the exact behavior of the import filter:
GenerateLines: The imported document is built from singular lines of text, terminated by a line break. This option is most suitable, if only the textual content of the PDF file is of interest.
GenerateParagraphs: The singular lines of text are grouped together to form paragraphs. This option eases post-import editing and is most suited to text heavy documents, such as legal contracts.
GenerateTextFrames: The imported blocks of text and images are organized into text frames and placed at the same position as in the original PDF file. This option produces documents, which are most similar to the original.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
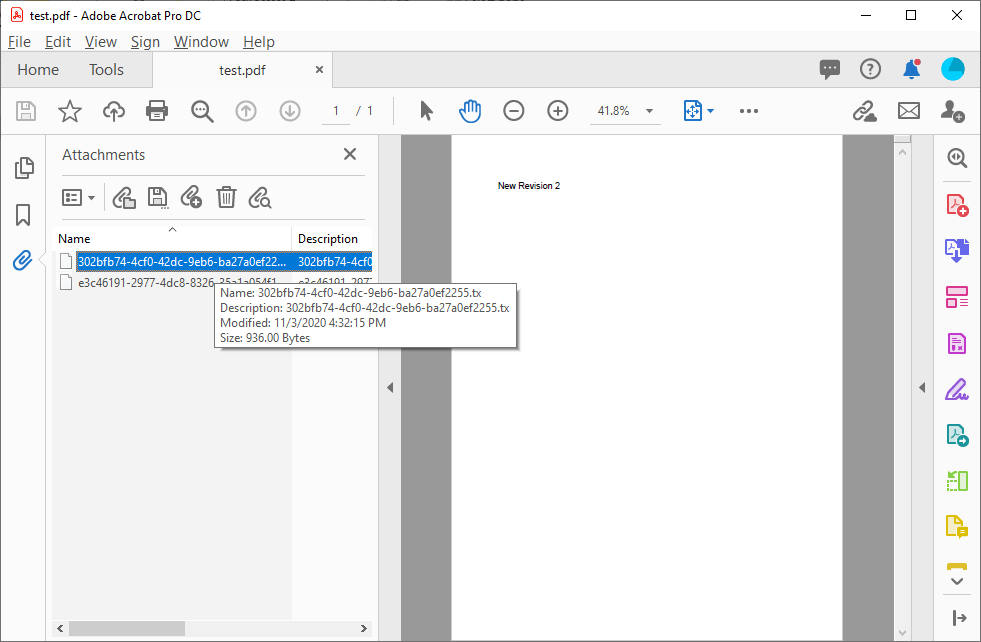
- Adobe PDF/
A-3b Export and Import PDF/A-3b allows the storage of attachments in PDF documents. With TX Text Control, you can import and export those attachments from and to PDF documents.PDF/A-3 allows attachments in any format to be added to PDF documents. The standard itself does not standardize the embedded documents, but the way in which they are embedded in the PDF structure. This enables applications to reliably extract the attached document from the PDF document, which enables readers to extract only the embedded documents without having to open the entire PDF document.
In the most recent iteration of the PDF/A specification, PDF/A-3 added a significant change to all predecessors. PDF/A-3 (ISO 19005-3:2012) permits the embedding of files of any format (including XML, MS Word and proprietary binary formats). This change allows for the migration from electronic paper to an electronic container that holds the human and machine-readable versions of documents.
The option to embed additional documents into standardized PDF documents is typically used in various industries, including healthcare and government, in order to attach additional, structured data to documents.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Adobe Portable Document Format Archive (PDF/
A) Export Export directly to PDF/A - the self-contained, device independent file format for the long-term archiving of page-oriented documents.PDF/A is a self-contained, device independent file format for the long-term archiving of page-oriented documents.
The ISO ratified standard (ISO 19005-1:2005) was developed by a working group of representatives from government, industry and academia.
All supported TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms formats can be exported to PDF/A-1b.
In addition to standard PDF export, the following data is also exported as PDF/A-1b:
- Only embeddable fonts are saved.
- Font data is stored, specifying which characters of a font have been used.
- A color profile is saved.
- Links to start other applications are not permitted.
- Access restrictions are not permitted.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms supports digital signatures in Adobe PDF/A documents. Signatures can be created with PFX, DER Cer or Base64 CER certificate files.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
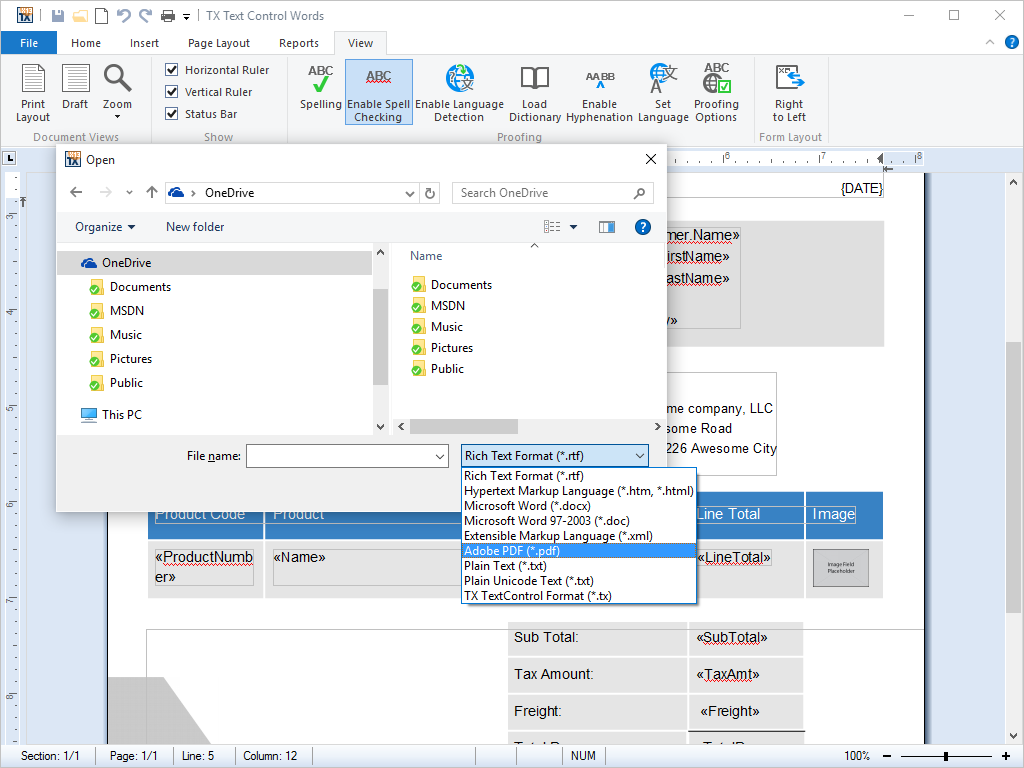
- Rich Text Format (RTF) RTF offers unmatched interoperability with other word applications. Load and save documents to and from RTF.
Rich Text Fomat (RTF) is a file format developed by Microsoft that allows end-users to save text files, keeping their formatting, font information, text color in tact. It is supported by virtually all word processing applications and is thus one of the best suited formats when it comes to exchanging data between different applications.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms can load and save RTF.
In addition, when text that is formated as RTF is copied into the clipboard, its formatting is retained. On pasting the clipboard back into a word processing document, the text is imported as RTF.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Microsoft Excel (XSLS) Load spreadsheets from Microsoft Excel documents (XSLS).
Spreadsheet tables can be imported from Microsoft Excel (XSLS) documents. When opening a document, users can choose from a list of available spreadsheets.
In TX Text Control, Excel compatible formulas can be imported to calculate results based on values and references to other cells in the same table. More than 100 different formulas are supported and can be combined.
Using the shipped open and save dialog boxes of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms files can be opened and saved in the DOCX file format.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Extensible Markup Language (XML) XML truly separates content from formatting. TX Text Control supports XML in conjunction with DTDs and CSS stylesheets.
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is the universal format in which to exchange data between applications and on the Internet. XML allows developers to easily describe and deliver rich, structured data from any application in a standard, consistent way. XML does not replace other file formats supported by TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms; rather, it compliments them.
Using TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's XML mode, non-technical end-users are able edit valid XML documents in a standardized WYSISYG word processing environment. They can save to XML, just as they can save to DOC, RTF or any of the other file formats that TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms supports. All of the (complex) XML handling is taken care of by TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms, empowering end-users to produce documents that adhere to corporate identity and structural rules
To the developer, TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms offers a rich set of properties and methods for manipulating XML documents and stylesheets from program code.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Cascading Style Sheet (CSS) TX Text Control uses CSS to render XML files. Different views of a document can be created by simply specifying another CSS file.
- Supported Programming Languages This category lists supported programming languages, frameworks and IDEs.
- Microsoft C# .
NET (2017, 2019, 2022) TX Text Control is a Windows Forms control that has been designed from scratch for the Visual Studio .NET framework.Visual C# .NET provides developers with a modern, component-oriented language with which they can quickly construct compelling, data-driven solutions. With rapid design, development, high-performance data-driven solutions, Visual C# .NET delivers superior functionality for streamlining business processes.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms has been built from scratch to benefit from the new object oriented design of Visual Studio .NET. This enables developers to take advantage of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's new, intuitive class design, resulting in more effective programming, shortening of development cycles and reduction of development costs.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Microsoft Visual Basic .
NET (2017, 2019, 2022) TX Text Control is a Windows Forms control that has been designed from scratch for the Visual Studio .NET framework.Visual Basic .NET provides developers with a modern, component-oriented language with which they can quickly construct compelling, data-driven solutions. With rapid design, development, high-performance data-driven solutions, Visual Basic .NET delivers superior functionality for streamlining business processes.
TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms has been built from scratch to benefit from the new object oriented design of Visual Studio .NET. This enables developers to take advantage of TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms's new, intuitive class design, resulting in more effective programming, shortening of development cycles and reduction of development costs.
This feature is available in:
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Express
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Professional
- TX Text Control .NET for Windows Forms Enterprise
- Microsoft C# .